Translation Manual
Introduction
Introduction to Translation Manual
This page answers the question: What is the Translation Manual?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
What Does the Translation Manual Teach?
This manual teaches translation theory and how to make a good translation for Other Languages (OLs). Some of the principles of translation in this manual also apply to Gateway Language translation. For specific instruction on how to translate the set of translation tools for Gateway Languages, however, please see the Gateway Language Manual. It will be very helpful to study many of these modules before starting any type of translation project. Other modules, such as the ones about grammar, are only needed for "just-in-time" learning.
Some highlights in the Translation Manual:
- The Qualities of a Good Translation - defining a good translation
- The Translation Process - how to achieve a good translation
- Choosing a Translation Team - some items to consider before starting a translation project
- Choosing What to Translate - what to start translating
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Why We Translate the Bible
- The Qualities of a Good Translation
- The Translation Process
- Choosing What to Translate
Terms to Know
This page answers the question: What terms should I know?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Important Words to Know
Note: These are terms are used in this manual. The translator will need to understand these terms in order to use the Translation Manual.
Term - A word or phrase that refers to one thing, idea, or action. For example, the term in English for pouring liquid into one's mouth is "drink." The term for a ceremony that marks an important transition in someone's life is "rite of passage." The difference between a term and a word is that a term can contain several words.
Text - A text is something that a speaker or writer is communicating to a hearer or reader by means of language. The speaker or writer has a certain meaning in mind, and so he or she chooses a form of the language to express that meaning.
Context - The words, phrases, sentences, and paragraphs surrounding the word, phrase, or sentence in question. The context is the text that surrounds the part of the text that you are examining. The meaning of individual words and phrases can change when they are in different contexts.
Form - The structure of the language as it appears on the page or as it is spoken. "Form" refers to the way that the language is arranged-it includes the words, the word order, the grammar, idioms, and any other features of the structure of the text.
Grammar - The way that sentences are put together in a language. This has to do with the order of its various parts, such as if the verb goes first or last or in the middle.
Noun - A kind of word that refers to a person, place, or thing. A proper noun is the name of a person or place. An abstract noun is a thing that we cannot see or touch, like "peace" or "unity." It refers to an idea or a state of being. Some languages do not use abstract nouns.
Verb - A kind of word that refers to an action, like "walk" or "arrive."
Modifier - A kind of word that says something about another word. Both adjectives and adverbs are modifiers.
Adjective - A kind of word that says something about a noun. For example, the word "tall" says something about the noun "man" in the following sentence. I see a tall man.
Adverb - A kind of word that says something about a verb. For example, the word "loudly" says something about the verb "spoke" in the following sentence. The man spoke loudly to the crowd of people.
Idiom - An expression that uses several words and that means something different as a whole than it would if the words were understood with the meanings that they have when they are used separately. Idioms cannot be translated literally, that is, with the meanings of the separate words. For example, "he kicked the bucket" is an idiom in English that means "he died."
Meaning - The underlying idea or concept that the text is trying to communicate to the reader or hearer. A speaker or writer can communicate the same meaning by using different forms of the language, and different people can understand different meanings from hearing or reading the same language form. In this way you can see that form and meaning are not the same thing.
Translation - The process of expressing in the form of a target language the same meaning that a writer or speaker expressed in the form of a source language.
Source Language - The language from which the translation is being made.
Source Text- The text from which the translation is being made.
Target Language - The language into which a translation is being made.
Target Text- The text being made by the translator as he or she translates the meaning from the source text.
Original Language - The language in which a Bible text was initially written. The Original Language of the New Testament is Greek. The Original Language of most of the Old Testament is Hebrew. However, the Original Language of some parts of Daniel and Ezra is Aramaic. The Original Language is always the most accurate language from which to translate a passage.
Language of Wider Communication - A language that is spoken over a broad area and by many people. For most people, this is not their first language, but is the language that they use to speak to people outside of their language community. Some people call this a trade language. Most Bibles will be translated using a language of wider communication as the source language.
Literal Translation - A translation that focuses on reproducing the form of the source text in the target text, even if the meaning changes as a result.
Meaning-based Translation (or Dynamic Translation) - A translation that focuses on reproducing the meaning of the source text in the target text, even if the form changes as a result.
Passage - A section of the Bible text that is being talked about. This can be as small as one verse, but it is usually several verses that together have one topic or tell one story.
Gateway Language - A Gateway Language (GL) is a language of wider communication that we have identified as being one of the languages into which we will translate all of our translation tools. The set of Gateway Languages is the smallest number of languages through which content can be delivered to every other language of the world, through translation by bilingual speakers.
Other Language - The Other Languages (OLs) are all of the languages of the world that are not Gateway Languages. We translate our Bible translation tools into the Gateway Languages so that people can use those tools to translate the Bible into the Other Languages.
End-user Bible - This is a Bible that people have translated so that it speaks in a natural way in the target language. It is meant to be used in churches and homes. In contrast, the ULB and UDB are Bibles that are translation tools. They do not speak naturally in any language, because the ULB is a literal translation and the UDB avoids using idioms and figures of speech, which a natural translation would use. Using these translation tools, a translator can produce an end-user Bible.
Participant - A participant is one of the actors in a sentence. This could be the person doing the action, or the person that is receiving the action, or mentioned as participating in some way. A participant could even be an object that is stated as participating in the action of the sentence. For example, in the following sentence, the participants are underlined: John and Mary sent a letter to Andrew. Sometimes participants are left unstated, but they are still part of the action. In this case, the participant is implied. For example, in the following sentence, there are only two participants stated: Andrew received a letter. The senders, John and Mary, are implied. In some languages, the implied participants must be stated.
Next we recommend you learn about:
What is Translation?
This page answers the question: What is Translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Definition
Translation is a process performed between different languages that requires a person (the translator) to understand the meaning that a writer or speaker intended to communicate to an original audience in the source language, and then to express that same meaning to a different audience in the target language.
This is how translation is supposed to work most of the time, but sometimes certain translations have other goals, such as to reproduce the form of a source language, as we will see below.
There are basically two kinds of translations: literal and dynamic (or meaning-based).
- Literal translations focus on representing words in the source language with words in the target language that have similar basic meanings. They also use phrases that have similar structures to the phrases in the source language. This kind of translation allows the reader to see the structure of the source text, but it can make it difficult or impossible for the reader to understand the meaning of the source text.
- Dynamic, meaning-based translations focus on representing the meaning of the source language sentence in its context, and will use whatever words and phrase structures are most appropriate to convey that meaning in the target language. The goal of this kind of translation is to make it easy for the reader to understand the meaning of the source text. This is the kind of translation recommended in this Translation Manual for Other Language (OL) translations.
The ULB is designed to be a literal translation, so that the OL translator can see the forms of the original biblical languages. The UDB is designed to be a dynamic translation, so that the OL translator can understand the meaning of these forms in the Bible. When translating these resources, please translate the ULB in a literal way and translate the UDB in a dynamic way. For more information about these resources, see the Gateway Manual.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Why We Translate the Bible
- The Qualities of a Good Translation
- The Translation Process
- Form and Meaning
- Literal Translations
- Meaning-Based Translations
More about Translation
This page answers the question: What more should I know about translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Translation is a process performed between different languages that requires a person (the translator) to understand the meaning that a writer or speaker intended to communicate to an original audience in the source language, and then to express that same meaning to a different audience in the target language.
Why do people translate texts?
Translators in general have different reasons for doing their work. Their reasons depend on the kind of document they are translating, and on the needs of the person who has asked them to translate it. In the case of Bible translation, people usually do their work because they want the Bible's ideas to affect the target language readers in the same way that the original readers and hearers of the biblical texts were affected. Because God's ideas in the Bible lead us to eternal life with him through Jesus Christ, translators also want the target language readers to know his ideas.
How do we as Bible translators usually expect to represent the biblical ideas?
There are various ways in which we can represent the ideas in a source text: we can put them into a list, we can summarize them using far less space on the written page, we can simplify them (as we often do in children's Bible story books and in other kinds of Bible helps), or we can even put them into diagrams or charts. However, Bible translators usually try to present the biblical ideas as completely as possible. This also means that they try to produce in translation the same kinds of documents as the original documents (a prophecy for a prophecy, a letter for a letter, a book of history for a book of history, etc.) Also, they try to recreate the same tensions in the translation that exist in the source texts.
What do we mean by "tension" in texts?
Examples of tension occur when a reader wonders what will happen next to the participants in a story, or when a reader follows the argument, encouragement, and warnings of an epistle writer or of a conversation that is reported in the text. A reader can feel tension when reading a psalm, since the praises of God affect the psalmist in various ways. When reading an Old Testament prophetic book, the reader can feel tension rise as the prophet condemns people for their sin, or as he warns them to turn back to God. Tension may also be felt when reading about God's promises for the future, as one considers when God fulfilled those promises, or when he will fulfill them. Good translators study the kinds of tension in the source documents, and they try to recreate those tensions in the target language.
Another way to talk about recreating the tensions in the source text is to say that the translation should have the same effect on the target audience that the source text had on the original audience. For example, if the source text is a rebuke to the original audience, the target audience should also feel the translation as a rebuke. A translator will need to think about how the target language expresses rebukes and other types communication, so that the translation will have the right kind of effect on the target audience.
How to Aim Your Bible Translation
This page answers the question: What should be the purpose of our Bible Translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
A translator is like a hunter
A translator is like a hunter, who must aim his gun at an animal if he wants to hit it. He must know the kind of animal he is hunting, because a hunter does not shoot birds with the same kind of bullets that he would use to kill an antelope, for example.
It is the same when we speak to other people. We do not speak to young children with exactly the same words that we would say to an adult. Neither do we speak to our friends in exactly the same way we would speak to the president or ruler of our country.
In all these cases, we decide to use different words and expressions. For example, if I am sharing the gospel with a young child, I should not say to him, "Repent, and the Lord will give you his grace." Instead, I should say something like, "Be sorry for the wrong things you have done, and tell Jesus that you are sorry. Then he will welcome you, because he loves you."
In every language, there are words that only adults use, words that children have not yet learned. Of course, the children will eventually learn to use many of these words. But if you say too many of these words to children at the same time, they will find it very difficult to understand you.
In addition, languages are like trees that grow new leaves and lose old ones: new words are always forming in languages, and some words are always dropping out of use. These words die and drop like leaves; they are words that the old people know but that the younger people never learn to use. After the older generation is gone, these old words will no longer be used in the language. Even if they are written down, in a dictionary for example, as they should be, the younger people will probably not use them again.
For these reasons, Bible translators must decide who are the people that they will aim their translation at. Here are their choices:
Aim to the Future
Translators can aim their translation at young mothers and their children who speak the target language, because these people represent the future of their language. If translators work in this way, they will avoid using old words that the younger people are not learning. Instead, they will use ordinary, everyday words as much as possible. In addition, such translators will follow these other rules:
- They do not try to transliterate common Bible words from other languages into the target language. For example, this means that they will not try to transform the Bible word "synagogue" into something like "sinagog" and then try to teach its meaning to the people. They will not try to transform the Bible word "angel" into something like "enjel" and then try to teach its meaning to the target language readers.
- They do not try to invent new words to signal ideas that they find in the Bible. For example, if the target language has no word that signals all the aspects included in "grace" or "sanctify," translators do not make up new words for them. Instead, they will find phrases suitable for expressing the main part of the word's meaning in the Bible passage that they are working on.
- They remember not to take known words in the target language and stuff them with new meaning. They know that if they try this, the people will simply ignore the new meaning. As a result, the people will misunderstand the meaning that you want the text to communicate.
- They remember to express the biblical ideas in ways that are clear and natural. (See: Create Clear Translations, Create Natural Translations)
When translators follow these rules, we call the result a common language version. If you are working to provide a language with its first Bible, then we recommend that you follow these guidelines. Common language versions in English include Today's English Version and The Common English Bible. But remember that your target language will probably want to express many ideas in ways that are very different from what you find in these English versions.
Aim for a Bible Study Translation
Translators can aim their translation at Christians who want to study the Bible in a way that is deeper than the way it is read by new Christians. Translators may decide to do this if the target language already has a good Bible that speaks well to unbelievers and new believers. If translators work in this way, they may decide to:
- Try to imitate more of the grammatical structures they find in the biblical languages. For example, when the Bible says, "The love of God," translators might decide to leave the expression ambiguous. If they do this, they will not decide whether it means "the love that people have for God" or "the love that God has for people." When the Bible says, "the love that we have in Christ Jesus," translators might decide not to say that it means "because of Christ Jesus" or "united to Christ Jesus."
- Try to say what Greek or Hebrew words "stand behind" various expressions in translation. For example, they can do this with footnotes.
- Try to invent new expressions in the target language that signal more of the meaning carried by biblical words. If translators do this, they must become creative with the target language.
We do not recommend that you follow this second path unless the target language already has a Bible translation that communicates in a clear and natural way.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Defining a Good Translation
The Qualities of a Good Translation
This page answers the question: What are the qualities of a good translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Four Main Qualities
There are four main qualities of a good translation. It must be:
- Clear - see Create Clear Translations
- Natural - see Create Natural Translations
- Accurate - see Create Accurate Translations
- Church-Approved - see Create Church-Approved Translations
We can think of each of these qualities as a leg of a four-legged stool. Each one is necessary. If one is missing, the stool will not stand. Likewise, each of these qualities must be present in a translation in order for it to be useful and faithful to the church.
Clear
Use whatever language structures are necessary to achieve the highest level of comprehension. This includes simplifying concepts, rearranging the form of a text, and using as many or as few terms as necessary to communicate the original meaning as accurately as possible. To learn how to make Clear Translations, see Create Clear Translations.
Natural
Use language forms that are effective and that reflect the way your language is used in corresponding contexts. To learn how to make Natural Translations, see Create Natural Translations.
Accurate
Translate accurately, without detracting from, changing, or adding to the meaning of the original text as it would have been understood by the original audience. Translate with the meaning of the text in mind and communicate accurately the implicit information, unknown concepts, and figures of speech. To learn how to make Accurate Translations, see Create Accurate Translations.
Church-Approved
If a translation is clear, natural and accurate, but the church does not approve of it or accept it, then it does not achieve the final goal of edifying the church. It is important that the church be involved in the translation, checking, and distribution of the translation. To learn how to make Church-Approved Translations, see Create Church-Approved Translations.
Six Other Qualities
In addition to being clear, natural, accurate, and church-approved, great translations should also be:
- Faithful - see Create Faithful Translations
- Authoritative - see Create Authoritative Translations
- Historical - see Create Historical Translations
- Equal - see Create Equal Translations
- Collaborative - see Create Collaborative Translations
- Ongoing - see Create Ongoing Translations
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Create Clear Translations
- Create Natural Translations
- Create Accurate Translations
- Create Church-Approved Translations
- The Translation Process
Create Clear Translations
This page answers the question: How do I create clear translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Clear Translations
A clear translation will use whatever language structures are needed to help readers easily read and understand it. This includes putting the text into a different form or arrangement and using as many or as few terms as necessary to communicate the original meaning as clearly as possible.
These guidelines are for Other Language translations, not for Gateway Language translations. When translating the ULB into a Gateway Language, you should not make these changes. It is not necessary to make these changes when translating the UDB into a Gateway Language, because they have already been done. Here are some ideas to create a clear translation from the source text:
Check Pronouns
You will need to check the pronouns in the source text and make it clear to whom or what each pronoun refers. Pronouns are words that stand in the place of a noun or a noun phrase. They refer to something that has already been mentioned.
Always check carefully that it is clear to whom or what each pronoun refers. If it is not clear, it may be necessary to put in the name of a person or thing instead of a pronoun.
Identify Participants
Next you need to understand who is doing the action. A clear translation will identify the participants. The participants in an event are the people or things that take part in that event. The subject that is doing the action and the object that has the action done to it are the main participants. When re-expressing an event idea as a verb, it is often necessary to state who or what are the participants in that event. Usually this will be clear from the context.
Clearly Express Event Ideas
Many event ideas may occur as nouns in the Gateway Language. A clear translation may need to express these event ideas as verbs.
When preparing to translate, it is helpful to look for any event ideas in the passage, especially those which are expressed by some form other than a verb. See if you can re-express the meaning using a verb to express the event idea. If, however, your language also uses nouns to express event ideas and the event or action sounds more natural as a noun, then use the noun form. See Abstract Nouns
You may also need to change each event idea into an active clause to be sure it is understood.
Passive Verbs
A clear translation may need to change any passive verbs to the active form. See Active or Passive
In the active form, the subject of the sentence is the person who does the action. In the passive form, the subject of the sentence is the person or thing to which the action is done. For example, "John hit Bill" is an active sentence. "Bill was hit by John" is a passive sentence.
Many languages do not have a passive form, only the active form exists. In this case, it would be necessary to turn a sentence from the passive form into the active form. Some languages, however, prefer to use passive forms. Translators should use the forms that are most natural in the target language.
Look at Each 'Of' Phrase
To make a clear translation, you will also need to look at each "of" phrase to identify the meaning of the relationship between the nouns connected by "of." In many languages, "of" constructions are not as frequent as they are in the original languages of the Bible. Study the meaning of each one and re-express the "of" phrase in a way which makes the relationship between the parts clear.
After you have checked these things and made your translation as clear as possible, you will need to read it to other people who speak your language to see if it is clear to them. If there are parts that they do not understand, it may be because that part is not clear. Together, you can think of a clearer way to say that part. Keep checking the translation with many people until all of it is clear.
Remember: Translation is re-telling, as exactly as possible, the meaning of the original message in a way that is clear and natural in the target language.
Writing Clearly
Asking yourself these questions can also help you to create a translation that communicates clearly:
- Have you used punctuation to help a reader know when to pause or breathe?
- Have you indicated which parts are direct speech?
- Are you separating paragraphs?
- Have you considered adding section headings?
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Create Natural Translations
- Create Accurate Translations
- Create Church-Approved Translations
- The Translation Process
Create Natural Translations
This page answers the question: How do I create natural translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Natural Translations
To translate the Bible so that it is natural means that:
The translation sounds like it was written by a member of the target group—not by a foreigner. Here are some ideas for making a natural translation:
Use Short Sentences
In order for a translation to sound natural, sometimes it is necessary to create shorter, simpler sentences from longer, complex ones. The Greek language often has long, grammatically complicated sentences. Some Bible translations follow the Greek structure closely and keep these long sentences in their translation, even when this does not sound natural or is confusing in the target language.
When preparing to translate, it is often helpful to rewrite the passage, breaking long sentences up into shorter sentences. This can help you to see the meaning more clearly and translate it better. In many languages, it is good style to have shorter sentences, or, when sentences are longer, to avoid having complicated sentences. So in re-expressing the meaning in the Target Language, it is sometimes necessary to break up some of the original long sentences into several shorter sentences. Because many languages use sentences with only one or two clause groupings, the shorter sentences will give a sense of naturalness. The shorter sentences will also give readers a better understanding, because the meaning will be clearer. Be sure to include clear connection words between the new, shorter clauses and sentences.
To make shorter sentences from longer, more complex sentences, identify the words in the sentence that relate directly to each other, that is, that belong together to form a clause. Generally, each verb or action word has words on either side of it that point back to or forward to the action of the verb. A grouping of words like this that can stand on its own may be written as an independent clause or a simple sentence. Keep each of those groups of words together and in that way divide the sentence into its separate ideas or parts. Read the new sentences to make sure they still make sense. If there is a problem, you may need to divide the long sentence in a different way. When you understand the message of the new sentences, translate them into the target language, making sentences that are a natural length and connect them in a natural way. Then test your translation by reading it to a member of the language community to see if it sounds natural.
Write the Way Your People Talk
Read the passage or chapter of the Bible and ask yourself, "what kind of message is this?" Then translate that passage or chapter in the way that your language would communicate that kind of message.
For example, if the passage is a poem, such as in the Psalms, then translate it in the form that your people will recognize as a poem. Or if the passage is an exhortation about the right way to live, such as in the New Testament letters, then translate it in a form that people in your language exhort each other. Or if the passage is a story about what someone did, translate it in the form of a story (that really happened). The Bible has a lot of these kinds of stories, and as part of these stories people say things to each other that also have their own form. For example, people make threats, give warnings, and praise or rebuke each other. To make your translation natural, you should translate each of these things in the way that people in your language make threats, give warnings, praise or rebuke each other, etc.
In order to know how to write these different things, you may have to listen to what people say around you, and practice writing down different things that people say and do, so that you become familiar with the form and words that people use for these different purposes.
A good translation will use the same vocabulary and expressions as the people of the target group normally use. It should be easy for them to read it or listen to it. There should not be any awkward or strange phrases. The translation should read as easily as a letter from a close friend.
Not for Gateway Language Translations
This section is not for Gateway Language translations of the ULB and UDB. These are Bibles that are designed to have characteristics that keep them from being natural in a target language. They are Bible translation tools, not end-user Bibles. For more information about this, see "Translating the ULB" and "Translating the UDB" in the Gateway Languages Manual.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Create Clear Translations
- Create Accurate Translations
- Create Church-Approved Translations
- The Translation Process
Create Accurate Translations
This page answers the question: How do I create accurate translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Accurate Translations
To create an accurate translation of the Bible means that the translation communicates the same message as the source. Here are some steps to follow:
- Discover the meaning of a passage.
- Identify the main idea.
- Translate with the author's message in mind.
Discover the Meaning
First, read each passage a few times to discover the meaning. Use the two versions of the Bible available in translationStudio: the Unlocked Dynamic Bible and the Unlocked Literal Bible. Also read the definitions of the translationWords and the translationNotes.
First read the Unlocked Literal Bible:
Whatever town you enter, and they receive you, eat what is set before you, and heal the sick that are there. Say to them, 'The kingdom of God has come close to you.' (Luke 10:8-9 ULB)
Look at the Unlocked Dynamic Bible in the translationHelps:
Whenever you enter a town and the people there welcome you, eat whatever food they provide for you. Heal the people there who are sick. Tell them, 'The kingdom of God is right here near you.' (Luke 10:8-9 UDB)
Do you notice the differences? There are some differences in the words each Bible version uses.
Did you discover the meaning is the same? In both versions Jesus is giving specific instructions, and they are the same instructions. Both versions are accurate translations.
Identify the Main Idea
Then, after discovering the meaning of the passage, you should identify the main idea.
Ask yourself, "Why is the author writing this, and how does he feel about these things?"
Look at the Luke 10 passage again. Why do you think the author is writing this? What do you think the author feels about what he wrote? What do you think? After you have read the passage several times, answer these questions:
- What is happening? Jesus gave instructions.
- When and where did these things take place? To answer this question, you would need to remember what happened earlier. Earlier Luke writes that Jesus and the disciples are on the way to Jerusalem, and chapter 10 starts with Jesus sending out 72 people to preach.
- Who is involved in this passage? Jesus and the 72 people he sent out.
- Why were the 72 sent out? To heal the sick and to tell everyone that the kingdom of God is near.
The Message of the Writer
Finally, part of translating the source text accurately is to think of the original audience and the message of the writer.
Do you think the author had specific things for the reader to know? Remember what we thought the author's main ideas were? The main ideas were:
- The instructions that Jesus gave
- That the 72 people whom Jesus sent out would have power to heal sick people
- That they would tell others that the kingdom of God was near
This is the message to the original audience. Allow the same message to come clearly into your mind in the target language.
Look at the passage and think how you would retell it in your own language. Keep this initial translation by writing it down. Use an alphabet that suits your language.
Remember: Translation is re-telling, as exactly as possible, the meaning of the original message in a way that is clear and natural in the target language.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Create Clear Translations
- Create Natural Translations
- Create Church-Approved Translations
- The Translation Process
Create Church-Approved Translations
This page answers the question: How do I create church-approved translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Church-Approved Translations
The first three qualities of a good translation are Clear (see Create Clear Translations), Natural (see Create Natural Translations), and Accurate (see Create Accurate Translations). All three of these directly affect the words and phrases that are used in the translation. If a translation is not one of these three, simply changing or reordering the words that were used can often fix the problem. The fourth quality, church-approved, has less to do with the words used and more to do with the process that is used.
The Goal of Translation
The goal of the translation of biblical content is not only to produce a high-quality translation, but to produce a high-quality translation that is used and loved by the church. High-quality translations must be clear, natural, and accurate. But for a translation to be used and loved by the church, it must be church-approved.
How to Create a Church-Approved Translation
Creating a church-approved translation is all about the process of translation, checking, and distribution. The more church networks that are involved in these processes, the more likely they will approve of the translation.
Before starting a translation project, as many church networks as possible should be contacted and encouraged to become a part of the translation and even to send some of their people to be a part of the translation team. They should be consulted and asked for their input into the translation project, its goals, and its process.
It is not necessary that the church actively lead the translation and coordinate all the efforts, but it is necessary that whoever is leading the translation be approved by the church networks, preferably before they even start.
Church Approval and the Checking Levels
The need for church-approval of a translation is clearly reflected in the Checking Levels. In fact, the Checking Levels are largely a measurement of how broadly the church approves of the translation.
- Level 1 states that the church-approved translation team has approved the translation.
- Level 2 states that the pastors and leaders of local churches approve the translation.
- Level 3 states that leaders of multiple church networks approve of the translation.
At each level, the people leading the translation should encourage participation and input from the church networks. By using this process, we hope to encourage church ownership of the translation among as many church networks as possible. With this approval, there should be nothing hindering the translation from being used to strengthen and encourage the church.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Create Clear Translations
- Create Natural Translations
- Create Accurate Translations
- Introduction to the Checking Manual
Create Faithful Translations
This page answers the question: What are faithful translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Faithful Translations
To make a translation that is faithful to the Bible, you must avoid any political, denominational, ideological, social, cultural, or theological bias in your translation. Use key terms that are faithful to the vocabulary of the original biblical languages. Use equivalent common language terms for the biblical words that describe the relationship between God the Father and God the Son. These may be clarified, as needed, in footnotes or other supplemental resources.
Your goal as a Bible translator is to communicate the same message that the original writer of the Bible intended to communicate. This means that you should not try to communicate your own message, or the message that you think the Bible should say, or that your church thinks the Bible should say. For any Bible passage, you must communicate what it says, all of what it says, and only what it says. You must resist the temptation to put any of your own interpretations or messages into the Bible or add any meaning to the message that is not there in the Bible passage. (The message of a Bible passage includes the implied information. See Assumed Knowledge and Implicit Information.)
You must also use key terms that are faithful to the vocabulary of the original biblical languages. Read the definitions of the translationWords to make sure that you understand the meanings of these words. Translate so that these key terms have these same meanings, and do not translate them in different ways just to please your pastor, your village leaders, or yourself.
Always translating faithfully can be difficult for several reasons:
-
You might be used to the way that your church interprets some Bible passages, and not know that there are other interpretations.
- Example: When you are translating the word "baptize," you might want to translate it with a word that means "sprinkle," because that is what your church does. But after reading translationWords, you learn that the word has a meaning in the range of "plunge," "dip," "wash," or "purify."
-
You might want to translate a Bible passage in a way that accords with your culture, rather than according to what it meant when it was written.
- Example: It is common in North American culture for women to speak and preach in churches. A translator from that culture might be tempted to translate the words of 1 Corinthians 14:34 in a way that is not as strict as the Apostle Paul wrote them: "... the women should keep silent in the churches." But a faithful translator will translate the meaning of the Bible passage just the way it is.
-
You might not like something that the Bible says, and be tempted to change it.
- Example: You might not like what Jesus says in John 6:53, "Truly, truly, unless you eat the flesh of the Son of Man and drink his blood, you will not have life in yourselves." This may seem disgusting to you. But you must translate it faithfully, so that your people can read it and contemplate what Jesus meant by it.
-
You might be afraid of what others in your village will think or do if they read a faithful translation of what the Bible says.
- Example: You might be tempted to translate God's words in Matthew 3:17, "This is my beloved Son. I am very pleased with him," with a word that does not mean "son." But you must remember that you do not have the right to change the meaning of what the Bible says.
-
You might know something extra about the Bible passage that you are translating and want to add that to your translation.
- Example: When you are translating Mark 10:11, "Whoever divorces his wife and marries another woman commits adultery against her," you might know that in Matthew 19:9 there is also the phrase, "...except for sexual immorality...." Even so, do not add this phrase into Mark 10:11, because that would not be translating faithfully. Also, do not add any of your own ideas or teachings from your church. Only translate the meaning that is there in the Bible passage.
In order to avoid these biases, especially the ones that you might not be aware of, you must study the translationNotes (see http://ufw.io/tn/), translationWords (see http://ufw.io/tw/) and the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (see http://ufw.io/udb/), as well as any other translation helps that you have. That way you will know what the meaning of the Bible passage is, and you will be less likely to translate in a biased, unfaithful way.
(You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/guidelines_faithful.)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Son of God and God the Father
This page answers the question: Who are the Son of God and God the Father?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
God is one being, and he exists as the Holy Trinity, that is, as the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit
The Bible teaches that there is only one God.
In the Old Testament:
Yahweh, he is God; there is no other God! (I Kings 8:60 ULB)
In the New Testament:
Jesus said,... "This is everlasting life: that they should know you, the only true God". (John 17:3 ULB)
(See also: Deuteronomy 4:35, Ephesians 4:5-6, 1 Timothy 2:5, James 2:19)
The Old Testament begins to reveal God's three persons.
God created the heavens... The Spirit of God was moving... "Let us make man in our image." (Genesis 1:1-2 ULB)
God has spoken to us by a Son... through whom he also made the universe. His Son is the radiance of his glory, the very character of his essence... about the Son he says,... "In the beginning, Lord, you laid earth's foundation; the heavens are the work of your hands." (Hebrews 1:2-3, and 8-10 ULB quoting Psalm 102:25)
The Church has always found it necessary to state what the New Testament says about God by affirming that he exists in three distinct persons: The Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
Jesus said, "...Baptize them into the name of the Father, of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit." (Matthew 28:19 ULB)
God sent his Son, born of a woman,... God sent the Spirit of his Son into our hearts, who calls, "Abba, Father." (Galatians 4:4-6 ULB)
See also: John 14:16-17, 1 Peter 1:2
Each person of God is fully God and is called "God" in the Bible.
Yet for us there is only one God the Father ... (1 Corinthians 8:6 ULB)
Thomas answered and said to him, "My Lord and my God." Jesus said to him, "Because you have seen me, you have believed. Blessed are those who have not seen, and yet have believed." (John 20:28-29 ULB)
But Peter said, "Ananias, why has Satan filled your heart to lie to the Holy Spirit and to keep back part of the price of the land?... You have not lied to men, but to God." (Acts 5:3-4 ULB)
Each person is also distinct from the other two persons. All three persons can appear separately at the same time. In the verses below, God the Son is baptized while God the Spirit comes down and God the Father speaks from heaven.
After he was baptized, Jesus came up... from the water... He saw the Spirit of God coming down..., and a voice [the Father's] came out of the heavens saying, "This is my Beloved Son..." (Matthew 3:16-17 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Translating Son and Father
This page answers the question: Why are these concepts important in referring to God?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Door43 supports Bible translations that represent these concepts when they refer to God.
Biblical Witness
"Father" and "Son" are names that God calls himself in the Bible. The Bible shows that God called Jesus his Son:
After he was baptized, Jesus came up immediately from the water, and... a voice came out of the heavens saying, "This is my beloved Son. I am very pleased with him." (Matthew 3:16-17 ULB)
The Bible shows that Jesus called God his Father:
Jesus said, "I praise you Father, Lord of heaven and earth,... no one knows the Son except the Father, and no one knows the Father except the Son" (Matthew 11:25-27 ULB) (See also: John 6:26-57)
Christians have found that "Father" and "Son" are the ideas that most essentially describe the eternal relationship of the First and Second Persons of the Trinity to each other. The Bible indeed refers to them in various ways, but no other terms reflect the eternal love and intimacy between these Persons, nor the interdependent eternal relationship between them.
Jesus referred to God in the following terms:
Baptize them into the name of the Father, of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit. (Matthew 28:19 ULB)
The intimate, loving relationship between the Father and the Son is eternal, just as they are eternal.
The Father loves the Son. (John 3:35-36; 5:19-20 ULB)
I love the Father, I do what the Father commands me, just as he gave me the commandment. (John 14:31 ULB)
... no one knows who the Son is except the Father, and no one knows who the Father is except the Son. (Luke 10:22 ULB)
The terms "Father" and "Son" also communicate that the Father and the Son are of the same essence; they are both eternal God.
Jesus said, "Father, glorify your Son so that the Son may glorify you... I glorified you on the earth,... Now Father, glorify me... with the glory that I had with you before the world was created." (John 17:1-5 ULB)
But in these last days, he [God the Father] has spoken to us through a Son, whom he appointed to be the heir of all things. It is through him that God also made the universe. He is the brightness of God's glory, the very character of his essence. He even holds everything together by the word of his power. (Hebrews 1:2-3 ULB)
Jesus said to him, "I have been with you for so long and you still do not know me, Philip? Whoever has seen me has seen the Father. How can you say, 'Show us the Father'? (John 14:9 ULB)
Human Relationships
Human fathers and sons are not perfect, but the Bible still uses those terms for the Father and Son, who are perfect.
Just as today, human father-son relationships during Bible times were never as loving or perfect as the relationship between Jesus and his Father. But this does not mean that the translator should avoid the concepts of father and son. The scriptures use these terms to refer to God, the perfect Father and Son, as well as to sinful human fathers and sons. In referring to God as Father and Son, choose words in your language that are widely used to refer to a human "father" and "son." In this way you will communicate that God the Father and God the Son are essentially the same (they are both God), just as a human father and son are essentially the same, both human and sharing the same characteristics.
Translation Strategies
- Think through all the possibilities that your language has to translate the words "son" and "father." Determine which words in your language best represent the divine "Son" and "Father."
- If your language has more than one word for "son," use the word that has the closest meaning to "only son" (or "first son" if necessary).
- If your language has more than one word for "father," use the word that has the closest meaning to "birth father," rather than "adoptive father."
(See God the Father and Son of God pages in translationWords for help translating "Father" and "Son.")
Create Authoritative Translations
This page answers the question: What are authoritative translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
An authoritative Bible translation is one that is based on the biblical texts in the original languages as the highest authority for the meaning of biblical content. Whenever two or more translations of the Bible disagree about the meaning of a Bible passage, it is the original languages that have the final authority for deciding the meaning. Sometimes people are very loyal to certain Bible translations that they are accustomed to reading, and might argue with other people who are loyal to a different Bible translation. But neither of those Bible translations are the highest authority, because they are only translations of the original. All translations are secondary in authority to the original languages. That is why we must always refer to the original biblical languages when deciding how to translate the Bible.
Since not all translation teams have a member who can read the original languages of the Bible, it is not always possible to refer to the biblical languages when translating the Bible. Instead, the translation team has to rely on translations that they are able to read that have, in turn, been based on the biblical languages. Many of the translations in the Gateway Languages were translated from the biblical languages, including the ULB, but some are translations of translations. It is easy for errors to be introduced when a translation is two or three steps removed from the original.
To help with this problem, the translation team can do three things:
- The translation team must use translationNotes, translationWords, and any other translation helps they have to help them translate in the best way. These translation helps were written by Bible scholars who know the original biblical languages.
- They should compare their translation with as many other reliable translations as they can, to make sure that it is communicating the same message as the others.
- Someone who has studied the biblical languages should review the translation to make sure that it is accurate. This person could be a church leader, pastor, seminary professor, or Bible translation professional.
Sometimes Bible translations differ because some passages in the Bible are unclear or ambiguous in the original biblical languages. In that case, the translation team must choose between them based on what Bible scholars say in translationNotes, translationWords, the UDB, and other translation helps.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Create Historical Translations
This page answers the question: What are historical translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
(see the video "Translating the Scriptures - Culture" at http://ufw.io/trans_culture.)
A historical definition translation communicates historical events and facts accurately. Providing additional information as needed in order to accurately communicate the intended message to people who do not share the same context and culture as the original recipients of the original content.
To communicate well with historical accuracy, you need to remember two things:
- The Bible is a historical document. The events of the Bible happened in the way that the Bible describes at different times in history. Therefore, when you translate the Bible, you need to communicate that these events happened, and do not change any of the details of what happened.
- The books of the Bible were written down at specific times in history for people of a certain culture. This means that some things in the Bible that were very clear to the original hearers and readers will not be clear to those who read the Bible in different times and in different cultures. This is because both the writer and the readers were familiar with many of the practices that the writer wrote about, and so the writer did not need to explain them. We, from other times and cultures, are not familiar with these things, and so we need someone to explain them to us. This kind of information is called "implicit (or implied) information." (see Assumed Knowledge and Implicit Information")
as translators, we need to translate the historical details accurately, but also provide some explanation when we think that our readers will need it so that they can understand what the translation is about.
- For example, Genesis 12:16 refers to camels. For readers in parts of the world where this animal is unknown, it might be good to provide a description. The best way to do this is in a footnote, or in a glossary entry such as the one in translationWords.
Some explanation can be included in the text, as long as it is brief and does not distract the reader from the main point of the text.
- For example, the New Testament writers often referred to events in the Old Testament, but without explaining what they were referring to. They knew that their readers were very familiar with the Old Testament, and did not need any explanation. But it is possible that readers from other times and places will need some explanation.
Let us compare 1 Corinthians 10:1 from the ULB and UDB.
"I want you to know, brothers and sisters that our fathers were all under the cloud and all passed through the sea. " (ULB)
"I want you to remember, brothers and sisters, that our Jewish ancestors were following God, who led them as a cloud during the day, as they passed through the Red Sea on dry land, long ago in the time of the Exodus." (UDB)
Notice that the UDB makes several points explicit: the 'fathers were all under the cloud' tells of the time that God led the Jewish ancestors as a cloud. The statement that 'our fathers passed through the sea' is also about the 'passing through the Red Sea in the time of the exodus.' The UDB translator decided to explicitly describe the historical events. This is a way to translate historical events that is more meaningful for those who have little knowledge of Old Testament history.
Include or refer to the needed implicit information intended by the original writer that will be necessary for your community to understand what is written.
Maintain the historical accuracy of the message. Avoid referring to items and events that were not present in the Bible times. Do not make your translation sound like it is a modern-day event.
Remember:
- Keep true to the historical text. The original message, historical events, and cultural background information should all be the same as it was written in the source text. For example, the translation must not have the message rewritten so that events happened at a different place or time.
- Communicate clearly by expressing the message in such a way that people in the Target Language culture will be able to understand the meaning that the original author intended to communicate.
- Only provide additional information as needed to accurately communicate the intended message to people who do not share the same context and culture as the recipients of the original content.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Create Equal Translations
This page answers the question: What is an equal translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
An equal translation communicates any expressive meaning from the source language in an equal way in the target language. Especially notice the forms in the source text that communicate certain kinds of emotions and choose forms in the target language that communicate the same emotions. Examples of some of these forms follow.
Idioms
Definition - An idiom is a group of words that has a meaning that is different from what one would understand from the meanings of the individual words. Determine the meaning of idioms, proverbs, and figures of speech and translate them with expressions in your language that have the same meaning.
Description - Usually idioms cannot be translated literally into another language. The meaning of the idiom has to be expressed in a way that is natural in the other language.
Here are three translations, all with the same meaning, of Acts 18:6:
- "Your blood be upon your heads! I am innocent." (RSV)
- "If you are lost, you yourselves must take the blame for it! I am not responsible." (GNB)
- "If God punishes you, it is because of you, not me!" (TFT)
These are all accusations of guilt. Some are using idioms with the word "blood" or "lost," while the third is more direct using the word "punishes." In order for your translation to be equal, it must also express an accusation in an emotional way, and may use an idiom, as long as both the form of the accusation and the idiom are appropriate for the target language and culture.
Figures of Speech
Definition - A figure of speech is a special way of saying something in order to catch the attention or express an emotion about what is said.
Description - The meaning of a figure of speech as a whole is different from the normal meaning of the individual words.
Here are some examples:
- I was shattered! The speaker was not literally broken, but he felt very bad.
- He closed his ears to what I was saying. Meaning, "he chose to not listen to what I was saying."
- The wind moaned in the trees. This means that the wind blowing through the trees sounded like a person moaning.
- The whole world came to the meeting. Everyone in the world did not attend the meeting. Most likely there were many people at the meeting.
Each language uses different figures of speech. Make sure you can:
- Recognize that a figure of speech is being used
- Recognize the purpose of the figure of speech
- Recognize the real meaning of the figure of speech
It is the real meaning of the whole figure of speech that should be translated into your language, not the meaning of the individual words. Once you understand the real meaning, you can choose an expression in the target language that communicates that same meaning and emotion.
(For more information, see the Figures of Speech information.)
Rhetorical Questions
Definition - Rhetorical questions are another way that the speaker captures the attention of the reader.
Description - Rhetorical questions are a type of question that does not expect an answer or ask for information. They usually express some kind of emotion and can be intended as a rebuke, a warning, to express surprise, or something else.
See, for example, Matthew 3:7: "You offspring of poisonous snakes, who warned you to flee from the wrath that is coming?"
Here no answer is expected. The speaker is not asking for information; he is rebuking his hearers. It does no good to warn these people of God's wrath, because they refuse the only way to escape it: to repent of their sins.
You may need to restate this rhetorical question as a statement when you translate, if your language does not use rhetorical questions in this way. But remember, be sure to keep the same purpose and meaning, and communicate the same emotion as the original rhetorical question had. If your language communicates the purpose, meaning, and emotion of a rhetorical question with a different kind of figure of speech, then use that figure of speech.
(see Rhetorical Questions)
Exclamations
Definition - Languages use exclamations to communicate emotion. Sometimes the exclamation word or words do not have meaning other than the expression of emotion, such as the words "alas" or "wow" in English.
See, for example, 1 Samuel 4:8: Woe to us! Who will protect us from the strength of these mighty gods? (ULB)
The Hebrew word translated as "woe" here expresses strong emotion about something bad happening. If possible, try to find an exclamation in your language that communicates this same emotion.
Poetry
Definition - One of the purposes of poetry is to express emotion about something.
Description - Poetry does this through many different ways that can be different in different languages. These ways can include everything discussed so far, such as figures of speech and exclamations. Poetry might also use grammar differently than ordinary speech, or use wordplays or words with similar sounds or certain rhythms to convey emotion.
See, for example, Psalm 36:5: Your covenant faithfulness, Yahweh, [reaches] to the heavens; your loyalty [reaches] to the clouds. (ULB)
This verse of poetry repeats a similar idea in two lines, which is good Hebrew poetic style. Also, there are no verbs in the Hebrew original, which is a different use of grammar than ordinary speech would use. Poetry in your language may have different things that mark it as poetry. When you are translating poetry, try to use the forms of your language that communicate to the reader that this is poetry, and that communicate the same emotions that the source poem is trying to communicate.
Remember: Communicate the feelings and attitudes of the original text. Translate them into forms that communicate in a similar way in your language. Consider how that meaning can best be Accurately, Clearly, Equally, and Naturally Expressed in the Target Language.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Create Collaborative Translations
This page answers the question: What are collaborative translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Bible translations that are collaborative are those that have been translated by a group of speakers of the same language. To ensure that your translation is of the highest quality, work together with other believers who speak your language to translate, check, and distribute the translated content.
Here are some ways to have others help improve the quality of the translation.
- Read the translation out loud to someone. Have him notice if the sentences connect well. Ask that person to point to words or phrases that do not sound right or are unclear. Make changes so that it sounds as if someone from your community is speaking.
- Ask someone to read your translation to check your spelling. You may have spelled a word differently when it was not necessary. Some words change in different situations, but some words can stay the same in every situation. Take note of these changes, so others can know what decisions you have made on the spelling of your language.
- Ask yourself if the way you wrote can be recognized easily by speakers of different dialects in your language community. Ask others how they would say something that is not clear in your translation.
Make changes to the translation before you distribute it to a wider audience.
Remember, if possible, work together with other believers who speak your language to translate, check, and distribute the translated content, ensuring that it is of the highest quality and that as many people as possible can read and understand it.
(You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/guidelines_collab.)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Create Ongoing Translations
This page answers the question: What are ongoing translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Bible translations should be ongoing. Share the translation with others to see if they understand the meaning of the message. Improve your translation with their input. Revising a translation to increase understanding and accuracy is always a good idea. Whenever someone has a good idea for making the translation better, you should edit the translation to incorporate that change. When you use translationStudio or other electronic text editors, you can keep this process of revision and improvement ongoing.
- Reviewers are needed who can read the translation and point to text that needs revision.
- Have people read the translation or listened to a recording of the translation. This will help you know if the translation has the same impact in your community that it had among the original audience (for example: giving comfort, encouragement, or guidance).
- Continue to make corrections to the translation that will make it more accurate, more clear, and more natural. The goal is always to make it communicate the same meaning as the source text.
Remember, encourage people to review the translation and to give you ideas for making it better. Talk to other people about these ideas. When several people agree that these are good ideas, then make these changes in the translation. In this way, the translation will get better and better.
(You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/guidelines_ongoing.)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Meaning-Based Translation
The Translation Process
This page answers the question: What are two things I do to translate?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
How to Translate
There are two things to do in translation:
- Discover the meaning in the source language text (See: Discover the Meaning of the Text)
- Re-tell the meaning in the target language translation (See: Re-telling the Meaning)
Instructions for translation sometimes divide these two things into smaller steps. The graphic below shows how these two fit into the translation process.
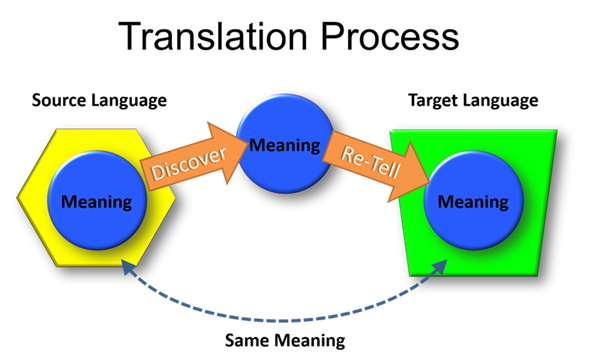
Next we recommend you learn about:
Discover the Meaning of the Text
This page answers the question: How Do I Discover the Meaning of the Text?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
How to Discover the Meaning
There are many different things that we can do to help us to discover the meaning of the text, that is, to make sure that we understand what the text is trying to say. Here are a few suggestions:
- Read the whole passage through before you translate it. Understand the main point of the whole passage before you begin to translate it. If it is a narrative passage, such as a story of one of Jesus' miracles, picture the original situation. Imagine you were there. Imagine how people felt.
-
When translating the Bible, always use at least two versions of the Bible together as your source text. Comparing two versions will help you to think about the meaning, so that you do not just follow the words of one version literally. The two versions should be:
- One version that follows the form of the original language fairly closely, such as the Unlocked Literal Bible (ULB).
- One meaning-based version, such as the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB).
-
Use the translationWords resources to learn about terms that you are not familiar with. Words sometimes have more than one meaning. Make sure that you have understood the right meaning of the word in the passage.
- Also use the translationNotes that are with the ULB Bible. These are available in the translationStudio program and the Door43 website. These will explain things about the passage that may not be clear. If possible, also use other reference books, such as other versions of the Bible, a Bible dictionary, or Bible commentaries.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Re-telling the Meaning
This page answers the question: How do I re-tell the meaning?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
How to Re-tell the Meaning
Following is a list of ordered steps. The purpose of these steps is to help the translator produce a translation that is natural, understandable, and accurate. One of the most common translator mistakes is failing to use the natural forms in the target language for developing a coherent text. By following these steps, the translator will produce a more natural and more understandable translation.
- Read the entire chosen passage in the source language. The passage could be a paragraph or one thing that happened in a story, or even a whole section (in some Bibles, everything from one heading to the next heading). In a difficult text, a passage might be only one or two verses.
- Without looking at the text in the source language, verbally tell it in the target language. Although you might forget some parts, continue telling what you remember right to the end.
- Again, look at the source language text. Now tell everything again in the target language.
- Looking again at the source language text, focus only on the parts you forgot, and then re-tell it all in the target language by memory.
- After remembering the entire passage, write it exactly as it you re-told it by memory.
- Once written, look at the source language to see if you have overlooked some detail. Insert any such detail in the most natural place.
- If you do not understand something in the source text, write into the translation '[not understood]' and continue writing the rest of the passage.
- Now, read what you wrote. Assess whether you understand it or not. Fix the parts that should be improved.
- Go on to the next section. Read it in the source language. Strictly follow steps 2 through 8.
Credits: Used by permission, © 2013, SIL International, Sharing Our Native Culture, p. 59.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Form and Meaning
This page answers the question: What is form and meaning?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Defining Form & Meaning
Two of the major terms used in translating text are "form" and "meaning." These terms are used in special ways in Bible translation. They have the following definitions:
- Form - The structure of the language as it appears on the page or as it is spoken. "Form" refers to the way that the language is arranged-it includes the words, the word order, the grammar, idioms, and any other features of the structure of the text.
- Meaning - The underlying idea or concept that the text is trying to communicate to the reader or hearer. A speaker or writer can communicate the same meaning by using different forms of the language, and different people can understand different meanings from hearing or reading the same language form. In this way you can see that form and meaning are not the same thing.
An Example
Let's consider an example from normal life. Suppose a friend sent you the note below:
- "I am having a very difficult week. My mother was sick and I spent all of my money to take her to the doctor and to buy medicine for her. I do not have anything left. My employer will not pay me until next weekend. I do not know how I am going to make it through the week. I do not even have money to buy food."
The Meaning
Why do you think the friend sent this note? Just to tell you about his week? Probably not. His true intention was more likely to tell you:
- "I would like you to give me money."
That is the primary meaning of the note that the sender wanted to communicate to you. It is not a report, but a request. However, it would be rude in some cultures to ask for money so directly-even from a friend. Therefore, he adjusted the form of the note to fill out the request and help you to understand his need. He wrote in a culturally acceptable way that presented his need for money but did not obligate you to respond. He explained why he had no money (his sick mother), that his need was only temporary (until he is paid), and that his situation was desperate (no food). In other cultures, a more direct form of request might be more appropriate to communicate this meaning.
The Form
In this example, the form is the entire text of the note. The meaning is "I would like you to give me money!"
We use these terms in a similar way. Form will refer to the entire text of the verses that we are translating. Meaning will refer to the idea or ideas that the text is trying to communicate. The best form for communicating a certain meaning will be different in different languages and cultures.
Next we recommend you learn about:
The Importance of Form
This page answers the question: What is the importance of form?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Why Form is Important
The meaning of a text is the most crucial element. However, the form of the text is also very important. It is more than just a "container" for the meaning. It affects the way the meaning is understood and received. So the form itself also has a meaning.
For example, look at the differences in form between two translations of Psalm 9:1-2:
From the New Life Version:
I will give thanks to the Lord with all my heart. I will tell of all the great things You have done. I will be glad and full of joy because of You. I will sing praise to Your name, O Most High.
From the New Revised Standard Version
I will give thanks to the LORD with my whole heart;
I will tell of all your wonderful deeds.
I will be glad and exult in you;
I will sing praise to your name, O Most High.
The first version puts the text into a form that is no different than the form it uses for telling stories. Each line of the Psalm is stated as a separate sentence.
In the second version, the text is arranged as lines of poetry are arranged in the target culture, with each line of the poem on a separate line of the page. Also, the first two lines are joined with a semi-colon, with the second line indented. These things indicate that the two lines are related-they say very similar things. The third and fourth lines also have the same arrangement.
A reader of the second version will know that this Psalm is a poem or a song because of the form that it has, while the reader of the first version may not get that understanding, because it was not communicated through the form of the text. The reader of the first version might be confused, because the Psalm seems to be a song, but it is not presented as one. The words are expressing a joyful emotion. As a translator, you should use the form for expressing a joyful song in your language.
Look also at the form of 2 Samuel 18:33b in the New International Version:
"O my son Absalom! My son, my son Absalom! If only I had died instead of you–O Absalom, my son, my son!"
Someone might say that the meaning contained in this part of the verse is, "I wish that I had died instead of my son Absalom." This does summarize the meaning contained in the words. But the form communicates much more than just that content. The repetition of "my son" so many times, the repetition of the name "Absalom," the expression "O," the wish form "If only…" all communicate a strong emotion of deep anguish on the part of a father who has lost a son. As a translator, you need to translate not just the meaning of the words, but also the meaning of the form. For 2 Samuel 18:33b, it is important that you use a form that communicates the same emotion as contained in the original language.
So we need to examine the form of the biblical text and ask ourselves why it has that form and not some other one. What attitude or emotion is it communicating? Other questions that might help us to understand the meaning of the form are:
- Who wrote it?
- Who received it?
- In what situation was it written?
- Which words and phrases were chosen and why?
- Are the words very emotional words, or is there anything special about the order of the words?
When we understand the meaning of the form, then we can choose a form that has that same meaning in the target language and culture.
Culture Affects Meaning
The meaning of forms is determined by culture. The same form might have different meanings in different cultures. In translation, the meaning must remain the same, including the meaning of the form. This means that the form of the text must change to fit the culture. The form includes the language of the text, its arrangement, any repetitions, or any expressions that imitate sounds like "O." You must examine all of these things, decide what they mean, and then decide which form will express that meaning in the best way for the target language and culture.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Levels of Meaning
This page answers the question: What are the Levels of Meaning?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Levels of Meaning
A good translation requires that the meaning be the same in the target language as in the source language.
There are many different levels of meaning in any text, including the Bible. These levels include:
- Meaning of words
- Meaning of phrases
- Meaning of sentences
- Meaning of paragraphs
- Meaning of chapters
- Meaning of books
Words Have Meaning
We are used to thinking that the meaning of a text is in the words. But this meaning is controlled by the context that each word is in. That is, the meaning of the individual words is controlled by the levels above it, including the phrases, sentences, and paragraphs. For example, a single word like "give" may have the following possible meanings, depending on the context (the higher levels):
- to grant a gift
- to collapse or break
- to surrender
- to quit
- to concede
- to supply
- etc.
Building the Larger Meaning
The translator must determine what each word means in each context, and then reproduce that same meaning in the translated text. That means that words cannot be translated individually, but only with the meaning that they have when they are combined together with the other words in the phrases, sentences, paragraphs, and chapters in which they form a part. That is why the translator must read the whole paragraph, chapter, or book that he is translating before starting to translate it. By reading the larger levels, he will understand how each of the lower levels fits into the whole, and will translate each part so that it communicates the meaning in a way that makes the most sense with the higher levels.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Literal Translations
This page answers the question: What are literal translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Definition
Literal translations try to reproduce, as far as possible, the form of the source text.
Other Names
Literal translations are also called:
- form-based
- word-for-word
- modified literal
Form Over Meaning
A literal translation is one that focuses on reproducing the form of the source text in the target text, even if the meaning changes, or is hard to understand, as a result. An extreme version of a literal translation would not be a translation at all—it would have the same characters and words as the source language. The next closest step would be to replace each word in the source language with an equivalent word from the target language. Because of differences in grammar between languages, the target language audience would probably not understand this kind of translation. Some translators of the Bible wrongly believe that they should keep the word order of the source text in the target text and only substitute target language words for source language words. They wrongly believe that this shows respect for the source text as God's word. But in fact this kind of translation keeps people from understanding God's word. God wants people to understand his word, so it shows the greatest respect for the Bible and for God to translate the Bible so that people can understand it.
Weaknesses of Literal Translation
Literal translations usually contain the following problems:
- foreign words that are not understood by the target audience
- word order that is strange or awkward in the target language
- idioms that are not used or understood in the target language
- names of objects that do not exist in the target culture
- descriptions of customs that are not understood in the target culture
- paragraphs that have no logical connections in the target language
- stories and explanations that do not make sense in the target language
- implied information is left out that is necessary for understanding the intended meaning
When to Translate Literally
The only time to translate literally is when translating Gateway Language Materials, such as the ULB, that will be used by Other Language translators. The purpose of the ULB is to show the translator what is in the original. Even so, the ULB is not strictly literal. It is a modified literal translation that uses the target language grammar so that readers can understand it (see the lesson Modified Literal Translation). For the places where the ULB uses the original expressions in the Bible that may be difficult to understand, we have provided the translationNotes to explain them.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Word-for-Word Substitution
This page answers the question: Why should I not translate using word for word substitution?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Definition
A word-for-word substitution is the most literal form of translation. It is not the best choice for doing good translations. A word-for-word translation simply substitutes an equivalent word in the target language for each word in the source language.
In word-for-word translations
- The focus is on one word at a time.
- The natural sentence structure, phrase structures and figures of speech of the target language are ignored.
- The process of word-for-word translation is very simple.
- The first word in the source text is translated by an equivalent word.
- Then the next word is done. This continues until the verse is translated.
- The word-for-word approach is attractive because it is so simple. However, it results in a poor quality translation.
Word-for-word substitution results in translations that are awkward to read. They are often confusing and give the wrong meaning or even no meaning at all. You should avoid doing this type of translation. Here are some examples:
Word Order
Here is an example of Luke 3:16 in the ULB:
John answered by saying to them all, "As for me, I baptize you with water, but someone is coming who is more powerful than I, and I am not worthy even to untie the strap of his sandals. He will baptize you with the Holy Spirit and with fire."
That translation is clear and easy to understand. But suppose the translators had used the word-for-word method. What would the translation be like?
Here, translated in English, are the words in the same order as the original Greek.
answered saying to all the John I indeed with water baptize you he comes but who mightier than I of whom not I am worthy untie the strap of the sandals of him he you will baptize with spirit holy and fire
This translation is awkward and does not make sense in English.
Look at the ULB version above again. The English ULB translators did not keep the original Greek word order. They moved words around in the sentence to fit the rules of English grammar. They also changed some of the phrasing. For example, the English ULB says, "John answered by saying to them all," rather than "John answered to all saying." They used different words in a different order to make the text sound natural so that it could successfully communicate the original meaning.
The translation must communicate the same meaning as the Greek text. In this example, the ULB is a much better English translation than the awkward word-for-word version.
Range of Word Meanings
In addition, word-for-word substitution usually does not take into account that most words in all languages have a range of meanings. In any one passage, usually the writer had only one of those meanings in mind. In a different passage, he may have had a different meaning in mind. But in word-for-word translations, usually only one meaning is chosen and used throughout the translation.
For example, the Greek word "aggelos" can refer to a human messenger or to an angel.
"This is he of whom it is written, 'See, I am sending my messenger before your face, Who will prepare your way before you.' (Luke 7:27)
Here the word "aggelos" refers to a human messenger. Jesus was talking about John the Baptist.
the angels had gone away from them into heaven (Luke 2:15)
Here the word "aggelos" refers to angels from heaven.
A word-for-word translation process might use the same word in both verses, even though it is used to refer to two different kinds of beings. This would be confusing to the reader.
Figures of Speech
Finally, figures of speech are not conveyed correctly in a word-for-word translation. Figures of speech have meanings that are different from the individual words that they are made up of. When they are translated word-for-word, the meaning of the figure of speech is lost. Even if they are translated so that they follow the normal word order of the target language, readers will not understand their meaning. See the Figures of Speech page to learn how to correctly translate them.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Problems with Literal Translations
This page answers the question: What are several problems with translations that are too literal?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
The meaning of forms change
Literal translations keep the form of the source text in the target text. Some translators might want to do this because, as we saw in the teaching module "The Importance of Form," the form of a text affects the meaning of the text. However, we must keep in mind that people from different cultures understand the meaning of forms differently. In different cultures, the same form may be understood in very different ways. Therefore it is not possible to protect the meaning from change by keeping the original forms. The only way to protect the meaning is to change the original form to a new form that communicates the same meaning in the new culture as the old form did in the old culture.
Different languages use different orders of words and phrases
If you keep the source word order in your translation, it will be very difficult, and sometimes impossible, for the people who speak your language to understand it. You must use the natural word order of the target language so that people can understand the meaning of the text.
Different languages use different idioms and expressions
Each language has its own idioms and other expressions, such as words that represent sounds or emotions. In order to express the meaning of these things, you must choose an idiom or expression that has that same meaning in the target language, not just translate each word. If you just translate each word, the idiom or expression will have the wrong meaning.
Some terms do not have equivalents in other cultures
The Bible contains many terms for things that no longer exist, such as ancient weights (stadia, cubit), money (denarius, stater) and measures (hin, ephah). Animals in Scripture may not exist in some parts of the world (fox, camel). Other words may be unknown in some cultures (snow, circumcision). It is not possible to simply substitute equivalent words for these terms in those situations. The translator must find another way to communicate the original meaning.
The Bible was intended to be understood
The testimony of the Scriptures themselves shows that they were meant to be understood. The Bible is written in three languages because the language that God's people used was different in different times. When the Jews returned from exile and no longer remembered Hebrew, the priests translated the Old Testament readings into Aramaic so they could understand (Neh 8:8). Later, when the New Testament was written, it was written in the common Koine Greek, which was the language that most people spoke at that time, rather than Hebrew or Aramaic or even classical Greek, which would have been harder for common people to understand.
These and other reasons demonstrate that God wants people to understand his word. So we know that he wants us to translate the meaning of the Bible, not reproduce the form. The meaning of the Scriptures is more important than the form.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Meaning-Based Translations
This page answers the question: What are Meaning Based Translations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Introduction
We have looked closely at literal translations. Now, we will look at meaning-based translations. These translations are also called:
- meaning-equivalent
- idiomatic
- dynamic
Key Characteristic
The key characteristic of meaning-based translations is that they give priority to translating the meaning over reproducing the form of the source text. That is, they change the form of the text as needed in order to make the meaning clear. The most common types of changes that meaning-based translations make are:
- change word order to match the grammar of the target language
- replace foreign grammatical structures with natural ones
- change order of reasons or results to match the normal order of the flow of logic in the target language
- substitute or explain idioms
- explain or translate terms from other languages ("Golgotha" = "place of the skull")
- use phrases with simpler words instead of trying to find single word equivalents for difficult or uncommon words in the source text
- replace terms that are unknown in the target culture with equivalent terms or descriptions
- replace connecting words that the target language does not use with connecting words that the target language needs
- substitute target language figures of speech that have the same meaning as the original figures of speech
- include implied information that is necessary to understand the meaning of the text
- explain unclear phrases or constructions
Examples of Meaning-Based Translations
What does a meaning-based translation look like? We will look at how different versions translate the same verse.
In Luke 3:8, John the Baptist rebukes the self-righteous people who came to be baptized.
The Greek text of the first half of the verse is shown below.
Ποιήσατε οὖν καρποὺς ἀξίους τῆς μετανοίας
The English translation in the same order as each Greek word, with some alternative English words to choose from, is below.
Do/make/produce therefore fruits fit/appropriate of the repentance
Literal
A literal translation would usually follow the words and order of the Greek text as closely as possible, such as the following.
Produce fruits that are worthy of repentance (Luke 3:8 ULB)
Note that this modified-literal translation retains the words "fruits" and "repentance." The word order is also very similar to the Greek text. This is because the ULB is designed to show translators what is in the original text. But it may not be the natural or clear way to communicate this meaning in your language.
Meaning-Based
Meaning-based translations, on the other hand, are more likely to change the words and order if the translators think it will help to clarify the meaning. Consider these three meaning-based translations:
From the Living Bible:
…prove that you have turned from sin by doing worthy deeds.
From the New Living Translation:
Prove by the way you live that you have repented of your sins and turned to God.
From the Unlocked Dynamic Bible
Do the things that show that you have truly turned away from your sinful behavior!
Notice that these translations have changed the word order to be more natural in English. Also, the word "fruits" no longer appears. In fact, the Living Bible translation uses almost none of the words in the ULB translation. Instead, rather than "fruits," the meaning-based translations refer to "deeds" or to "the way you live." "Fruits" in this verse is used as part of a metaphor. The meaning of "fruits" in this metaphor is "the things that a person does." (See Metaphor.)
So these translations translated the meaning in context, rather than just the words. They also used more understandable phrases such as "turned from sin" or "turned away from your sinful behavior" rather than the single difficult word "repentance," or they explained the word by saying, "repented of your sins and turned to God." The meaning in all of them is the same, but the form is very different. In the meaning-based translations, the meaning is much clearer.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Translate for Meaning
This page answers the question: Why should I translate for meaning?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
The Importance of Meaning
The people who wrote the Bible had messages from God that God wanted people to understand. These original writers used the language that their people spoke so that they and their people could understand God's messages. God wants people today to understand those same messages. But people today do not speak those languages that the Bible was written in long ago. So God has given us the task of translating the Bible into the languages that people speak today.
The particular language that people use to communicate God's messages is not important. The specific words that are used are not important. What is important is the meaning that those words communicate. The meaning is the message, not the words or the language. What we must translate, then, is not the words or the forms of the sentences of the source languages, but the meaning.
Look at the pairs of sentences below.
-
It rained all night. / Rain fell all night.
-
John was very surprised when he heard the news. / The news very much amazed John when he heard it.
-
It was a hot day. / The day was hot.
-
Peter's house / The house that belongs to Peter
You can see that the meaning of each pair of sentences is the same, even though they use different words. This is the way it is in a good translation. We will use different words than the source text, but we will keep the meaning the same. We will use words that our people understand and use them in a way that is natural for our language. Communicating the same meaning as the source text in a clear and natural way is the goal of translation.
Credits: Example sentences from Barnwell, pp. 19-20, (c) SIL International 1986, used by permission.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Before Translating
Make a First Draft
This page answers the question: How do I do make a first draft?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
How do I start?
- Pray that God would help you to understand the passage that you are translating and that he would help you to find the best way to communicate that passage in your language.
- If you are translating Open Bible Stories, read the entire story before starting to translate it. If you are translating the Bible, read the entire chapter before you start to translate any part of it. This way you will understand how the part you are translating fits into the larger context, and you will translate it better.
- Read the passage that you plan to translate in as many different translations as you have. The ULB will help you to see the form of the original text, and the UDB will help you to understand the meaning of the original text. Think about how to communicate the meaning in the form that people would use in your language. Also read any Bible helps or commentaries that you have talk address that passage.
- Read the translationNotes for the passage that you plan to translate.
- Read the definitions of important terms in the list called "translationWords" for each highlighted word in the passage that you plan to translate.
- Discuss the passage, the translationNotes, and the translationWords with others in the translation team.
- When you understand well what the passage is saying, write down (or record) what it is saying in your language, in the way that someone from your language community would say it. Write down (or record) the whole passage (the chunk of text) without looking at the source text. This will help you to say these things in a way that is natural for your language, rather than in a way that was natural for the source language but that is not the best way to say it in your language.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Choosing a Translation Team
This page answers the question: How do I choose a translation team?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Importance of a Translation Team
Translating the Bible is a very large and difficult task that may take many people to accomplish. This module will discuss the skills that will be needed by members of the Bible translation team, and the responsibilities that these people will have. Some people will have many skills and responsibilities, and other people will have only a few. But it is important that every Bible translation team includes enough people to make sure that all of these skills are represented on the team.
Church Leaders
Before starting a translation project, as many church networks as possible should be contacted and encouraged to become a part of the translation and even to send some of their people to be a part of the translation team. They should be consulted and asked for their input into the translation project, its goals, and its process.
Translation Committee
It is good if the leaders of these churches and church networks can form a committee to guide the work, choose the translators, resolve problems that arise, and encourage the churches to pray for the work and to support the work financially.
This committee can also choose the people who will check the translation for accuracy at levels 2 and 3.
When it comes time, this committee can also make decisions about the format of the translation, how it will be distributed, and they can encourage the churches to use the translated Scriptures.
Translators
These are the people who will do the work of making the translation drafts. They will be appointed by the Translation Committee. They need to be people who are native speakers of the target language, who can read the source language (the Gateway Language) very well, and who are respected in the community for their Christian character. For more details about these things, see Translator Qualifications.
As well as making the first drafts, these people will form the core of the translation team that will check each other's work, check the translation with the language community, and receive the suggestions for revision from the level 2 and level 3 checkers. After each review or checking session, these translators are responsible to make the changes to the translation that are necessary so that it communicates what it should in the best way. So they will revise the translation many, many times.
Typists
If the translators themselves are not inputting the translation draft into a computer or tablet, then someone else on the team needs to do this. This needs to be someone who can type without making a lot of errors. This person also needs to know how to use punctuation marks correctly and consistently. This person may also need to type the revisions and corrections to the translation after each round of checking.
Translation Testers
Some people need to test the translation with members of the language community to make sure that the translation is clear and sounds natural in the target language. Usually these are the translators, but they could be other people. These testers need to read the translation to people and then ask them questions to see how they are understanding it. For a description of this task, see Other Methods.
Checkers
The people who are selected to check the translation for accuracy should be people who already know the Bible well in the source language. They should be able to read well in the source language. They will be comparing the translation to the source Bible, to make sure that the translation communicates everything that is in the source Bible. They should be people who are interested in the translation work and who have time to do a good job of checking. It is good if these people can include members of the different church groups who speak the target language and who will use the translation. The level 2 checkers should be leaders in their local church. The level 3 checkers should be leaders of groups of churches, or respected very widely in the language area. Since many of these people are very busy, it may work best to send different books or chapters to different people, and not burden one or two people with the whole translation.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Translator Qualifications
- Choosing a Source Text
- Alphabet/Orthography
- Decisions for Writing Your Language
Translator Qualifications
This page answers the question: What are the qualifications of a translator?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Qualifications of the Translator or Translation Team
The leaders of the church networks that will be involved in the translation should consider the following questions when choosing the people who will be members of the translation team. These questions will help the church and community leaders know if the people that they choose will be able to successfully translate the Bible or the Open Bible Stories.
-
Is the person known to be a very good speaker of the target language? It is important that the person speak the target language very well.
- Can this person read and write the target language well?
- Has the person been living in the language community for much of his or her life? Someone who has lived away from the language area for a very long period of time might have difficulty making a natural translation.
- Do people respect the way this person speaks their own language?
- What is the age and local language background of each translator? It is usually good to have people from different places in the language area and of different ages, because people of different places and ages might use the language differently. These people then need to agree on a way to say things that sound good to all of them.
-
Does the person have a very good understanding of the source language?
- What level of education have they received, and how have they obtained skills in the source language?
- Does the Christian community recognize that this person has adequate skills to speak the source language and an education sufficient to use the Notes or other exegetical helps provided?
- Can the person read and write the source language with fluency and understanding?
-
Is the person respected in the community as a follower of Christ? The person must be humble and willing to listen to suggestions or corrections from others concerning his or her translation work. The person must be always willing to learn from others.
- How long have they been a Christian, and are they in good standing with their Christian community?
- How has this person shown himself to be committed to Christ as a disciple? Bible translation is difficult, involves many revisions, and requires dedication to the task.
After the translators have been working for awhile, the translation committee will need to make sure that they are working well. They may ask:
- Does their work meet the expectations of their fellow translators and local church leaders? (Has the translator been willing to work with others in testing and checking their translation?)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Choosing What to Translate
This page answers the question: What should I translate first?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
What Should I Translate First?
At some point, the translation team will have to figure out what they should translate first, or, if they have already done some translation, what they should translate next. There are several factors that need to be considered:
- What does the church want to be translated?
- How experienced is the translation team?
- How much Biblical content has been translated into this language?
The answers to these questions are all important. But remember this:
Translation is a skill that grows with experience.
Because translation is a skill that grows, it is wise to start translating content that is less complicated so that the translators can learn the skill while translating something simple.
Translation Difficulty
Wycliffe Bible Translators have rated the difficulty of translating the different books of the Bible. In their rating system, the most complicated books to translate receive a level 5 difficulty. The easiest books to translate are a level 1.
In general, books that have more abstract, poetic, and theologically loaded terms and ideas are more difficult to translate. Books that are more narrative and concrete are generally easier to translate.
Difficulty Level 5 (Most Difficult to Translate)
- Old Testament
- Job, Psalms, Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel
- New Testament
- Romans, Galatians, Ephesians, Philippians, Colossians, Hebrews
Difficulty Level 4
- Old Testament
- Leviticus, Proverbs, Ecclesiastes, Song of Solomon, Lamentations, Daniel, Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephanaiah, Haggai, Zechariah, Malachi
- New Testament
- John, 1-2 Corinthians, 1-2 Thessalonians, 1-2 Peter, 1 John, Jude
Difficulty Level 3
- Old Testament
- Genesis, Exodus, Numbers, Deuteronomy
- New Testament
- Matthew, Mark, Luke, Acts, 1-2 Timothy, Titus, Philemon, James, 2-3 John, Revelation
Difficulty Level 2
- Old Testament
- Joshua, Judges, Ruth, 1-2 Samuel, 1-2 Kings, 1-2 Chronicles, Ezra, Nehemiah, Esther, Jonah
- New Testament
- none
Difficulty Level 1 (Easiest to Translate)
- none
Open Bible Stories
Though Open Bible Stories was not assessed according to this rating system, it should fall under Difficulty Level 1. We recommend that you begin by translating Open Bible Stories. There are many good reasons to start by translating Open Bible Stories:
- Open Bible Stories was designed to be easily translated.
- It is largely narrative.
- Many difficult phrases and words have been simplified.
- It has many pictures to help the translator understand the text.
- Open Bible Stories is much shorter than the Bible or even the New Testament, so it can be quickly completed and distributed to the Church.
- Since it is not Scripture, Open Bible Stories removes the fear that many translators have of translating the Word of God.
- Translating Open Bible Stories before translating the Bible gives the translators experience and training in translation, so that when they translate the.
Bible, they will do it well. By translating Open Bible Stories, the translation team will gain:
- Experience in creating a translation and checking team
- Experience in doing the translation and checking process
- Experience in using the Door43 translation tools
- Experience in resolving translation conflicts
- Experience in getting church and community participation
- Experience in publishing and distributing content
- Open Bible Stories is a great tool to teach the church, evangelize the lost, and train the translators in what the Bible is all about.
You can work your way through the Stories in whatever order that you want, but we have found that Story #31 (see http://ufw.io/en-obs-31) is a good first story to translate since it is short and easy to understand.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the church needs to decide what they want to translate, and in what order. But because translation is a skill that improves with use, and because the translation and checking teams can learn so much about translating the Bible by translating Open Bible Stories, and because of the immense value that the translated Open Bible Stories gives to the local church, we highly recommend starting your translation project with Open Bible Stories.
After translating Open Bible Stories, the church will need to decide if it would be more beneficial to start with how everything began (Genesis, Exodus) or with Jesus (New Testament gospels). In either case, we recommend starting Bible translation with some of the Difficulty Level 2 and 3 books (like Genesis, Ruth, and Mark). Finally, after the translation team has a lot of experience, then they can start translating Difficulty Level 4 and 5 books (like John, Hebrews, and Psalms). If the translation team follows this schedule, they will make better translations with far fewer mistakes.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Translator Qualifications
- Choosing a Source Text
- Alphabet/Orthography
- Decisions for Writing Your Language
Choosing a Source Text
This page answers the question: What factors should be considered when choosing a source text?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Factors to Consider for a Source Text
When choosing a source text, there are a number of factors that must be considered:
- Statement of Faith - Is the text in line with the Statement of Faith?
- Translation Guidelines - Is the text in line with the Translation Guidelines?
- Language - Is the text in a suitable language that translators and checkers understand well?
- Copyrights, Licensing, and Source Texts - Is the text released under a license that gives sufficient legal freedom?
- Source Texts and Version Numbers - Is the text the latest, most updated version?
- The Original and Source Languages - Does the translation team understand the difference between source languages and original languages?
- Original Manuscripts - Does the translation team understand about Original Manuscripts and Textual Variants?
It is important the the leaders of the churches in the language group agree that the source text is a good one. The Open Bible Stories are available in many source languages on http://ufw.io/stories/. There are also translations of the Bible there to be used as sources for translation in English, and soon other languages, as well.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Copyrights, Licensing, and Source Texts
- Source Texts and Version Numbers
- The Original and Source Languages
Copyrights, Licensing, and Source Texts
This page answers the question: What copyright and licensing considerations should be taken when choosing a source text?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Why Is It Important?
When choosing a source text from which to do a translation, considering the copyright/licensing issue is important for two reasons. First, if you translate from a copyrighted work without prior permission, you are breaking the law because translation is a right reserved for the owner of the content. In some places, copyright infringement is a criminal offense and may be prosecuted by the government without the copyright holder's consent! Second, when a translation is done off of a copyrighted work, the translation is the intellectual property of the copyright holder of the source text. They maintain all the rights of the translation just as they do with the source text. For these and other reasons, unfoldingWord will only distribute translations that are not in violation of copyright law.
What License Do We Use?
All content published by unfoldingWord is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 License (CC BY-SA) (see http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/). We believe this license is the greatest help to the church because it is permissive enough to allow translation and other derivatives to be made from it, but not so permissive that those derivatives can be locked up under restrictive licenses. For a complete discussion on this issue, read The Christian Commons (see http://thechristiancommons.com/).
What Source Texts Can Be Used?
Source texts can be used if they are in the public domain or are available under one of the following licenses, which permit translated work to be released under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License:
- CC0 Public Domain Dedication (CC0) (see http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/)
- CC Attribution (CC BY) (see http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
- CC Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-SA) (see http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/)
- Works released under the Free Translate License (see http://ufw.io/freetranslate/)
For all other works in question, please contact help@door43.org.
Note:
- All source texts that appear as source texts in translationStudio have been reviewed and are legal for use by anyone as a source text.
- Before anything is published by unfoldingWord, the source text must be reviewed and available under one of the licenses listed above. Please check your source text before you start translating to avoid being unable to have your translation published.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Source Texts and Version Numbers
This page answers the question: How can version numbers help me select a source text?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Importance of Version Numbers
Especially in an open project like unfoldingWord, it is important to keep track of published versions. It is important because translations (and source texts) can change frequently. Being able to identify each version helps bring clarity about which iteration is being talked about. Version numbers are also important because all translations should be based off of the latest source text. If the source text changes, the translation should eventually be updated to match the latest version.
Before starting a translation project, please ensure that you have the latest version of the source text.
How Versioning Works
Version numbers are only given when a work is released, not when they are edited. Revision history is kept in Door43, but this is different than a work being given a version number.
Each source text is given a whole number for each release (version 1, 2, 3, etc). Any translations based on that source text will take the version number of the source text and add .1 (a translation from English OBS version 4 would become version 4.1). Any further translation based on the intermediate translation would add another .1 to the version number it was created from (for example 4.1.1). New releases of any of these texts increment their "decimal place" by 1.
Please see http://ufw.io/versioning for more details.
Where to Find the Latest Version
https://unfoldingword.org always has the latest published version of each resource. See the Dashboard page at http://ufw.io/dashboard for version history of each resource. Note: translationStudio and the unfoldingWord app do not always have the latest versions since updating content does not happen automatically.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Decisions for Writing Your Language
This page answers the question: What are some decisions we need to make for writing our language?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Important Questions to Answer About Writing
When a language is first written, the translator must decide how to indicate certain features of all written languages.
These questions will give the wider community an understanding of some of the preliminary decisions made by the translator for writing the local language in the areas of punctuation, spelling and the writing of names in the Bible. The translation team and the community should agree on how to do this.
- Does your language have a way of highlighting direct or quoted speech? How do you show it?
- What guidelines have you followed for indicating verse numbering, quoted speech and Old Testament quotations? (Are you following the style of the national language? What variations have you decided to use to suit your language?)
- What guidelines have you followed in writing names in the Bible? Do you use the names written in the national language Bible? Do you have guidelines from your own language as to how names are pronounced and if they need added titles? (Has this decision been acceptable to the community?)
- Have you taken note of any spelling rules for your language that you would like to share with others, such as where a word changes its form or two words combine? (Are these rules acceptable to the community?)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Alphabet/Orthography
This page answers the question: How can I create an alphabet for my language?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Creating an Alphabet
If your language has not been written down before, then you will need to create an alphabet so that you can write it. There are many things to think about when creating an alphabet, and creating a good one can be very difficult. If this seems to be too difficult, you could do an audio translation instead of a written one.
The goal of a good alphabet is to have one letter to represent each different sound of your language.
If a neighboring language already has an alphabet, and if that language has similar sounds to your language, it might work well to simply borrow their alphabet. If not, then the next best thing is to borrow the alphabet from the national language that you learned in school. However, it is likely that your language has sounds that the national language does not, and so it will be difficult to use this alphabet to represent all of the sounds of your language. In that case, it is good to think about each sound in your language. Write out the national language alphabet on a piece of paper from top to bottom. Then write a word from your language next to each letter that either starts with that sound or has that sound in it. Underline the letter that makes that sound in each of the words.
There may be letters in the national alphabet that your language does not use. That is fine. Now think about the sounds from these words that you had a hard time writing, or that you could not find a letter for. If the sound is similar to a sound that you did find a letter for, then maybe you can modify that letter to represent the other sound. For example, if you have a sound represented by "s", and a similar sound that there was no letter for, you could add a mark to the letter for the similar sound, such as putting ' or ^ or ~ on top of it. If you find that there is a group of sounds that seem to all have the same kind of difference from the national language sounds, then it is good to modify that group of letters in the same way.
Once you have finished this exercise and cannot think of any more sounds in your language, try writing a story or write down something that happened recently. As you write, you will probably discover sounds that you had not thought of earlier. Continue to modify letters so that you can write these sounds. Add these sounds to the list you made earlier.
Take your list of sounds to other speakers of your language who also read the national language and see what they think about it. Maybe they can suggest a different way to modify some letters that is simpler or easier to read. Also show these other people the story you wrote and teach them to read it by referring to your list of words and letter-sounds. If they can learn to read it easily, then your alphabet is good. If it is difficult, then there might be parts of the alphabet that still need work to be simpler, or there may be different sounds that are being represented by the same letter, or there may be some sounds that you still need to find letters for.
It is good to continue to work on this alphabet together with other speakers of your language who are good readers in the national language. You can discuss the different sounds and decide on the best way to represent them together.
If the national language uses a writing system other than the Roman alphabet, then think about the different marks that you could use to modify the symbols so that they can represent the sounds of your language. It is best if you can mark the symbols in ways that can be reproduced on a computer. (You can experiment with the writing systems in a word processor or with the keyboards in translationKeyboard. http://ufw.io/tk/) If you need help creating a keyboard, send an email request to help@door43.org. When you use symbols that can be typed on a computer keyboard, then your translation can be stored, copied, and distributed electronically, and then people can get it for no cost and read it on tablets or cell phones.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Alphabet Development
This page answers the question: How do sounds form into words?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Definitions
These are definitions of words that we use to talk about how people make the sounds that form into words, and also definitions of words that refer to the parts of words.
Consonant
These are the sounds that people make when the air flow from their lungs is interrupted or limited by the position of the tongue, teeth or lips. The majority of letters in the alphabet are consonant letters. Most consonant letters have only one sound.
Vowel
These sounds are made by the mouth when the breath flows out through the mouth without being blocked by the teeth, tongue, or lips. (In English, vowels are a, e, i, o, u and sometimes y.)
Syllable (syl-ab-al)
A part of a word that has only one vowel sound, with or without surrounding consonants. Some words have only one syllable.
Affix
Something that is added to a word that changes its meaning. This could be at the beginning, or the end, or in the body of a word.
Root
The most basic part of a word; what is left when all the affixes are removed.
Morpheme
A word or a part of a word that has a meaning and that contains no smaller part that has a meaning. (For example, “syllable” has 3 syllables, but only 1 morpheme, while “syllables” has 3 syllables and two morphemes (syl-lab-les). (The final "s" is a morpheme that means "plural.")
How Syllables Make Words
Every language has sounds which combine to form syllables. An affix of a word or the root of a word may have a single syllable, or it may have a number of syllables. Sounds combine to make syllables which also join together to make morphemes. Morphemes work together to make meaningful words. It is important to understand the way syllables are formed in your language and how those syllables influence one another so that spelling rules can be formed and people can more easily learn to read your language.
Vowel sounds are the basic part of syllables. English has only five vowels symbols, “a, e, i, o, u”, but it has up to 11 vowel sounds that are written with vowel combinations and many other ways. The sounds of individual English vowels can be found in words such as, “beat, bit, bait, bet, bat, but, body, bought, boat, book, boot.”
[add articulation picture]
The Vowels of English
Position in the Mouth Front – Mid – Back
Rounding (unrounded) (unrounded) (rounded)
Tongue Height High i “beat” u “boot”
Mid-High i “bit” u “book”
Mid e “bait” u “but” o “boat”
Low-Mid e “bet” o “bought”
Low a “bat” a “body”
(Each of these vowels has its own symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet.)
The vowel sounds form the middle of each syllable, and the consonant sounds come before and after the vowels.
Articulation is the description of how air comes through the mouth or nose to produce the sounds that we can recognize as speech.
Points of articulation are those places along the throat or mouth where air is constricted or its flow is stopped. Common points of articulation include the lips, the teeth, the dental (alveolar) ridge, the palate (hard roof of the mouth), the velum (soft roof of the mouth), uvula, and the vocal cords (or glottis).
Articulators are the moving parts of the mouth, particularly the parts of the tongue that slow the flow of air. The parts of the tongue that can do this include the tongue root, the back, the blade, and the tip. The lips can also slow the air flow through the mouth without the use of the tongue. Sounds made with the lips include consonants such as “b," "v," and "m."
The manner of articulation describes how the airflow is slowed. It can come to a complete stop (as with “p” or “b”, which are called stop consonants or stops), have heavy friction (like “f” or “v,” called fricatives), or be only slightly restricted (like “w” or “y,” called semi-vowels, because they are almost as free as vowels.)
Voicing shows whether or not the vocal chords are vibrating when the air passes through them. Most vowels, such as “a, e, i, u, o” are voiced sounds. Consonants can be voiced (+v), like “b,d,g,v,” or voiceless (-v) such as “p,t,k,f." These are made at the same point of articulation and with the same articulators as the voiced consonants first mentioned. The only difference between “b,d,g,v” and “p,t,k,f” is voicing (+v and –v).
The consonants of English
Points of Articulation Lips Teeth Ridge Palate Velum Uvula Glottis
Voicing -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v
Articulator - Manner
Lips - Stop p / b
Lip - Fricative f / v
Tongue Tip -
Stop t / d
Liquid / l / r
Tongue Blade -
Fricative ch/dg
Tongue Back -
Stop k / g
Tongue Root -
Semi-Vowel / w / y h /
Nose – Continuant / m / n
Naming the sounds can be done by calling their features. The sound of “b” is called a Voiced Bilabial (two lips) Stop. The sound of “f” is known as a Voicelss Labio-dental (lip-teeth) Fricative. The sound of “n” is called a Voiced Alveolar (Ridge) Nasal.
Symbolizing the sounds can be done one of two ways. Either we can use the symbol for that sound found in the International Phonetic Alphabet, or we can use well-known symbols from an alphabet known by the reader.
Consonant Chart – a consonant symbol chart is offered here without mentioning the Articulators. As you explore the sounds of your language, listening for voicing and feeling the position of your tongue and lips when you make the sound, you can fill out the charts in this article with symbols to represent those sounds.
Points of Articulation Lips Teeth Ridge Palate Velum Uvula Glottis
Voicing -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v -v/+v
Manner Stop p/ b t/ d k/ g
Fricative f/ v ch/dg
Liquid /l /r
Semi-vowel /w /y h/
Nasals /m /n
Next we recommend you learn about:
File Formats
This page answers the question: What file formats are acceptable?
The Technical Nature of Translation
While a large part of translation has to do with language, words, and sentences, it is also true that a major aspect of translation is technical in nature. From creating alphabets, typing, typesetting, formatting, publishing, and distributing, there are many technical aspects to translation. In order to make all this possible, there are some standards that have been adopted.
USFM: Bible Translation Format
For many years, the standard format for Bible translation has been USFM (which stands for Unified Standard Format Markers). We have adopted this standard as well.
USFM is a type of markup language that tells a computer program how to format the text. For instance, each chapter is marked like this ''\c 1'' or ''\c 33''. Verse markers might look like ''\v 8'' or ''\v 14''. Paragraphs are marked ''\p''. There are many other markers like this that have specific meaning. So a passage like John 1:1-2 in USFM will look like this:
\c 1
\p
\v 1 In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God.
\v 2 This one, the Word, was in the beginning with God.
When a computer program that can read USFM sees this, it is able to format all of the chapter markers the same way (for instance, with a larger number) and all the verse numbers the same way (for instance, with a small superscript number).
Bible translations must be in USFM for us to be able to use it!
To read more about USFM notation, please read http://paratext.org/about/usfm .
How To Do a Bible Translation in USFM
Most people do not know how to write in USFM. This is one of the reasons why we created translationStudio (http://ufw.io/ts/). When you do a translation in translationStudio, what you see looks very similar to a normal word processor document without any markup language. However, translationStudio is formatting the Bible translation in USFM underneath what you see. This way, when you upload your translation from translationStudio, what is being uploaded is already formatted in USFM and can be immediately published in a variety of formats.
Converting a Translation to USFM
Though it is strongly encouraged to only do a translation using USFM notation, sometimes a translation is done without using USFM markup. This type of translation still can be used, but first the USFM markers must be added. One way to do this is to copy and paste it into translationStudio, then place the verse markers in the correct place. When this is done, the translation will be able to be exported as USFM. This is a very arduous task, so we strongly recommend doing your Bible translation work from the beginning in translationStudio or some other program that uses USFM.
Markdown for Other Content
Markdown is a very common markup language that is used in many places on the Internet. Using Markdown makes it very easy for the same text to be used in a variety of formats (such as webpage, mobile app, PDF, etc).
Markdown supports bold and italic, written like this:
Markdown supports **bold** and *italic*.
Markdown also supports headings like this:
# Heading 1
## Heading 2
### Heading 3
Markdown also supports links. Links display like this https://unfoldingword.org and are written like this:
[https://unfoldingword.org](https://unfoldingword.org)
Customized wording for links are also supported, like this:
[uW Website](https://unfoldingword.org)
Note that HTML is also valid Markdown. For a complete listing of Markdown syntax please visit http://ufw.io/md.
Conclusion
The easiest way to get content marked up with USFM or Markdown is by using an editor that is specifically designed to do that. If a word processor or a text editor is used, these markings must be manually entered.
Note: Making text bold, italic, or underlined in a word processor does not make it bold, italic, or underlined in a markup language. This type of formatting must be done by writing the designated symbols.
When contemplating which software to use, please keep in mind that translation is not just about words; there are a lot of technical aspects that need to be taken into consideration. Whatever software is used, just remember that Bible translations need to be put into USFM, and everything else needs to be put into Markdown.
How to Start Translating
Help with Translating
This page answers the question: Where do I find help for translating?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Using translationHelps
To help translators make the best translation possible, translationNotes, translationWords, and translationQuestions have been created.
translationNotes are cultural, linguistic, and exegetical notes that help to describe and explain some of the Bible background that the translator needs to know to translate accurately. The translationNotes also inform translators about different ways that they might express the same meaning. See http://ufw.io/tn/.
The translationWords are key terms found in Open Bible Stories and the Bible that are important to translate correctly. Each of these words or phrases has a small article written about it as well as cross-references to other places where that term is used in either Open Bible Stories or the Bible. This is to show the translator other ways that the translationWord is used and to ensure that it has been translated correctly in those places, too. See http://ufw.io/tw/.
The translationQuestions are comprehension questions that can be used to self-check your translation. If you can correctly answer the translationQuestions using only the Target Language translation, then it is an accurate translation. The translationQuestions are also a good tool to use for checking with the target language community. See http://ufw.io/tq/.
Once you have consulted the translationNotes, translationWords and translationQuestions, then you are ready to make the best translation.
Please consult the translationNotes and translationWords when doing your translation!
Next we recommend you learn about:
Unlocked Bible Text
The Original and Source Languages
This page answers the question: What is the difference between the original language and the source language?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
The Text in the Original Language is the most Accurate
Definition - The original language is the language in which a Bible text was initially written.
Description - The original language of the New Testament is Greek. The original language of most of the Old Testament is Hebrew. However, the original language of some parts of the books of Daniel and Ezra is Aramaic. The original language is always the most accurate language from which to translate a passage.
The source language is the language from which the translation is being made. If a translator is translating the Bible from the original languages, then the original language and the source language for his translation are the same. However, only people who have spent many years studying the original languages understand them and can use them as a source language. For that reason, most translators use Bibles that have been translated into a language of wider communication as their source language text.
If you are translating from a language of wider communication, it is a good idea to have someone who has studied the original languages compare the meaning in the target language translation with the meaning in the original language to make sure that the meaning is the same. Another way to make sure that the meaning of the target language translation is accurate is to check the translation with translation helps that have been written by people who know the original languages. These would include Bible commentaries and dictionaries, as well as the unfoldingWord translationNotes, translationWords definitions, and translationQuestions with their answers.
The Text in the Source Language may not be Accurate
If the translator does not understand the original language, he will have to use a language of wider communication as a source language. The meaning in the source may be correct, depending on how carefully it was translated from the original. But it is still a translation, so it is a step away from the original and is not quite the same. In some cases, the source may have actually been translated from another source, rather than from the original, putting it two steps away from the original.
Consider the example below. A translator uses a Swahili New Testament as the source for a new target language translation. However, the particular Swahili Bible version he is using was actually translated from English — not directly from the Greek (the original language of the NT). So it is possible that some of the meaning has changed in the chain of translation from the original to the target languages.
The only way to make sure the translation is as accurate as possible is to compare the new translation with the original languages. Where this is not possible, use the ULB as the source text, along with other Bible translations that were translated from the original languages.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Original Manuscripts
This page answers the question: Is there more information about the Original Language text?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
The Writing of the Original Manuscripts
The Bible was written many hundreds of years ago by God's prophets and apostles as God directed them to write it. The people of Israel spoke Hebrew, so most of the Old Testament books were written in Hebrew. When they lived as strangers in Assyria and Babylon, they learned to speak Aramaic, so some later parts of the Old Testament were written in Aramaic.
About three hundred years before Christ came, Greek became the language of wider communication. Many people in Europe and the Middle East spoke Greek as a second language. So the Old Testament was translated into Greek. When Christ came, many people in those areas of the world still spoke Greek as a second language, and the New Testament books were all written in Greek.
Back then there were no printers, so the authors wrote these books by hand. These were the original manuscripts. Those who copied these manuscripts also did so by hand. These were also manuscripts. These books are extremely important, so the copiers got special training and were very careful to try to copy them accurately.
Over hundreds of years, people made thousands of copies of the Bible books. The manuscripts that the authors originally wrote have all been lost or fallen apart, so we do not have them. But we do have many of the copies that were written by hand long ago. Some of these copies have survived for many hundreds and even thousands of years.
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Chapter and Verse Numbers
- Original Manuscripts
- The Original and Source Languages
- Terms to Know
- Textual Variants
Structure of the Bible
This page answers the question: How is the Bible organized?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
The Bible is made up of 66 "books." Although they are called "books," they vary greatly in length and the shortest ones are only a page or two long. The Bible has two main parts. The first part was written first and is called the Old Testament. The second part was written later and is called the New Testament. The Old Testament has 39 books and the New Testament has 27 books. (Some of the books in the New Testament are letters to people.)
Each book is divided into chapters. Most books have more than one chapter, but Obadiah, Philemon, 2 John, 3 John, and Jude each have only one chapter. All the chapters are divided into verses.
When we want to refer to a verse, we first write the name of the book, then the chapter, and then the verse. For example "John 3:16" means the book of John, chapter 3, verse 16.
When we refer to two or more verses that are next to each other, we put a line between them. "John 3:16-18" means John, chapter 3, verses 16, 17, and 18.
When we refer to verses that are not next to each other, we use commas to separate them. "John 3:2, 6, 9" means John chapter 3, verses 2, 6, and 9.
After the chapter and verse numbers, we put the abbreviation for the translation of the Bible that we used. In the example below, "ULB" stands for the Unlocked Literal Bible.
In translationAcademy we use this system to tell where portions of scripture come from. However, this does not mean that the whole verse or set of verses is shown. The text below comes from Judges, chapter 6, verse 28, but it is not the whole verse. The verse has more at the end. In translationAcademy, we only show the part of the verse that we want to talk about.
In the morning when the men of the town got up, the altar of Baal was broken down ... (Judges 6:28 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Chapter and Verse Numbers
This page answers the question: Why are the chapter and verse numbers in my Bible different from those in your Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
When the books of the Bible were first written, there were no breaks for chapters and verses. People added these later, and then others numbered the chapters and verses to make it easier to find particular parts of the Bible. Since more than one person did this, there are different numbering systems used in different translations. If the numbering system in the ULB is different from the numbering system in another Bible that you use, you will probably want to use the system from that Bible.
Reason this is a translation issue
People who speak your language may also use a Bible written in another language. If that Bible and your translation use different chapter and verse numbers, it will be hard for people to know which verse someone is talking about when they say a chapter and verse number.
Examples from the Bible
14 But I expect to see you soon, and we will speak face to face. 15 Peace be to you. The friends greet you. Greet the friends by name. (3 John 1:14-15 ULB)
Since 3 John has only one chapter, some versions do not mark the chapter number. In the ULB and UDB it is marked as chapter 1. Also, some versions do not divide verses 14 and 15 into two verses. Instead they mark it all as verse 14.
A psalm of David, when he fled from Absalom his son.
1 Yahweh, how many are my enemies! (Psalm 3:1 ULB)
Some of the psalms have an explanation before them. In some versions the explanation is not given a verse number, as in the ULB and UDB. In other versions the explanation is verse 1, and the actual psalm starts with verse 2.
... and Darius the Mede received the kingdom when he was about sixty-two years old. (Daniel 5:31 ULB)
In some versions this is the last verse of Daniel 5. In other versions this is the first verse of Daniel 6.
Translation Strategies
- If the people who speak your language have another Bible that they use, number the chapters and verses the way it does. Read the instructions on how to mark verses in the translationStudio APP.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
If the people who speak your language have another Bible that they use, number the chapters and verses the way it does.
The example below is from 3 John 1. Some Bibles mark this text as verses 14 and 15, and some mark it all as verse 14. You may mark the verse numbers as your other Bible does.
- 14 But I expect to see you soon, and we will speak face to face. 15 Peace be to you. The friends greet you. Greet the friends by name. (3 John 1:14-15 ULB)
- "14 But I expect to see you soon, and we will speak face to face. Peace be to you. The friends greet you. Greet the friends by name."(3 John 14)
Next is an example from Psalm 3. Some Bibles do not mark the explanation at the beginning of the psalm as a verse, and others mark it as verse 1. You may mark the verse numbers as your other Bible does.
A psalm of David, when he fled from Absalom his son.
1 Yahweh, how many are my enemies!
Many have turned away and attacked me.
2 Many say about me,
"There is no help for him from God." *Selah*
1 A psalm of David, when he fled from Absalom his son.
2 Yahweh, how many are my enemies!
Many have turned away and attacked me.
3 Many say about me,
"There is no help for him from God." Selah
Next we recommend you learn about:
ULB and UDB Formatting Signals
This page answers the question: What do some of the formatting signals in the ULB and UDB show?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The Unlocked Literal Bible (ULB) and Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB) use ellipsis marks, long dashes, parentheses, and indentation to show how information in the text is related to what is around it.
Ellipsis marks
Definition - Ellipsis marks (...) are used to show that either someone did not finish a sentence he started, or that the author did not quote all of what someone said.
In Matthew 9:4-6, the ellipsis mark shows that Jesus did not finish his sentence to the scribes when he turned his attention to the paralyzed man and spoke to him:
Behold, some of the scribes said among themselves, "This man is blaspheming."Jesus knew their thoughts and said, "Why are you thinking evil in your hearts? For which is easier to say, 'Your sins are forgiven,' or to say, 'Get up and walk'? But that you may know that the Son of Man has authority on earth to forgive sins,..." he said to the paralytic, "Get up, pick up your mat, and go to your house." (ULB)
In Mark 11:31-33, the ellipsis mark shows that either the religious leaders did not finish their sentence, or Mark did not finish writing what they said.
They discussed between themselves and argued and said, "If we say, 'From heaven,' he will say, 'Why then did you not believe him?' But if we say, 'From men,' ..." They feared the people, for they all held that John was a prophet. Then they answered Jesus and said, "We do not know." Then Jesus said to them, "Neither will I tell you by what authority I do these things." (ULB)
Long Dashes
Definition - Long dashes (—) introduce information that is immediately relevant to what came before it. For example:
Then two men will be in a field—one will be taken, and one will be left behind. Two women will be grinding with a mill—one will be taken, and one will be left. Therefore be on your guard, for you do not know on what day your Lord will come. (Matthew 24:40-41 ULB)
Parentheses
Definition - Parentheses "( )" show that some information is an explanation or afterthought.
It is background information that the writer put in that place to help the reader understand the material around it.
In John 6:6, John interrupted the story he was writing to explain that Jesus already knew what he was going to do. This is put in parentheses.
5When Jesus looked up and saw a great crowd coming to him, he said to Philip, "Where are we going to buy bread so that these may eat?" 6 (Now Jesus said this to test Philip, for he himself knew what he was going to do.) 7Philip answered him, "Two hundred denarii worth of bread would not be sufficient for each one to have even a little." (John 6:5-7 ULB)
The words in the parentheses below are not what Jesus was saying, but what Matthew was saying to the reader, to alert the reader that Jesus was using words that they would need to think about and interpret.
"Therefore, when you see the abomination of desolation, which was spoken of by Daniel the prophet, standing in the holy place" (let the reader understand), "let those who are in Judea flee to the mountains, let him who is on the housetop not go down to take out anything that is in his house, 18and let him who is in the field not return to take his cloak." (Matthew 24:15-18 ULB)
Indentation
Definition - When text is indented, it means that the line of text starts further to the right than the lines of text above and below it that are not indented.
This is done for poetry and some lists, to show that the indented lines form a part of the non-indented line above them. For example:
5 These are the names of the leaders who must fight with you:
From the tribe of Reuben, Elizur son of Shedeur;
6 from the tribe of Simeon, Shelumiel son of Zurishaddai;
7 from the tribe of Judah, Nahshon son of Amminadab; (Numbers 1:5-7 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
How to Use the ULB and UDB when Translating the Bible
This page answers the question: What is the best way to use the ULB and UDB in translating the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
As translators, you can best use the ULB and UDB if you remember the following differences between the ULB and UDB, and if you learn how the target language can best deal with the issues that these differences represent.
Order of Ideas
The ULB tries to present ideas in the same order as they appear in the source text.
The UDB tries to present ideas in an order that is more natural in English, or that follows the order of logic or the order of sequence in time.
When you translate, you should put ideas into an order that is natural in the target language. (see Order of Events)
1 Paul, a servant of Jesus Christ, called to be an apostle, and set apart for the gospel of God...7 This letter is to all who are in Rome, the beloved of God. (Romans 1:1,7 ULB)
1 I, Paul, who serve Christ Jesus, am writing this letter to all of you believers in the city of Rome. (Romans 1:1 UDB)
The ULB shows Paul's style of beginning his letters. He does not say who his audience is until verse 7. However, the UDB follows a style that is much more natural in English and many other languages today.
Implied Information
The ULB often presents ideas that imply or assume other ideas that are important for the reader to understand.
The UDB often makes those other ideas explicit. The UDB does this in order to remind you that you should perhaps do the same in your translation if you think that your audience will need to know this information in order to understand the text.
When you translate, you should decide which of these implied ideas would be understood by your audience without being included. If your audience understands these ideas without including them in the text, then you do not need to make those ideas explicit. Remember also that you might even offend your audience if you needlessly present implied ideas that they would understand anyway. (see Assumed Knowledge and Implicit Information)
And Jesus said to Simon, "Do not be afraid, because from now on you will catch men." (Luke 5:10 ULB)
But Jesus said to Simon, "Do not be afraid! Until now you gathered in fish, but from now on you will gather in people to become my disciples." (Luke 5:10 UDB)
Here the UDB reminds the reader that Simon was a fisherman by trade. It also makes clear the similarity that Jesus was drawing between Simon's previous work and his future work. In addition, the UDB makes it clear why Jesus wanted Simon to "catch men" (ULB), that is, to lead them "to become my disciples" (UDB).
When he saw Jesus, he fell on his face and begged him, saying, "Lord, if you are willing, you can make me clean." (Luke 5:12 ULB)
When he saw Jesus, he bowed down to the ground in front of him and pleaded with him, "Lord, please heal me, because you are able to heal me if you are willing!" (Luke 5:12 UDB)
Here the UDB makes it clear that the man who had leprosy did not fall to the ground by accident. Instead, he deliberately bowed down to the ground. Also, the UDB makes it clear that he is asking Jesus to heal him. In the ULB, he only implies this request.
Symbolic Actions
Definition - A symbolic action is something that someone does in order to express a certain idea.
The ULB often simply presents the symbolic action with no explanation of what it means. The UDB often presents the meaning expressed by the symbolic action as well.
When you translate, you should decide whether your audience will correctly understand a symbolic action. If your audience will not understand, then you should do as the UDB does. (see Symbolic Action)
The high priest tore his garments (Mark 14:63 ULB)
In response to Jesus' words, the high priest was so shocked that he tore his outer garment. (Mark 14:63 UDB)
Here the UDB makes it clear that it was not by accident that the high priest tore his garment. It also makes clear that it was probably only his outer garment that he tore, and that he did so because he wanted to show that he was sad or angry or both.
Because the high priest actually tore his garment, the UDB must, of course, say that he did. However, if a symbolic action never actually took place, you do not have to state that action. Here is such an example:
Present that to your governor; will he accept you or will he lift up your face?" (Malachi 1:8 ULB)
You would not dare to offer such gifts to your own governor! You know that he would not take them. You know that he would be displeased with you and would not welcome you! (Malachi 1:8 UDB)
Here the symbolic action "lift up someone's face," represented in this way in the ULB, is presented only as its meaning in the UDB: "he would be displeased with you and would not welcome you." It can be presented in this way because Malachi is not actually referring to a particular event that actually took place. He is only referring to the idea represented by that event.
Passive Verb Forms
Both Biblical Hebrew and Greek often use passive verb forms, while many other languages do not have that possibility. The ULB tries to use passive verb forms when the original languages use them. However, the UDB usually does not use these passive verb forms. As a result, the UDB restructures many phrases.
When you translate, you must decide whether the target language can present events or states using a passive expression, as in the following examples. If you cannot use a passive verb form in a particular context, then you may find in the UDB one possible way to restructure the phrase. (see Active or Passive)
Examples from the Bible
For he was amazed, and all who were with him, at the catch of fish which they had taken. (Luke 5:9 ULB)
He said this because he marveled at the huge number of fish that they had caught. All the men who were with him also marveled. (Luke 5:9 UDB)
Here the UDB uses a verb in the active voice "he marveled" instead of the ULB's verb in the passive voice "was amazed."
Large crowds of people came together to hear him teach and to be healed of their sicknesses. (Luke 5:15 ULB)
The result was that large crowds came to Jesus to hear him teach and to have him heal them from their sicknesses. (Luke 5:15 UDB)
Here the UDB avoids the ULB's passive verb form "to be healed." It does this by restructuring the phrase. It says who the healer is: "to have him [Jesus] heal them."
Metaphors and Other Figures of Speech
Definition - The ULB tries to represent the figures of speech found in the biblical texts as closely as possible.
The UDB often presents the meaning of these ideas in other ways.
When you translate, you will have to decide whether the target language readers will understand a figure of speech with little effort, with some effort, or not at all. If they have to make a great effort to understand, or if they do not understand at all, you will have to present the essential meaning of the figure of speech using other words.
He has made you rich in every way, in all speech and with all knowledge. (1 Corinthians 1:5 ULB)
Christ has given you so many things. He helped you to speak his truth and to know God. (1 Corinthians 1:5 UDB)
Paul uses a metaphor of material wealth, expressed in the word "rich." Even though he immediately explains what he means "in all speech and with all knowledge," some readers might not understand. The UDB presents the idea in a different way, without using the metaphor of material wealth. (see Metaphor)
I send you out as sheep in the midst of wolves, (Matthew 10:16 ULB)
When I send you out, you will be as defenseless as sheep, among people who are as dangerous as wolves. (Matthew 10:16 UDB)
Jesus uses a simile that compares his apostles going to others as sheep going out among wolves. Some readers might not understand how the apostles would be like sheep while the other people would be like wolves. The UDB clarifies that the apostles would be defenseless, and that their enemies would be dangerous. (see Simile)
You are separated from Christ, all you who are "justified" by the law. You have fallen away from grace. (Galatians 5:4 ULB)
If you expect God to declare you good in his sight because you try to keep the law, you have separated yourself from Christ; God will no longer act kindly toward you. (Galatians 5:4 UDB)
Paul uses irony when he refers to them as being justified by the law. He had already taught them that no one can be justified by the law. The ULB uses quote marks around "justified" to show that Paul did not really believe that they were justified by the law. The UDB translates the same idea by making it clear that it was what the other people believed. (see Irony)
Abstract Expressions
The ULB often uses abstract nouns, adjectives, and other parts of speech, because it tries to closely resemble the biblical texts. The UDB tries not to use such abstract expressions, because many languages do not use abstract expressions.
When you translate, you will have to decide how the target language prefers to present these ideas. (see Abstract Nouns)
He has made you rich in every way, in all speech and with all knowledge. (1 Corinthians 1:5 ULB)
Christ has given you so many things. He helped you to speak his truth and to know God. (1 Corinthians 1:5 UDB)
Here the ULB expressions "all speech" and "all knowledge" are abstract noun expressions. One problem with them is that readers might not know who is supposed to do the speaking and what they are to speak, or who is doing the knowing and what it is that they know. The UDB answers these questions.
Conclusion
In summary, the ULB will help you translate because it can help you understand to a great degree what form the original biblical texts have. The UDB can help you translate because it can help make the ULB text's meaning clear, and also because it can give you various possible ways to make the ideas in the biblical text clear in your own translation.
Use the translationHelps when Translating
Notes with Links
This page answers the question: Why should I use the links in the translationNotes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
There are two types of links in the translationNotes: links to a translationAcademy topic page and links for repeated words or phrases within the same book.
translationAcademy Topics
The translationAcademy topics are intended to enable anyone, anywhere to learn the basics of how to translate the Bible into their own language. They are intended to be highly flexible for just-in-time learning in web and offline mobile video formats.
Each translationNote follows a phrase from the ULB and will provide immediate help on how to translate that phrase. Sometimes there will be a statement in parenthesis at the end of the suggested translation that may look like this: (See: Metaphor). The word or words in green are a link to a translationAcademy topic. You can click on the link to learn more about the topic.
There are several reasons to read the translationAcademy topic information:
- Learning about the topic will help the translator to translate more accurately.
- The topics have been chosen to provide a basic understanding of the principles and strategies of translation.
Examples
- evening and morning - This refers to the whole day. Two parts of the day are used to refer to the whole day. In the Jewish culture, a day begins when the sun sets. (See: Merism)
- walking - "obeying" (See: Metaphor)
- made it known - "communicated it" (See: Idiom)
Repeated Phrases in a Book
Sometimes a phrase is used multiple times in one book. When this happens, there will be a link in the translationNotes-green chapter and verse numbers that you can click on-that will take you back to where you have translated that phrase before. There are several reasons why you will want to go to the place where the word or phrase was translated before:
- This will make it easier for you to translate this phrase by reminding you of how you have already translated it.
- This will make your translation faster and more consistent because you will be reminded to translate that phrase in the same way each time.
If a translation that you have used before for the same phrase does not fit a new context, then you will have to think of a new way to translate it. In this case, you should make a note of it and discuss it with others on the translation team.
These links will only take you back to notes in the book that you are working on.
Examples
- be fruitful and multiply - See how you translated these commands in Genesis 1:28.
- everything that creeps along the ground - This includes all types of small animals. See how you translated this in Genesis 1:25.
- will be blessed in him - AT: "will be blessed because of Abraham" or "will be blessed because I have blessed Abraham." For translating "in him," see how you translated "through you" in Genesis 12:3.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Using the translationNotes
This page answers the question: What are the different types of translationNotes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
To translate from the ULB
- Read the ULB. Do you understand the meaning of the text so that you can accurately, clearly, and naturally translate the meaning into your language?
- YES? Start translating.
- NO? Look at the UDB. Does the UDB help you understand the meaning of the ULB text?
- YES? Start translating.
- NO? Read the translationNotes for help.
TranslationNotes are words or phrases copied from the ULB and then explained. In English, every Note that explains the ULB starts the same. There is a bullet point, the ULB text is in bold followed by a dash, and then there are translation suggestions or information for the translator. The Notes follow this format:
- copied ULB text - translation suggestion or information for the translator.
Types of Notes
There are many different types of notes in the Translation Notes. Each type of note gives the explanation in a different way. Knowing the type of note will help the translator make decisions on the best way to translate the Bible text into their language.
-
Notes with Definitions - Sometimes you may not know what a word in the ULB means. Simple definitions of words or phrases are added without quotes or sentence format.
-
Notes that Explain - Simple explanations about words or phrases are in sentence format.
-
Notes that Suggest Other Ways to Translate - Because there are many different kinds of these Notes, they are explained in more detail below.
Suggested Translations
There are several types of suggested translations.
-
Notes with Synonyms and Equivalent Phrases - Sometimes the Notes provide a translation suggestion that can replace the word or phrases in the ULB. These replacements can fit into the sentence without changing the meaning of the sentence. These are synonyms and equivalent phrases and are written in double-quotes. These mean the same as the text in the ULB.
-
Notes with Alternate Translations (AT) - An alternate translation is a suggested change to the form or content of the ULB because the target language may prefer a different form. The alternate translation should only be used when the ULB form or content is not accurate or natural in your language.
-
Notes that Clarify the UDB Translation - When the UDB provides a good alternate translation for the ULB, then there may be no Note providing an Alternate Translation. However, on occasion a Note will provide Alternate Translations in addition to the text from the UDB, and sometimes it will quote the text from the UDB as an Alternate Translation. In that case, the Note will say "(UDB)" after the text from the UDB.
-
Notes that have Alternate Meanings - Some Notes provide Alternate Meanings when a word or phrase can be understood in more than one way. When this happens, the Note will put the most probable meaning first.
-
Notes with Probable or Possible Meanings - Sometimes Bible scholars do not know for sure, or do not agree on, what a particular phrase or sentence in the Bible means. Some reasons for this include: there are minor differences in the ancient Bible texts, or a word may have more than one meaning or use, or it may not be clear what a word (such as a pronoun) refers to in a particular phrase. In this case, the Note will give the most probable meaning, or will list several possible meanings, with the most probable meaning first.
-
Notes that Identify Figures of Speech - When there is a Figure of Speech in the ULB text, then the notes will provide an explanation of how to translate that Figure of Speech. Sometimes an Alternate Translation (AT:) is provided. There will also be a link to the translationAcademy page for additional information and translation strategies to help the translator accurately translate the meaning of that type of Figure of Speech.
-
Notes that Identify Indirect and Direct Quotes - There are two kinds of quotations: direct quotation and indirect quotation. When translating a quotation, translators need to decide whether to translate it as a direct quotation or an indirect quotation. These Notes will alert the translator to the choice that needs to be made.
-
Notes for Long ULB Phrases - Sometimes there are Notes that refer to a phrase and separate Notes that refer to portions of that phrase. In that case, the Note for the larger phrase is first, and the Notes for its smaller parts follow afterward. In that way, the Notes can give translation suggestions or explanations for the whole as well as each part.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Connecting Statement and General Information in the Notes
This page answers the question: Why do some translationNotes not have any ULB text at the beginning?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes, at the top of the list of notes, there are notes that start with Connecting Statement or General Information.
A connecting statement tells how the scripture in a chunk is related to scripture in earlier chunks. The following are some of the kinds of information in the connecting statements.
- whether this chunk is at the beginning, middle, or end of a passage
- who is speaking
- whom the speaker is speaking to
A general information note tells about issues in the chunk that cover more than one phrase. The following are some of the kinds of information that appear in a general information statement.
- the person or thing that pronouns refer to
- important background or implied information that is needed to understand the text in the chunk
- logical arguments and conclusions
Both types of notes are to help you understand the passage better and be aware of issues that you might need to address in translation.
Examples
Whether this chunk is at the beginning, continuation, or end of a passage
1It came about that when Jesus had finished instructing his twelve disciples, he departed from there to teach and preach in their cities. 2Now when John heard in the prison about the deeds of the Christ, he sent a message by his disciples 3and said to him, "Are you the Coming One, or is there another person we should be looking for?" (Matthew 11:1-3 ULB)
- General Information: - This is the beginning of a new part of the story where the writer tells of how Jesus responded to disciples of John the Baptist. (See: Introduction of New Event)
This note alerts you to the beginning of a new part of a story and gives you a link to a page that tells more about new events and issues concerning translating them.
Who is speaking
17For he was one of us and received his share of the benefits of this ministry." 18(Now this man bought a field with the earnings of his evil act. Then he fell head first, and his body burst wide open, and all his bowels poured out. 19It became known to all those living in Jerusalem that the field was called in their own language Akeldama, that is, The field of blood.) (Acts 1:17-19 ULB)
- Connecting Statement: - Peter continues his speech to the believers that he began in Acts 1:16.
This note tells you that it is still Peter speaking in verse 17 so you can mark that correctly in your language.
The person or thing that pronouns refer to
20And Isaiah is very bold and says,
"I was found by those who did not seek me.
I appeared to those who did not ask for me."
21But to Israel he says, "All the day long I reached out my hands
to a disobedient and resistant people." (Romans 10:20-21 ULB)
- General Information: - Here the words "I," "me," and "my" refer to God.
This note lets you know who the pronouns refer to. You may need to add something so that readers will know that Isaiah is not speaking for himself, but is quoting what God said.
Important background or implied information
26Now an angel of the Lord spoke to Philip and said, "Arise and go toward the south to the road that goes down from Jerusalem to Gaza." (This road is in a desert.) 27He arose and went. Behold, there was a man from Ethiopia, a eunuch of great authority under Candace, queen of the Ethiopians. He was in charge of all her treasure. He had come to Jerusalem to worship. 28He was returning and sitting in his chariot, and was reading the prophet Isaiah. (Acts 8:26-28 ULB)
- General Information: - This is the beginning of the part of the story about Philip and the man from Ethiopia. Verse 27 gives background information about the man from Ethiopia. (See: Backgrounds)
This note alerts you to the beginning of a new part of a story and to some background information so you can be aware of these things and use your language's ways of showing these things. The note includes a link to the page about background information so you can learn more about how to translate that kind of information.
Notes with Definitions
This page answers the question: What translating decision should I make when I see a definition in the notes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes you may not know what a word in the ULB means. The notes may have a definition or a description of the word or phrase to help you understand what it means.
Translation Notes Examples
Simple definitions of words or phrases are added without quotes or sentence format. Here are examples:
It is like children playing in the marketplace, who sit and call to one another and say, "We played a flute for you." (Matthew 11:16-17 ULB)
- marketplace - a large, open-air area where people would come to sell their goods
- flute - a long, hollow musical instrument which is played by blowing air in or over one end
people who dress in splendid clothing and live in luxury are in kings' palaces (Luke 7:25 ULB)
- kings' palaces - a large, expensive house that a king lives in
Translation Principles
- Use words that are already part of your language if possible.
- Keep expressions short if possible.
- Represent God's commands and historical facts accurately.
Translation Strategies
See Translate Unknowns for more information on translating words or phrases that are not known in your language.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Notes that Explain
This page answers the question: What translating decision should I make when I see an explanation in the notes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes you may not know what a word or phrase means in the ULB, and it may also be used in the UDB. In this case, it will be explained in the notes. These explanations are meant to help you understand the word or phrase. Do not translate the explanations into your Bible. Use them to help you understand the meaning so you can translate the Bible text correctly.
Translation Notes Examples
Simple explanations about words or phrases are written as full sentences. They begin with a capital letter and end with a period (".").
The fishermen had gotten out of them and were washing their nets.(Luke 5:2 ULB)
- washing their nets - They were cleaning their fishing nets in order to use them again to catch fish.
If you did not know that fishermen used nets to catch fish, you might wonder why the fishermen were cleaning their nets. This explanation can help you choose good words for "were washing" and "nets."
they motioned to their partners in the other boat (Luke 5:7 ULB)
- motioned - They were too far from shore to call so they made gestures, probably waving their arms.
This note can help you understand what kind of motion the people made. It was a motion that people would be able to see from a distance. This will help you choose a good word or phrase for "motioned."
He will be filled with the Holy Spirit, even while in his mother's womb. (Luke 1:14 ULB)
- even while in his mother's womb - The word "even" here indicates that this is especially surprising news. People had been filled with the Holy Spirit before, but no one had heard of an unborn baby being filled with the Holy Spirit.
This note can help you understand what the word "even" means in this sentence, so that you can find a way of showing how surprising this was.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Notes with Synonyms and Equivalent Phrases
This page answers the question: What translating decision should I make when I see words in double quote marks in the notes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some Notes provide a translation suggestion that can replace the word or phrase that they quote from the ULB. These replacements can fit into the sentence without changing the meaning of the sentence. These are synonyms and equivalent phrases and are written in double-quotes. These mean the same as the text in the ULB. This kind of Note can help you to think of other ways to say the same thing, in case the word or phrase in the ULB does not seem to have a natural equivalent in your language.
Translation Notes Examples
Make ready the way of the Lord, (Luke 3:4 ULB)
- the way - "the path" or "the road"
In this example, the words "the path" or the words "the road" can replace the words "the way" in the ULB. You can decide whether it is natural to say "way," "path," or "road" in your language.
Deacons, likewise, should be dignified, not double-talkers. (1 Timothy 3:8 ULB)
- Deacons, likewise - "In the same way, deacons" or "Deacons, like overseers"
In this example, the words "In the same way, deacons" or "Deacons, like overseers" can replace the words "Deacons, likewise" in the ULB. You, as the translator, can decide what is natural for your language.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Notes with Alternate Translations (AT)
This page answers the question: What translating decision should I make when I see "AT:" in the notes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
An alternate translation is a possible way to change the form of the ULB in case the target language prefers or needs a different form. The alternate translation should only be used when the ULB form or content would give a wrong meaning, or would be unclear or unnatural.
The alternate translation suggestion may involve, for example, stating implicit information clearly, changing passive voice to active, or rewording rhetorical questions as statements. The notes often explain why there is an alternate translation and have a link to a page that explains the topic.
Translation Notes Examples
The "AT:" indicates that this is an alternate translation. Some examples are:
Making Implicit Information Clear
it is the law of the Medes and Persians, that no decree or statute that the king issues can be changed. (Daniel 6:15 ULB)
- no decree...can be changed - An additional sentence may be added here to aid in understanding. AT: "no decree...can be changed. So they must throw Daniel into the pit of lions." (See: Explicit)
The additional sentence shows what the speaker wanted the king to understand from his reminder that the king's decrees and statues cannot be changed. Translators may need to state some things clearly in the translation that the original speaker or writer left unstated or implicit.
Passive to Active
to him who blasphemes against the Holy Spirit, it will not be forgiven. (Luke 12:10 ULB)
- it will not be forgiven - This can be expressed with an active verb. AT: God will not forgive him. This can also be expressed in a positive way using a verb that means the opposite of "forgive." AT: "God will consider him guilty forever" (See: Active Passive)
This Note provides an example of how translators can translate this passive sentence if their languages do not use passive sentences.
Rhetorical Question
Saul, Saul, why are you persecuting me? (Acts 9:4 ULB)
- why are you persecuting me? - This rhetorical question communicates a rebuke to Saul. In some languages, a statement would be more natural (AT): "You are persecuting me!" or a command (AT): "Stop persecuting me!" (See: Rhetorical Questions)
The translation suggestion here provides an alternate way to translate (AT) the rhetorical question if your language does not use that form of rhetorical question to rebuke someone.
Notes that Include a Quote from the UDB
This page answers the question: Why do some translationNotes have quotes from the UDB?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes a Note suggests a translation from the UDB. In that case the text from the UDB will be followed by "(UDB)."
Translation Notes Examples
He who sits in the heavens will sneer at them (Psalms 2:4 ULB)
But the one who sits on his throne in heaven laughs at them (Psalms 2:4 UDB)
The Note for this verse says:
- sits in the heavens - Here sitting represents ruling. What he sits on can be stated clearly. AT: "rules in the heavens" or "sits on his throne in heaven" (UDB) (See: Metonymy and Explicit)
Here there are two suggested translations for the phrase 'sits in the heavens.' The first expresses clearly what "sits in the heavens" represents. The second gives a hint about the idea of ruling by stated clearly that he sits on his "throne." This suggestion is from the UDB.
When he saw Jesus, he fell on his face. (Luke 5:12 ULB)
When he saw Jesus, he bowed down to the ground. (Luke 5:12 UDB)
The Note for this verse says:
- he fell on his face - "he knelt and touched the ground with his face" or "he bowed down to the ground" (UDB)
Here the words from the UDB are provided as another translation suggestion.
Notes That Have Alternate Meanings
This page answers the question: Why do some translationNotes have numbered translation suggestions?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Alternate meanings refer to when Bible scholars have different understandings of what a word or phrase means.
The note will have the ULB text followed by an explanation starting with the words "Possible meanings are." The meanings are numbered, and the first one is the one that most Bible scholars consider to be correct. If a meaning is given in a way that it can be used as a translation, it will have quote marks around it.
The translator needs to decide which meaning to translate. Translators may choose the first meaning, or they may choose one of the other meanings if the people in their community use and respect another Bible version that has one of those other meanings.
Translation Notes Examples
But take a small number of hairs from them and tie them into the folds of your robe. (Ezekiel 5:3 ULB)
- the folds of your robe -- Possible meanings are 1) "the cloth on your arms" ("your sleeves") (UDB) or 2) "the end of the cloth on your robe" ("your hem") or 3) the fold in the garment where it is tucked into the belt.
This note has the ULB text followed by three possible meanings. The word translated by "the folds of your robe" refers to the loose parts of the robe. Most scholars believe it refers here to the sleeves, but it could also refer to the loose part at the bottom or also to the folds in the middle, around the belt.
But Simon Peter, when he saw it, fell down at Jesus' knees (Luke 5:8 ULB)
- fell down at Jesus' knees - Possible meanings are 1) "knelt down before Jesus" or 2) "bowed down at Jesus' feet" or 3) "lay down on the ground at Jesus' feet." Peter did not fall accidentally. He did this as a sign of humility and respect for Jesus.
This note explains what "fell down at Jesus' knees" might mean. The first meaning is most likely correct, but the other meanings are also possible. If your language does not have a general expression that could include various actions like these, you may need to choose one of these possibilities that describe more specifically what Simon Peter did. It is also helpful to think about why Simon Peter did this, and what kind of action would communicate the same attitude of humility and respect in your culture.
Notes with Possible Meanings
This page answers the question: What translating decision should I make when I see the word "possible" in the note?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes Bible scholars do not know for sure, or do not agree on, what a particular phrase or sentence in the Bible means. Some reasons for this include:
- There are minor differences in the ancient Bible texts.
- A word may have more than one meaning or use.
- It may not be clear what a word (such as a pronoun) refers to in a particular phrase.
Translation Notes Examples
When many scholars say that a word or phrase means one thing, and many others say that it means other things, we show the most common meanings that they give. Our notes for these situations begin with "Possible meanings are" and then give a numbered list. We recommend that you use the first meaning given. However, if people in your community have access to another Bible that uses one of the other possible meanings, you may decide that it is better to use that meaning.
But Simon Peter, when he saw it, fell down at Jesus' knees, saying, "Depart from me, for I am a sinful man, Lord." (Luke 5:8 ULB)
- fell down at Jesus' knees - Possible meanings are 1) "knelt down before Jesus" or 2) "bowed down at Jesus feet" or 3) "lay down on the ground at Jesus feet." Peter did not fall accidentally. He did this as a sign of humility and respect for Jesus.
Translation Strategies
- Translate it in such a way that the reader could understand either meaning as a possibility.
- If it is not possible to do that in your language, then choose a meaning and translate it with that meaning.
- If not choosing a meaning would make it hard for the readers to understand the passage in general, then choose a meaning and translate it with that meaning.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Notes that Identify Figures of Speech
This page answers the question: How will I know if the translationNote is about a Figure of Speech?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Figures of speech are ways of saying things that use words in non-literal ways. That is, the meaning of a figure of speech is not the same as the more direct meaning of its words. There are many different types of figures of speech.
In the translationNotes there will be an explanation about the meaning of a figure of speech that is in the passage. Sometimes an alternate translation is provided. This is marked as "AT," which is the initial letters of "Alternate Translation." There will also be a link to a translationAcademy (tA) page that gives additional information and translation strategies for that kind of figure of speech.
In order to translate the meaning, you need to be able to recognize the figure of speech and know what it means in the source language. Then you can choose either a figure of speech or a direct way to communicate that same meaning in the target language.
Translation Notes Examples
Many will come in my name and say, 'I am he,' and they will lead many astray. (Mark 13:6 ULB)
- in my name - Possible meanings are 1) AT: "claiming my authority" or 2) "claiming that God sent them." (See: Metonymy and Idiom)
The figure of speech in this Note is called a metonymy. The phrase "in my name" does not refer to the speaker's name (Jesus), but to his person and authority. The Note explains the metonymy in this passage by giving two alternate translations. After that, there is a link to the tA page about metonymy. Click on the link to learn about metonymy and general strategies for translating metonymys. Because this phrase is also a common idiom, the Note includes a link to the tA page that explains idioms.
"You offspring of vipers! Who warned you to run away from the wrath that is coming? (Luke 3:7 ULB)
- You offspring of vipers - In this metaphor, John compares the crowd to vipers, which were deadly or dangerous snakes and represent evil. AT: "You evil poisonous snakes" or "People should stay away from you just like they avoid poisonous snakes" (See: Metaphor)
The figure of speech in this Note is called a metaphor. The Note explains the metaphor and gives two alternate translations. After that, there is a link to the tA page about metaphors. Click on the link to learn about metaphors and general strategies for translating them.
Notes that Identify Indirect and Direct Quotes
This page answers the question: How will translationNotes help me translate indirect and direct quotes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
There are two kinds of quotations: direct quotation and indirect quotation. When translating a quotation, translators need to decide whether to translate it as a direct quotation or an indirect quotation. (See: Direct and Indirect Quotations)
When there is a direct or indirect quote in the ULB, the notes may have an option for translating it as the other kind of quote. The translation suggestion may start with "It can be translated as a direct quote:" or "It can be translated as an indirect quote:" and it will be followed by that kind of quote. This will be followed by a link to the information page called "Direct and Indirect Quotations" that explains both kinds of quotations.
There may be a note about direct and indirect quotes when a quote has another quote inside of it, because these can be confusing. In some languages it may be more natural to translate one of these quotes with a direct quote and the other quote with an indirect quote. The note will end with a link to the information page called "Quotes within Quotes."
Translation Notes Examples
He instructed him to tell no one (Luke 5:14 ULB)
- to tell no one - This can be translated as a direct quote: "Do not tell anyone" There is implied information that can also be stated explicitly (AT): "do not tell anyone that you have been healed" (See: Direct and Indirect Quotations and Ellipsis)
Here the translationNote shows how to change the indirect quote to a direct quote, in case that would be clearer or more natural in the target language.
At the time of the harvest I will say to the reapers, "First pull out the weeds and tie them in bundles to burn them, but gather the wheat into my barn." (Matthew 13:30 ULB)
- I will say to the reapers, "First pull out the weeds and tie them in bundles to burn them, but gather the wheat into my barn" - You can translate this as an indirect quote: "I will tell the reapers to first gather up the weeds and tie them in bundles to burn them, then gather the wheat into my barn." (See: Direct and Indirect Quotations)
Here the translationNote shows how to change the direct quote to an indirect quote, in case that would be clearer or more natural in the target language.
Notes for Long ULB Phrases
This page answers the question: Why do some translationNotes seem to repeat a previous note?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes there are notes for a phrase and separate notes for portions of that phrase. In that case, the larger phrase is explained first, and its parts afterward.
Translation Notes Examples
But it is to the extent of your hardness and unrepentant heart that you are storing up for yourself wrath in the day of wrath (Romans 2:5 ULB)
- But it is to the extent of your hardness and unrepentant heart - Paul uses a metaphor to compare a person who refuses to obey God to something hard, like a stone. He also uses the metonym "heart" to represent the whole person. AT: "It is because you refuse to listen and repent" (See: Metaphor and Metonymy)
- hardness and unrepentant heart - The phrase "unrepentant heart" explains the word "hardness" (See: Doublet)
In this example the first note explains the metaphor and the metonymy, and the second explains the doublet in the same passage.
Using translationWords
This page answers the question: How can translationWords help me make a better translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
translationWords
It is the duty of the translator, to the best of his ability, to make sure that each Bible passage he translates has the meaning that the writer of that Bible passage intended it to communicate. In order to do this, he will need to study translation helps prepared by Bible scholars, including the translationWords resource.
In order to use translationWords, follow these steps:
- Identify the important words and any words in the source text that are ambiguous or difficult to understand.
- Look at the section called "translationWords."
- Find the words that you identified as important or difficult, and click on the first one.
- Read the translationWords entry for that word.
- After reading the definition, read the Bible passage again, thinking about the definition that you read in translationWords.
- Think of possible ways to translate the word in your language that fit the Bible context and the definition. It can be helpful to compare words and phrases in your language that have similar meaning and try each one.
- Choose the one that you think is best and write it down.
- Repeat the above steps for other translationWords that you identified.
- When you have thought of a good translation for each of the translationWords, then translate the whole passage.
- Test your translated passage by reading it to others. Change to a different word or phrase in places where others do not understand the meaning.
Once you have found a good translation for a translationWord, you should use it consistently throughout the translation. If you find a place where that translation does not fit, then think through the process again. It could be that a word with similar meaning will fit better in the new context. Keep track of which word or words you are using to translate each translationWord and make this information available to everyone on the translation team. This will help everyone on the translation team to know which words they should be using.
Unknown Ideas
Sometimes a translationWord refers to a thing or custom that is unknown in the target language. Possible solutions are to use a descriptive phrase, substitute something similar, use a foreign word from another language, use a more general word or use more specific words. See the lesson on Translate Unknowns for more information.
One kind of 'unknown idea' are words that refer to Jewish and Christian religious customs and beliefs. Some common unknown ideas are:
Names of places such as:
- Temple (a building where the Israelites offered sacrifices to God)
- Synagogue (a building where Jewish people assemble to worship God)
- Sacrificial altar (a raised structure on which sacrifices were burned as gifts, or offerings, to God.)
Titles of people who hold an office such as:
- Priest (someone who is chosen to offer sacrifices to God on behalf of his people)
- Pharisee (important group of Israel's religious leaders in Jesus' time)
- Prophet (person who delivers messages that come directly from God)
- Son of Man
- Son of God
- King (ruler of an independent city, state or country).
Key Biblical Concepts such as:
- Forgiveness (to not resent that person and not be angry at him for doing something hurtful)
- Salvation (being saved or rescued from evil, enemies, or from danger)
- Redemption (the act of buying back something that was previously owned or that was held captive)
- Mercy (helping people who are in need)
- Grace (help or regard that is given to someone who has not earned it)
(Notice that all of these are nouns, but they represent events, so they may need to be translated by verb (action) clauses.)
You may need to discuss the definitions of these translationWords with other members of the translation team or people from your church or village in order to discover the best way to translate them.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Using translationQuestions
This page answers the question: How can translationQuestions help me make a better translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
It is the duty of the translator, to the best of his ability, to make sure that each Bible passage he translates has the meaning that the writer of that Bible passage intended it to communicate. In order to do this, he will need to study translation helps prepared by Bible scholars, including translationQuestions.
The translationQuestions (tQ) are based on the text of the ULB, but they can be used to check any Bible translation. They ask questions about the content of the Bible, which should not change as it is translated into different languages. Along with each question, tQ provides a suggested answer for that question. You can use these sets of questions and answers as a way to check the accuracy of your translation, and you can also use them with members of the language community.
Using tQ during community checks will help the translator know if the Target Language translation is clearly communicating the right thing. If the community member can correctly answer the questions after hearing the translation of the Bible chapter, then the translation is clear and accurate.
Checking Translations with tQ
In order to use tQ when doing a self-check, follow these steps:
- Translate a passage, or chapter, of the Bible.
- Look at the section called "Questions."
- Read the question entry for that passage.
- Think of the answer from the translation. Try to not answer from what you know from other Bible translations.
- Click on the question to have the answer displayed.
- If your answer is correct, you may have done a good translation. But remember, you still need to test the translation with the language community, to see if it communicates that same meaning to others.
In order to use tQ for a community check, follow these steps:
- Read the newly completed translation of a Bible chapter to one or more community members.
- Tell the listeners to only answer the questions from this translation and to not answer using what they know from other translations of the Bible. This is a test of the translation, not of the people. Because of this, testing the translation with people who do not know the Bible well is very useful.
- Look at the section called "Questions."
- Read the first question entry for that chapter.
- Ask the community members to answer the question. Remind them to think of the answer only from the translation.
- Click on the question to have the answer displayed. If the community member's answer is very similar to the answer displayed, then the translation is clearly communicating the right thing. If the person cannot answer the question or answers incorrectly, the translation may not be communicating well and may need to be changed.
- Continue with the rest of the questions for the chapter.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Just-in-Time Learning Modules
Figures of Speech
Figures of Speech
This page answers the question: What are some figures of speech?
Figures of speech have special meanings that are not the same as the meanings of their individual words. There are different kinds of figures of speech. This page lists and defines some of those that are used in the Bible.
Definition
Figures of speech are ways of saying things that use words in non-literal ways. That is, the meaning of a figure of speech is not the same as the more direct meaning of its words. In order to translate the meaning, you need to be able to recognize figures of speech and know what the figure of speech means in the source language. Then you can choose either a figure of speech or a direct way to communicate that same meaning in the target language.
Types
Listed below are different types of Figures of Speech. If you would like additional information simply click the colored word to be directed to a page containing definitions, examples, and videos for each figure of speech.
-
Apostrophe - An apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone who is not there, or addresses a thing that is not a person.
-
Doublet - A doublet is a pair of words or very short phrases that mean the same thing and that are used in the same phrase. In the Bible, doublets are often used in poetry, prophecy, and sermons to emphasize an idea.
-
Euphemism - A euphemism is a mild or polite way of referring to something that is unpleasant or embarrassing. Its purpose is to avoid offending the people who hear or read it.
-
Hendiadys - In hendiadys a single idea is expressed with two words connected with "and," when one word could be used to modify the other.
-
Hyperbole - A hyperbole is a deliberate exaggeration used to indicate the speaker's feeling or opinion about something.
-
Idiom - An idiom is a group of words that has a meaning that is different from what one would understand from the meanings of the individual words.
-
Irony - Irony is a figure of speech in which the sense that the speaker intends to communicate is actually the opposite of the literal meaning of the words.
-
Litotes - Litotes is an emphatic statement about something made by negating an opposite expression.
-
Merism - Merism is a figure of speech in which a person refers to something by listing some of its parts or by speaking of two extreme parts of it.
-
Metaphor - A metaphor is a figure in which one concept is used in place of another, unrelated concept. This invites the hearer to think of what the unrelated concepts have in common. That is, metaphor is an implied comparison between two unrelated things.
-
Metonymy - Metonymy is a figure of speech in which a thing or idea is called not by its own name, but by the name of something closely associated with it. A metonym is a word or phrase used as a substitute for something it is associated with.
-
Parallelism - In parallelism two phrases or clauses that are similar in structure or idea are used together. It is found throughout the whole of the Hebrew Bible, most commonly in the poetry of the books of Psalms and Proverbs.
-
Personification - Personification is a figure in which an idea or something that is not human is referred to as if it were a person and could do the things that people do or have the qualities that people have.
-
Predictive Past - The predictive past is a form that some languages use to refer to things that will happen in the future. This is sometimes done in prophecy to show that the event will certainly happen.
-
Rhetorical Question - A rhetorical question is a question that is used for something other than getting information. Often it indicates the speaker's attitude toward the topic or the listener. Often it is used for rebuking or scolding, but some languages have other purposes as well.
-
Simile - A simile is a comparison of two things that are not normally thought to be similar. It focuses on a particular trait that the two items have in common, and it includes words such as "like," "as," or "than" to make the comparison explicit.
-
Synecdoche - Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which 1) the name of a part of something is used to refer to the whole thing, or 2) the name of a whole thing is used to refer to just one part of it.
Apostrophe
This page answers the question: What is the figure of speech called apostrophe?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Definition
An apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker turns his attention away from his listeners and speaks to someone or something that he knows cannot hear him.
Description
He does this to tell his listeners his message or feelings about that person or thing in a very strong way.
Reason this is a translation issue
Many languages do not use apostrophe, and readers could be confused by it. They may wonder who the speaker is talking to, or think that the speaker is crazy to talk to things or people who cannot hear.
Examples from the Bible
Mountains of Gilboa, let there not be dew or rain on you (2 Samuel 1:21 ULB)
King Saul was killed on Mount Gilboa, and David sang a sad song about it. By telling these mountains that he wanted them to have no dew or rain, he showed how sad he was.
Jerusalem, Jerusalem, who kills the prophets and stones those sent to you. (Luke 13:34 ULB)
Jesus was expressing his feelings for the people of Jerusalem in front of his disciples and a group of Pharisees. By speaking directly to Jerusalem as though its people could hear him, Jesus showed how deeply he cared about them.
He cried against the altar by the word of Yahweh: "Altar, altar! This is what Yahweh says, 'See, … on you they will burn human bones.' " (1 Kings 13:2 ULB)
The man of God spoke as if the altar could hear him, but he really wanted the king, who was standing there, to hear him.
Translation Strategies
If apostrophe would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here is another option.
- If this way of speaking would be confusing to your people, let the speaker continue speaking to the people that are listening to him as he tells them his message or feelings about the people or thing that cannot hear him.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If this way of speaking would be confusing to your people, let the speaker continue speaking to the people that are listening to him as he tells them his message or feelings about the people or thing that cannot hear him.
-
He cried against the altar by the word of Yahweh: "Altar, altar! This is what Yahweh says, 'See, … on you they will burn human bones.' " (1 Kings 13:2 ULB)
- He said this about the altar: "This is what Yahweh says about this altar. 'See, … they will burn people's bones on it.' "
-
Mountains of Gilboa, let there not be dew or rain on you (2 Samuel 1:21 ULB)
- As for these mountains of Gilboa, let there not be dew or rain on them
-
Doublet
This page answers the question: What are doublets and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
We are using the word "doublet" to refer to two words or very short phrases that mean the same thing or very close to the same thing and that are used together. Often they are joined with the word "and." Often they are used to emphasize or intensify the idea expressed by the two words.
Reason this is a translation issue
In some languages people do not use doublets. Or they may use doublets, but only in certain situations, so a doublet might not make sense in their language in some verses. In either case, translators may need to find some other way to express the meaning expressed by the doublet.
Examples from the Bible
King David was old and advanced in years. (1 Kings 1:1 ULB)
The underlined words mean the same thing. Together they mean that he was "very old."
... he attacked two men more righteous and better than himself ... (1 Kings 2:32 ULB)
This means that they were "much more righteous" than he was.
You have decided to prepare false and deceptive words (Daniel 2:9 ULB)
This means that they had prepared "many false things to say."
... as of a lamb without blemish and without spot. (1 Peter 1:19 ULB)
This means that he was like a lamb that did not have any blemish--not even one.
Translation Strategies
If a doublet would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using one. If not, consider these strategies.
- Translate only one of the words.
- If the doublet is used to intensify the meaning, translate one of the words and add a word that intensifies it such as "very" or "great" or "many."
- If the doublet is used to intensify or emphasize the meaning, use one of your language's ways of doing that.
Translation Strategies Applied
-
Translate only one of the words.
- You have decided to prepare false and deceptive words (Daniel 2:9 ULB)
- "You have decided to prepare false things to say."
- You have decided to prepare false and deceptive words (Daniel 2:9 ULB)
-
If the doublet is used to intensify the meaning, translate one of the words and add a word that intensifies it such as "very" or "great" or "many."
- King David was old and advanced in years. (1 Kings 1:1 ULB)
- "King David was very old."
- King David was old and advanced in years. (1 Kings 1:1 ULB)
-
If the doublet is used to intensify or emphasize the meaning, use one of your language's ways of doing that.
- ... a lamb without blemish and without spot... (1 Peter 1:19 ULB) - English can emphasize this with "any" and "at all."
- " ... a lamb without any blemish at all ..."
- ... a lamb without blemish and without spot... (1 Peter 1:19 ULB) - English can emphasize this with "any" and "at all."
Euphemism
This page answers the question: What is a Euphemism?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
A euphemism is a mild or polite way of referring to something that is unpleasant, embarrassing, or socially unacceptable, such as death or activities usually done in private.
Definition
... they found Saul and his sons fallen on Mount Gilboa. (1 Chronicles 10:8 ULB)
This means that Saul and his sons "were dead". It is a euphemism because the important thing was not that Saul and his sons had fallen but that they were dead. Sometimes people do not like to speak directly about death because it is unpleasant.
Reason this is a translation issue
Different languages use different euphemisms. If the target language does not use the same euphemism as in the source language, readers may not understand what it means and they may think that the writer means only what the words literally say.
Examples from the Bible
... where there was a cave. Saul went inside to relieve himself ... (1 Samuel 24:3 ULB)
The original hearers would have understood that Saul went into the cave to use it as a toilet, but the writer wanted to avoid offending or distracting them, so he did not say specifically what Saul did or what he left in the cave.
Mary said to the angel, “How will this happen, since I have not slept with any man?” (Luke 1:34 ULB)
In order to be polite, Mary uses a euphemism to say that she has never had sexual intercourse with a man.
Translation Strategies
If euphemism would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are other options:
- Use a euphemism from your own culture.
- State the information plainly without a euphemism if it would not be offensive.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Use a euphemism from your own culture.
-
... where there was a cave. Saul went inside to relieve himself. (1 Samuel 24:3 ULB) - Some languages might use euphemisms like these:
- "...where there was a cave. Saul went into the cave to dig a hole"
- "...where there was a cave. Saul went into the cave to have some time alone"
-
Mary said to the angel, “How will this happen, since I have not slept with any man?” (Luke 1:34 ULB)
- Mary said to the angel, “How will this happen, since I do not know a man?” - (This is the euphemism used in the original Greek)
2) State the information plainly without a euphemism if it would not be offensive.
- they found Saul and his sons fallen on Mount Gilboa. (1 Chronicles 10:8 ULB)
- "they found Saul and his sons dead on Mount Gilboa."
Extended Metaphor
This page answers the question: What is an extended metaphor?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
An extended metaphor occurs when someone speaks of a situation as if it were a different situation. He does this in order to effectively describe the first situation by implying that in some important way it is similar to the other. The second situation has multiple images of people, things, and actions that represent those in the first situation.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- People may not realize that the images represent other things.
- People may not be familiar with the things that are used as images.
- Extended metaphors are often so profound that it would be impossible for a translator to show all of the meaning generated by the metaphor.
Translation Principles
- Make the meaning of the extended metaphor as clear to the target audience as it was to the original audience.
- Do not make the meaning more clear to the target audience than it was to the original audience.
- When someone uses an extended metaphor, the images are an important part of what he is trying to say.
- If the target audience is not familiar with some of the images, you will need to find some way of helping them understand the images so they can understand the whole extended metaphor.
Examples from the Bible
In Psalm 23:1-4, the writer says that God's concern and care for his people can be pictured as the care that a shepherd has for his flock of sheep. Shepherds give sheep what they need, take them to safe places, rescue them, guide them, and protect them. What God does for his people is like these actions.
1Yahweh is my shepherd; I will lack nothing.
2He makes me to lie down in green pastures;
he leads me beside tranquil water.
3He brings back my life;
he guides me along right paths for his name's sake.
4Even though I walk through a valley of darkest shadow,
I will not fear harm since you are with me;
your rod and your staff comfort me. (ULB)
In Isaiah 5:1-7, Isaiah presents God's disappointment with his people as the disappointment that a farmer would feel if his vineyard only produced bad fruit. Farmers care for their gardens, but if they only produce bad fruit, farmers eventually stop caring for them. Verses 1 through 6 appear to be simply about a farmer and his vineyard, but verse 7 makes it clear that it is about God and his people.
1...My well beloved had a vineyard on a very fertile hill.
2He spaded it and removed the stones, and planted it with the choicest vine.
He built a tower in the middle of it, and also built a winepress.
He waited for it to produce grapes, but it produced wild grapes.3So now, inhabitants of Jerusalem and men of Judah;
judge between me and my vineyard.
4What more could have been done for my vineyard, that I have not done for it?
When I looked for it to produce grapes, why did it produce wild grapes?
5 Now I will inform you what I will do to my vineyard; I will remove the hedge;
I will turn it into a pasture; I will break down its wall, and it will be trampled on.
6I will lay it waste, and it will not be pruned nor hoed. But briers and thorns will spring up,
I will also command the clouds not to rain on it.7For the vineyard of Yahweh of hosts is the house of Israel,
and the men of Judah his pleasant planting;
he waited for justice, but instead, there was killing;
for righteousness, but, instead, a cry for help. (ULB)
Translation Strategies
Consider using the same extended metaphor if your readers will understand it in the same way the original readers would have understood it. If not, here are some other strategies:
- If the target audience would think that the images should be understood literally, translate it as a simile by using "like" or "as." It may be enough to to do this in just the first sentence or two.
- If the target audience would not know the image, find a way of translating it so they can understand what the image is.
- If the target audience still would not understand, then state it clearly.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) If the target audience would think that the images should be understood literally, translate it as a simile by using "like" or "as." It may be enough to to do this in just the first sentence or two. See Psalm 23:1-2 as an example:
Yahweh is my shepherd; I will lack nothing.
He makes me to lie down in green pastures;
he leads me beside tranquil water. (ULB)
Can be translated as:
"Yahweh is like a shepherd to me, so I will lack nothing.
Like a shepherd who makes his sheep lie down in green pastures and leads them by peaceful waters,
Yahweh helps me to rest peacefully."
2) If the target audience would not know the image, find a way of translating it so they can understand what the image is.
My well beloved had a vineyard on a very fertile hill.
He spaded it and removed the stones, and planted it with the choicest vine.
He built a tower in the middle of it, and also built a winepress.
He waited for it to produce grapes, but it produced wild grapes.(Isaiah 5:1-2 ULB)
May be translated as:
"My well beloved had a grapevine garden on a very fertile hill.
He dug up the ground and removed the stones, and planted it with the best grapevines.
He built a watchtower in the middle of it, and also built a tank where he could crush the juice out of the grapes.
He waited for it to produce grapes, but it produced wild grapes that were not good for making wine."
3) If the target audience still would not understand, then state it clearly.
Yahweh is my shepherd; I will lack nothing.** (Psalm 23:1 ULB)
- "Yahweh cares for me like a shepherd that cares for his sheep, so I will lack nothing."
For the vineyard of Yahweh of hosts is the house of Israel,
and the men of Judah his pleasant planting;
he waited for justice, but instead, there was killing;
for righteousness, but, instead, a cry for help. (Isaiah 5:7 ULB)
Can be translated as:
For the vineyard of Yahweh of hosts represents the house of Israel,
and the men of Judah are like his pleasant planting;
he waited for justice, but instead, there was killing;
for righteousness, but, instead, a cry for help.
OR
- So as a farmer stops caring for a grapevine garden that produces bad fruit,
- Yahweh will stop protecting Israel and Judah,
- because they do not do what is right.
- he waited for justice, but instead, there was killing;
- for righteousness, but, instead, a cry for help.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Hendiadys
This page answers the question: What is hendiadys and how can I translate phrases that have it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
When a speaker expresses a single idea by using two words that are connected with "and," it is called "hendiadys." In hendiadys, the two words work together. Usually one of the words is the primary idea and the other word further describes the primary one.
... his own kingdom and glory. (1 Thessalonians 2:12 ULB)
Though "kingdom" and "glory" are both nouns, "glory" actually tells what kind of kingdom it is: it is a kingdom of glory or a glorious kingdom.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Often hendiadys contains an abstract noun. Some languages may not have a noun with the same meaning.
- Many languages do not use hendiadys, so people may not understand how the two words work together; one word describing the other.
Examples from the Bible
... for I will give you words and wisdom ... (Luke 21:15 ULB)
"Words" and "wisdom" are nouns, but in this figure of speech "wisdom" describes "words."
... if you are willing and obedient ... (Isaiah 1:19 ULB)
"Willing" and "obedient" are adjectives, but "willing" describes "obedient."
Translation Strategies
If the hendiadys would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are other options:
- Substitute the describing noun with an adjective that means the same thing.
- Substitute the describing noun with a phrase that means the same thing.
- Substitute the describing adjective with an adverb that means the same thing.
- Substitute other parts of speech that mean the same thing and show that one word describes the other.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Substitute the describing noun with an adjective that means the same thing.
-
for I will give you words and wisdom (Luke 21:15 ULB)
- for I will give you wise words
-
that you should walk in a manner that is worthy of God, who calls you to his own kingdom and glory. (1 Thessalonians 2:12 ULB)
- that you should walk in a manner that is worthy of God, who calls you to his own glorious kingdom.
-
-
Substitute the describing noun with a phrase that means the same thing.
-
for I will give you words and wisdom. (Luke 21:15 ULB)
- for I will give you words of wisdom.
-
that you should walk in a manner that is worthy of God, who calls you to his own kingdom and glory. (1 Thessalonians 2:12 ULB)
- that you should walk in a manner that is worthy of God, who calls you to his own kingdom of glory.
-
-
Substitute the describing adjective with an adverb that means the same thing.
- if you are willing and obedient (Isaiah 1:19 ULB)
- if you are willingly obedient
- if you are willing and obedient (Isaiah 1:19 ULB)
-
Substitute other parts of speech that mean the same thing and show that one word describes the other.
- if you are, willing and obedient (Isaiah 1:19 ULB) - The adjective "obedient" can be substituted with the verb "obey."
- if you obey willingly
- if you are, willing and obedient (Isaiah 1:19 ULB) - The adjective "obedient" can be substituted with the verb "obey."
Next we recommend you learn about:
Hyperbole and Generalization
This page answers the question: What are hyperboles? What are generalizations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
A speaker or writer can use exactly the same words to say something he means as completely true, as generally true, or as a hyperbole. This is why it can be hard to decide how to understand a statement.
-
It rains here every night.
-
The speaker means this as literally true if he means that it really does rain here every night.
- The speaker means this as a generalization if he means that it rains here most nights.
- The speaker means this as a hyperbole if he wants to say it rains more than it actually does, usually in order to express a strong attitude toward the amount of rain, such as being annoyed or being happy.
Hyperbole: This is a figure of speech that uses exaggeration. A speaker deliberately describes something by an extreme or even unreal statement, usually to show his strong feeling or opinion about it. He expects people to understand that he is exaggerating.
They will not leave one stone upon another (Luke 19:44 ULB)
- This is an exaggeration. It means that the enemies will completely destroy Jerusalem.
Generalization: This is a statement that is true most of the time or in most situations that it could apply to.
The one who ignores instruction will have poverty and shame, but honor will come to him who learns from correction. (Proverbs 13:18)
- These generalizations tell about what normally happens to people who ignore instruction and what normally happens to people who learn from correction.
And when you pray, do not make useless repetitions as the Gentiles do, for they think that they will be heard because of their many words. (Matthew 6:7)
- This generalization tells about what Gentiles were known for doing. Many Gentiles may have done this.
Even though a generalization may have a strong-sounding word like "all," "always," "none," or "never," it does not necessarliy mean exactly "all," "always," "none," or "never." It simply means "most, "most of the time," "hardly any" or "rarely."
Moses was educated in all the learning of the Egyptians (Acts 7:22 ULB)
- This generalization means that he had learned much of what the Egyptians knew and taught.
Reason this is a translation issue
- Readers need to be able to understand whether or not a statement is completely true.
- If readers realize that a statement is not completely true, they need to be able to understand whether it is a hyperbole, a generalization, or a lie. (Though the Bible is completely true, it tells about people who did not always tell the truth.)
Examples from the Bible
Examples of Exaggeration
If your hand causes you to stumble, cut it off. It is better for you to enter into life maimed… (Mark 9:43 ULB)
When Jesus said to cut off your hand, he meant that we should do whatever extreme things we need to do in order not to sin. He used this hyperbole to show how extremely important it is to try to stop sinning.
The Philistines gathered together to fight against Israel: thirty thousand chariots, six thousand men to drive the chariots, and troops as numerous as the sand on the seashore. (1 Samuel 13:5 ULB)
The underlined phrase is an exaggeration. It means that there were many, many soldiers in the Philistine army.
Examples of Generalization
They found him, and they said to him, "Everyone is looking for you." (Mark 1:37 ULB)
The disciples told Jesus that everyone was looking looking for him. They probably did not mean that everyone in the city was looking for him, but that many people were looking for him, or that all of Jesus' closest friends there were looking for him.
But as his anointing teaches you about all things and is true and is not a lie, and even as it has taught you, remain in him. (1 John 2:27 ULB)
This is a generalization. God's Spirit teaches us about all things that we need to know, not about everything that is possible to know.
Caution
Do not assume that something is an exaggeration just because it seems to be impossible. God does miraculous things.
… they saw Jesus walking on the sea and coming near the boat … (John 6:19 ULB)
This is not hyperbole. Jesus really walked on the water. It is a literal statement.
Do not assume that the word "all" is always a generalization that means "most."
Yahweh is righteous in all his ways and gracious in all he does. (Psalms 145:17 ULB)
Yahweh is always righteous. This is a completely true statement.
Translation Strategies
If the exaggeration or generalization would be natural and people would understand it and not think that it is a lie, consider using it. If not, here are other options.
- Express the meaning without the exaggeration.
- For a generalization, show that it is a generalization by using a phrase like "in general" or "in most cases."
- For a generalization, add a word like "most" or "almost" to show that the generalization is not exact.
- For a generalization that has a word like "all," always," "none," or "never," consider deleting that word.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Express the meaning without the exaggeration.
- The Philistines gathered together to fight against Israel: thirty thousand chariots, six thousand men to drive the chariots, and troops as numerous as the sand on the seashore. (1 Samuel 13:5 ULB)
- The Philistines gathered together to fight against Israel: thirty thousand chariots, six thousand men to drive the chariots, and a great number of troops.
- The Philistines gathered together to fight against Israel: thirty thousand chariots, six thousand men to drive the chariots, and troops as numerous as the sand on the seashore. (1 Samuel 13:5 ULB)
-
For a generalization, show that it is a generalization by using a phrase like "in general" or "in most cases."
- The one who ignores instruction will have poverty and shame ... (Proverbs 13:18 ULB)
- In general, the one who ignores instruction will have poverty and shame
- And when you pray, do not make useless repetitions as the Gentiles do, for they think that they will be heard because of their many words. (Matthew 6:7)
- "And when you pray, do not make useless repetitions as the Gentiles generally do, for they think that they will be heard because of their many words."
- The one who ignores instruction will have poverty and shame ... (Proverbs 13:18 ULB)
-
For a generalization, add a word like "most" or "almost" to show that the generalization is not exact.
- The whole country of Judea and all the people of Jerusalem went out to him. (Mark 1:5 ULB)
- Almost all the country of Judea and almost all the people of Jerusalem went out to him."
- Most of the country of Judea and most of the people of Jerusalem went out to him."
- The whole country of Judea and all the people of Jerusalem went out to him. (Mark 1:5 ULB)
-
For a generalization that has a word like "all," always," "none," or "never," consider deleting that word.
- The whole country of Judea and all the people of Jerusalem went out to him. (Mark 1:5 ULB)
- The country of Judea and the people of Jerusalem went out to him.
- The whole country of Judea and all the people of Jerusalem went out to him. (Mark 1:5 ULB)
Idiom
This page answers the question: What are idioms and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
An idiom is a figure of speech made up of a group of words that, as a whole, has a meaning that is different from what one would understand from the meanings of the individual words. Someone from outside of the culture usually cannot understand an idiom without someone inside the culture explaining its true meaning. Every language uses idioms. Some English examples are:
- You are pulling my leg (This means, "You are telling me a lie")
- Do not push the envelope (This means, "Do not take a matter to its extreme")
- This house is under water (This means, "The debt owed for this house is greater than its actual value")
- We are painting the town red (This means, "We are going around town tonight celebrating very intensely")
Description
An idiom is a phrase that has a special meaning to the people of the language or culture who use it. Its meaning is different than what a person would understand from the meanings of the individual words that form the phrase.
he resolutely set his face to go to Jerusalem. (Luke 9:51 ULB)
The words "set his face" is an idiom that means "decided."
Sometimes people may be able to understand an idiom from another culture, but it might sound like a strange way to express the meaning.
I am not worthy that you should enter under my roof. (Luke 7:6 ULB)
The phrase "enter under my roof" is an idiom that means "enter my house."
Let these words go deeply into your ears. (Luke 9:44 ULB)
This idiom means "Listen carefully and remember what I say."
Purpose: An idiom is created in a culture probably somewhat by accident when someone describes something in an unusual way. But, when that unusual way communicates the message powerfully and people understand it clearly, other people start to use it. After a while, it becomes a normal way of talking in that language.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- People can easily misunderstand idioms in the original languages of the Bible if they do not know the cultures that produced the Bible.
- People can easily misunderstand idioms that are in the source language Bibles if they do not know the cultures that made those translations.
- It is useless to translate idioms literally (according to the meaning of each word) when the target language audience will not understand what they mean.
Examples from the Bible
Then all Israel came to David at Hebron and said, "Look, we are your flesh and bone." (1 Chronicles 11:1 ULB)
This means, "We and you belong to the same race, the same family."
the children of Israel went out with a high hand. (Exodus 14:8 ASV)
This means, "The Israelites went out defiantly."
the one who lifts up my head (Psalm 3:3 ULB)
This means, "the one who helps me."
Translation Strategies
If the idiom would be clearly understood in your language, consider using it. If not, here are some other options.
- Translate the meaning plainly without using an idiom.
- Use a different idiom that people use in your own language that has the same meaning.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Translate the meaning plainly without using an idiom.
-
Then all Israel came to David at Hebron and said, "Look, we are your flesh and bone." ( 1 Chronicles 11:1 ULB)
- ...Look, we all belong to the same nation.
-
he resolutely set his face to go to Jerusalem. (Luke 9:51 ULB)
- He started to travel to Jerusalem, determined to reach it.
-
I am not worthy that you should enter under my roof. (Luke 7:6 ULB)
- I am not worthy that you should enter my house.
-
-
Use an idiom that people use in your own language that has the same meaning.
-
Let these words go deeply into your ears (Luke 9:44 ULB)
- Be all ears when I say these words to you.
-
"My eyes grow dim from grief (Psalm 6:7 ULB)
- I am crying my eyes out
-
Irony
This page answers the question: What is irony and how can I translate it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Irony is a figure of speech in which the sense that the speaker intends to communicate is actually the opposite of the literal meaning of the words. Sometimes a person does this by using someone else's words, but in a way that communicates that he does not agree with them. People do this to emphasize how different something is from what it should be, or how someone else's belief about something is wrong or foolish. It is often humorous.
Jesus answered them, "People who are in good health do not need a physician, only people who are sick need one. I did not come to call righteous people to repentance, but to call sinners to repentance." (Luke 5:31-32 ULB)
When Jesus spoke of "righteous people," he was not referring to people who were truly righteous, but to people who wrongly believed that they were righteous. By using irony, Jesus communicated that they were wrong to think that they were better than others and did not need to repent.
Reason this is a translation issue
- If someone does not realize that a speaker is using irony, he will think that the speaker actually believes what he is saying. He will understand the passage to mean the opposite of what it was intended to mean.
Examples from the Bible
How well you reject the commandment of God so you may keep your tradition! (Mark 7:9 ULB)
Here Jesus praises the Pharisees for doing something that is obviously wrong. Through irony, he communicates the opposite of praise: He communicates that the Pharisees, who take great pride in keeping the commandments, are so far from God that they do not even recognize that their traditions are breaking God's commandments. The use of irony makes the Pharisee's sin more obvious and startling.
"Present your case," says Yahweh; "present your best arguments for your idols," says the King of Jacob. "Let them bring us their own arguments; have them come forward and declare to us what will happen, so we may know these things well. Have them tell us of earlier predictive declarations, so we can reflect on them and know how they were fulfilled." (Isaiah 41:21-22 ULB)
People worshiped idols as if their idols had knowledge or power, and Yahweh was angry at them for doing that. So he used irony and challenged their idols to tell what would happen in the future. He knew that the idols could not do this, but by speaking as if they could, he mocked the idols, making their inability more obvious, and rebuked the people for worshiping them.
Can you lead light and darkness to their places of work?
Can you find the way back to their houses for them?
Undoubtedly you know, for you were born then;
"the number of your days is so large!" (Job 38:20, 21 ULB)
Job thought that he was wise. Yahweh used irony to show Job that he was not so wise. The two underlined phrases above are irony. They emphasize the opposite of what they say, because they are so obviously false. They emphasize that Job could not possibly answer God's questions about the creation of light because Job was not born until many, many years later.
Already you have all you could want! Already you have become rich! You began to reign—and that quite apart from us! (1 Corinthians 4:8 ULB)
The Corinthians considered themselves to be very wise, self-sufficient, and not in need of any instruction from the Apostle Paul. Paul used irony, speaking as if he agreed with them, to show how proudly they were acting and how far from being wise they really were.
Translation Strategies
If the irony would be understood correctly in your language, translate it as it is stated. If not, here are some other strategies.
- Translate it in a way that shows that the speaker is saying what someone else believes.
- Translate the actual, intended meaning of the statement of irony. The actual meaning of the irony is not found in the literal words of the speaker, but instead the true meaning is found in the opposite of the literal meaning of the speaker's words.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Translate it in a way that shows that the speaker is saying what someone else believes.
-
How well you reject the commandment of God so you may keep your tradition! (Mark 7:9 ULB)
- You think that you are doing well when you reject God's commandment so you may keep your tradition!
- You act like it is good to reject God's commandment so you may keep your tradition!
-
I did not come to call righteous people to repentance, but to call sinners to repentance. (Luke 5:32 ULB)
- I did not come to call people who think that they are righteous to repentance, but to call sinners to repentance.
2) Translate the actual, intended meaning of the statement of irony.
-
How well you reject the commandment of God so you may keep your tradition! (Mark 7:9 ULB)
- You are doing a terrible thing when you reject the commandment of God so you may keep your tradition!
-
"Present your case," says Yahweh; "present your best arguments for your idols," says the King of Jacob. "Let them bring us their own arguments; have them come forward and declare to us what will happen, so we may know these things well. Have them tell us of earlier predictive declarations, so we can reflect on them and know how they were fulfilled." (Isaiah 41:21-22 ULB)
- 'Present your case,' says Yahweh; 'present your best arguments for your idols,' says the King of Jacob. Your idols cannot bring us their own arguments or come forward to declare to us what will happen so we may know these things well. We cannot hear them because they cannot speak to tell us their earlier predictive declarations, so we cannot reflect on them and know how they were fulfilled.
-
Can you lead light and darkness to their places of work?
Can you find the way back to their houses for them?
Undoubtedly you know, for you were born then;
the number of your days is so large!" (Job 38:20, 21 ULB)
- Can you lead light and darkness to their places of work? Can you find the way back to their houses for them? You act like you know how light and darkness were created, as if you were there; as if you are as old as creation, but you are not!
Next we recommend you learn about:
Litotes
This page answers the question: What is litotes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Litotes is a figure of speech in which the speaker expresses a strong positive meaning by using two negative words or a negative word with a word that means the opposite of the meaning he intends. A few examples of negative words are "no," "not," "none," and "never." The opposite of "good" is "bad." Someone could say that something is "not bad" to mean that it is extremely good.
Reason this is a translation issue
Some languages do not use litotes. People who speak those languages might not understand that a statement using litotes actually strengthens the positive meaning. Instead, they might think that it weakens or even cancels the positive meaning.
Examples from the Bible
For you yourselves know, brothers, our coming to you was not useless, (1 Thessalonians 2:1 ULB)
By using litotes, Paul emphasized that his visit with them was very useful.
Now when it became day, there was no small excitement among the soldiers, regarding what had happened to Peter. (Acts 12:18 ULB)
By using litotes, Luke emphasized that there was a lot of excitement or anxiety among the soldiers about what happened to Peter. (Peter had been in prison, and even though there were soldiers guarding him, he escaped when an angel let him out. So they were very agitated.)
And you, Bethlehem, in the land of Judah,
are not the least among the leaders of Judah,
for from you will come a ruler
who will shepherd my people Israel. (Matthew 2:6 ULB)
By using litotes, the prophet emphasized that Bethlehem would be a very important city.
Translation Strategies
If the litotes would be understood correctly, consider using it.
- If the meaning with the negative would not be clear, give the positive meaning in a strong way.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If the meaning with the negative would not be clear, give the positive meaning in a strong way.
-
For you yourselves know, brothers, our coming to you was not useless. (1 Thessalonians 2:1 ULB)
- "For you yourselves know, brothers, our visit to you did much good."
-
Now when it became day, there was no small excitement among the soldiers, regarding what had happened to Peter. (Acts 12:18 ULB)
- "Now when it became day, there was great excitement among the soldiers, regarding what had happened to Peter."
- "Now when it became day, the soldiers were very concerned because of what had happened to Peter."
-
Merism
This page answers the question: What does the word merism mean and how can I translate phrases that have it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Definition
Merism is a figure of speech in which a person refers to something by speaking of two extreme parts of it. By referring to the extreme parts, the speaker intends to include also everything in between those parts.
"I am the Alpha and the Omega," says the Lord God, "the one who is, and who was, and who is to come, the Almighty." (Revelation 1:8, ULB)
I am the Alpha and the Omega, the First and the Last, the Beginning and the End. (Revelation 22:13, ULB)
Alpha and Omega are the first and last letters of the Greek alphabet. This is a merism that includes everything from the beginning to the end. It means eternal.
I praise you, Father, Lord of heaven and earth ..., (Matthew 11:25 ULB)
Heaven and earth is a merism that includes everything that exists.
Reason this is a translation issue
Some languages do not use merism. The readers of those languages may think that the phrase only applies to the items mentioned. They may not realize that it refers to those two things and everything in between.
Examples from the Bible
From the rising of the sun to its setting, Yahweh's name should be praised. (Psalm 113:3 ULB)
This underlined phrase is a merism because it speaks of the east and the west and everywhere in between. It means "everywhere."
He will bless those who honor him, both young and old. (Psalm 115:13)
The underlined phrase is merism because it speaks of, old people and young people and everyone in between. It means "everyone."
Translation Strategies
If the merism would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are other options:
- Identify what the merism refers to without mentioning the parts.
- Identify what the merism refers to and include the parts.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Identify what the merism refers to without mentioning the parts.
-
I praise you, Father, Lord of heaven and earth ... (Matthew 11:25 ULB)
- I praise you, Father, Lord of everything ...
-
From the rising of the sun to its setting, Yahweh's name should be praised. (Psalm 113:3 ULB)
- In all places, people should praise Yahweh's name.
-
-
Identify what the merism refers to and include the parts.
-
I praise you, Father, Lord of heaven and earth. (Matthew 11:25 ULB)
- I praise you, Father, Lord of everything, including both what is in heaven and what is on earth.
-
He will bless those who honor him, both young and old. (Psalm 115:13 ULB)
- He will bless all those who honor him, regardless of whether they are young or old.
-
Metaphor
This page answers the question: What is a metaphor and how can I translate a sentence that has one?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
A metaphor is a figure of speech in which one concept (the "image") stands for another concept (the "topic"). That is, the topic is spoken of as if it were the image. For example, someone might say,
- The girl I love is a red rose.
Here the topic is "the girl I love," and the image is "a red rose." The girl is spoken of as if she were a red rose.
Anything in a language can serve as a metaphor. For example, verb forms can be used in unusual ways, as in,
- The Apostle Paul tells us that Christians will rise to life again.
In this case, the English present tense form "tells" is a metaphor for the past tense form "told," because the Apostle Paul lived long ago.
Sometimes speakers use metaphors that are very common in their language. However, sometimes speakers use metaphors that are uncommon, and even some metaphors that are unique.
Speakers most often use metaphors in order to strengthen their message, to express their feelings better, to say something that is hard to say in any other way, or to help people remember their message.
Kinds of Metaphors
There are several kinds of metaphors: "live" metaphors, "dead" metaphors, and patterned metaphors.
Live Metaphors
These are metaphors that people recognize as one concept standing for another concept. People also easily recognize them as giving strength and unusual qualities to the message. For this reason, people pay attention to these metaphors. For example,
For you who fear my name, the sun of righteousness will rise with healing in its wings. (Malachi 4:2 ULB)
Here God speaks about his salvation as if it were the sun rising in order to shine its rays on the people whom he loves. He also speaks of the sun's rays as if they were wings. Also, he speaks of these wings as if they were bringing medicine that would heal his people.
Here is another example: Jesus said, 'Go and tell that fox...,'" where "that fox" refers to King Herod. The people listening to Jesus certainly understood that Jesus was referring to Herod either as a very evil, cunning person or as a king who was only pretending to be great.
Dead Metaphors
A dead metaphor is a metaphor that has been used so much in the language that its speakers no longer regard it as one concept standing for another. Examples in English are "table leg," "family tree," "leaf" meaning a page in a book, and "crane" meaning a large machine for lifting heavy loads. English speakers simply think of these words as having more than one meaning. Examples in Biblical Hebrew are probably "heal" meaning "repair," and "sick" meaning "spiritually powerless because of sin."
Patterned Pairs of Concepts acting as Metaphors
Many ways of metaphorical speaking depend on pairs of concepts, where one underlying concept frequently stands for a different underlying concept. For example, in English, the direction UP often stands for the concept of MORE. Because of this pair of underlying concepts, we can make sentences such as "The price of gasoline is going up," "A highly intelligent man," and also the opposite kind of idea: "The heat is going down," and "The stock market took a tumble."
Patterned pairs of concepts are constantly used for metaphorical purposes in the world's languages, because they serve as convenient ways to organize thought. In general, people like to speak of abstract qualities, such as power, presence, emotions, and moral qualities, as if they were objects that could be seen or held, as if they were body parts, or as if they were events that could be watched as they happened.
When these metaphors are used in normal ways, it is rare that the speaker and audience regard them as figurative speech. Examples of metaphors in English that go unrecognized are:
- "Turn the heat up." MORE is spoken of as UP.
- "Let us go ahead with our debate." DOING WHAT WAS PLANNED is spoken of as WALKING or ADVANCING.
- "You defend your theory well." ARGUMENT is spoken of as WAR.
- "A flow of words" WORDS are spoken of as LIQUIDS.
English speakers do not view them as unusual expressions, so it would be wrong to translate them into other languages in a way that would lead people to pay special attention to them as figurative speech.
For a description of important patterns of this kind of metaphor in biblical languages, please see Biblical Imagery - Common Patternsand the pages it will direct you to.
Parts of a Metaphor
When talking about metaphors, it can be helpful to talk about their parts. A metaphor has three parts.
- Topic - The thing someone speaks of is called the topic.
- Image - The thing he calls it is the image.
- Points of Comparison - The ways in which the author claims that the topic and image are similar in some manner are their points of comparison.
In the metaphor below, the speaker describes the woman he loves as a red rose. The woman (his "love") is the topic, and "red rose" is the image. Beauty and delicacy are the points of comparison that the speaker sees as similarities between both the topic and image. Note, however, that a rose's beauty is not identical to a woman's beauty. Neither are the two kinds of delicacy the same. So these points of comparison are not built upon identical characteristics, but rather upon characteristics that are seen by the writer as similar in some way.
- My love is a red, red rose.
Often, as in the metaphor above, the speaker explicitly states the topic and the image, but he does not state the points of comparison. The speaker leaves it to the hearer to think of those points of comparison. Because the hearers must do that, the speaker's message tends to be more powerful.
Also in the Bible, normally the topic and the image are stated clearly, but not the points of comparison. The writer hopes that the audience will understand the points of comparison that are implied.
Jesus said to them. "I am the bread of life; he who comes to me will not be hungry, and he who believes in me will never be thirsty." (John 6:35 ULB)
In this metaphor, Jesus called himself the bread of life. The topic is "I," and the image is "bread." Bread is a food that people ate all the time. The point of comparison between bread and Jesus is that people needed break every day for nourishment. In a similar way, people need Jesus every day in order to live spiritually.
Note that this metaphor is really several metaphors. The first metaphor is that bread is used to represent Jesus. The second metaphor, which is inside the first one, is that physical life represents the spiritual life, which consists of living with God forever. The third metaphor is that eating bread represents benefitting from Jesus, who enables us to live with God forever.
Purposes of Metaphor
- One purpose of metaphor is to teach people about something that they do not know (the topic) by showing that it is like something that they already do know (the image).
- Another purpose is to emphasize that something has a particular quality or to show that it has that quality in an extreme way.
- Another purpose is to lead people to feel the same way about one thing as they would feel about the other.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- People may not recognize that something is a metaphor. In other words, they may mistake a metaphor for a literal statement, and thus misunderstand it.
- People may not be familiar with the thing that is used as an image, and so not be able to understand the metaphor.
- If the topic is not stated, people may not know what the topic is.
- People may not know the points of comparison that the speaker is thinking of and wants them to understand. If they fail to think of these points of comparison, they will not understand the metaphor.
Translation Principles
- Make the meaning of a metaphor as clear to the target audience as it was to the original audience.
- Do not make the meaning of a metaphor more clear to the target audience than you think it was to the original audience.
Examples from the Bible
Listen to this word, you cows of Bashan, (Amos 4:1 ULB)
In this metaphor Amos speaks to the upper-class women of Samaria (the topic is "you") with as if they were cows (the image). Amos does not say what points of comparison between these women and the cows he has mind, but from the context it seems that he means that both the women and the cows are fat and interested only in eating.
Note, however, that Amos does not actually mean that the women are cows, for he speaks to them as human beings.
And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the clay. You are our potter; and we all are the work of your hand. (Isaiah 64:8 ULB)
The example above has two related metaphors. The topics are "we" and "you," and the images are "clay and "potter." The intended point of comparison between a potter and God is the fact that both make what they wish: the potter makes what he wishes out of the clay, and God makes what he wishes out of his people Israel. The point of comparison between the potter's clay and "us" is that both the clay and the people of Israel are made into something different from what they were before.
Jesus said to them, "Take heed and beware of the yeast of the Pharisees and Sadducees." The disciples reasoned among themselves and said, "It is because we took no bread." (Matthew 16:6-7 ULB)
Jesus used a metaphor here, but his disciples did not realize it. When he said "yeast," they thought he was talking about bread, but "yeast" was the image in his metaphor, and the topic was the teaching of the Pharisees and Sadducees. Since the disciples (the original audience) did not understand what Jesus meant, it would not be good to state clearly here what Jesus meant.
Translation Strategies
If people would understand the metaphor in the same way that the original readers probably understood it, go ahead and use it. Be sure to test the translation to make sure that people do understand it.
If people do not or would not understand it, here are some other strategies.
- If the metaphor is a common expression of a patterned pair of concepts in a biblical language, express the main idea in the simplest way preferred by your language. (See Biblical Imagery - Common Patterns for lists of some of these patterned pairs of concepts.)
- If the metaphor seems to be a "live" metaphor, you can translate it literally if you think that the target language also uses this metaphor. If you do this, be sure to test it to make sure that the language community understands it correctly.
- If the target audience does not realize that it is a metaphor, then change the metaphor to a simile. Some languages do this by adding words such as "like" or "as." See Simile.
- If the target audience would not know the image, see Translate Unknowns for ideas on how to translate that image.
- If the target audience would not use that image for that meaning, use an image from your own culture instead. Be sure that it is an image that could have been possible in Bible times.
- If the target audience would not know what the topic is, then state the topic clearly. (However, do not do this if the original audience did not know what the topic was.)
- If the target audience will not know the intended points of comparison between the image and topic, then state them clearly.
- If none of these strategies is satisfactory, then simply state the idea plainly without using a metaphor.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If the metaphor is a common expression of a patterned pair of concepts in a biblical language, express the main idea in the simplest way preferred by your language.
- Then one of the leaders of the synagogue, named Jairus, came, and when he saw him, fell at his feet. (Mark 5:22 ULB)
- Then one of the leaders of the synagogue, named Jairus, came, and when he saw him, immediately bowed down in front of him.
- Then one of the leaders of the synagogue, named Jairus, came, and when he saw him, fell at his feet. (Mark 5:22 ULB)
-
If the metaphor seems to be a "live" metaphor, you can translate it literally if you think that the target language also uses this metaphor. If you do this, be sure to test it to make sure that the language community understands it correctly.
- It was because of your hard hearts that he wrote you this law, (Mark 10:5 ULB)
- It was because of your hard hearts that he wrote you this law,
- It was because of your hard hearts that he wrote you this law, (Mark 10:5 ULB)
There is no change to this one - but it must be tested to make sure that the target audience correctly understands this metaphor.
-
If the target audience does not realize that it is a metaphor, then change the metaphor to a simile. Some languages do this by adding words such as "like" or "as."
- And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the clay. You are our potter; and we all are the work of your hand. (Isaiah 64:8 ULB)
- And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are like clay. You are like a potter; and we all are the work of your hand.
- And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the clay. You are our potter; and we all are the work of your hand. (Isaiah 64:8 ULB)
-
If the target audience would not know the image, see Translate Unknowns for ideas on how to translate that image.
- Saul, Saul, why do you persecute me? It is hard for you to kick a goad. (Acts 26:14 ULB)
- Saul, Saul, why do you persecute me? It is hard for you to kick against a pointed stick.
- Saul, Saul, why do you persecute me? It is hard for you to kick a goad. (Acts 26:14 ULB)
-
If the target audience would not use that image for that meaning, use an image from your own culture instead. Be sure that it is an image that could have been possible in Bible times.
- And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the clay. You are our potter; and we all are the work of your hand. (Isaiah 64:8 ULB)
- "And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the wood. You are our carver; and we all are the work of your hand."
- "And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the string. You are the weaver; and we all are the work of your hand."
- And yet, Yahweh, you are our father; we are the clay. You are our potter; and we all are the work of your hand. (Isaiah 64:8 ULB)
-
If the target audience would not know what the topic is, then state the topic clearly. (However, do not do this if the original audience did not know what the topic was.)
- Yahweh lives; may my rock be praised. May the God of my salvation be exalted. (Psalm 18:46 ULB)
- Yahweh lives; He is my rock. May he be praised. May the God of my salvation be exalted.
- Yahweh lives; may my rock be praised. May the God of my salvation be exalted. (Psalm 18:46 ULB)
-
If the target audience will not know the intended points of comparison between the image and the topic, then state them clearly.
-
Yahweh lives; may my rock be praised. May the God of my salvation be exalted. (Psalm 18:46 ULB)
- Yahweh lives; may he be praised because he is the rock under which I can hide from my enemies. May the God of my salvation be exalted.
-
Saul, Saul, why do you persecute me? It is hard for you to kick a goad. (Acts 26:14 ULB)
- Saul, Saul, why do you persecute me? You fight against me and hurt yourself like an ox that kicks against its owner's pointed stick.
-
-
If none of these strategies are satisfactory, then simply state the idea plainly without using a metaphor.
- I will make you become fishers of men. (Mark 1:17 ULB)
- I will make you become people who gather men.
- Now you gather fish. I will make you gather people.
- I will make you become fishers of men. (Mark 1:17 ULB)
To learn more about specific metaphors read:
Metonymy
This page answers the question: What is a metonymy?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Metonymy is a figure of speech in which a thing or idea is called not by its own name, but by the name of something closely associated with it. A metonym is a word or phrase used as a substitute for something it is associated with.
and the blood of Jesus his Son cleanses us from all sin. (1 John 1:7 ULB)
The blood represents Christ's death.
He took the cup in the same way after supper, saying, "This cup is the new covenant in my blood, which is poured out for you. (Luke 22:20 ULB)
The cup represents the wine that is in the cup.
Metonymy can be used
- to a shorter way of referring to something
- to make an abstract idea more meaningful by referring to it with the name of a physical object associated with it
Reason this is a translation issue
The Bible uses metonymy very often. Speakers of some languages are not used to metonymy and they may not recognize it when they read it in the Bible. If they do not recognize the metonymy, they will not understand the passage or, worse yet, they will get a wrong understanding of the passage. Whenever a metonym is used, people need to be able to understand what it represents.
Examples from the Bible
The Lord God will give him the throne of his father, David. (Luke 1:32 ULB)
A throne represents the authority of a king. "Throne" is a metonym for "kingly authority," "kingship" or "reign." This means that God would make him become the king that would follow King David.
Immediately his mouth was opened (Luke 1:64 ULB)
The mouth here represents the power to speak. This means that he was able to talk again.
... who warned you to flee from the wrath that is coming? (Luke 3:7 ULB)
The word "wrath" or "anger" is a metonym for "punishment." God was extremely angry with the people, and as a result, he would punish them.
Translation Strategies
If people would easily understand the metonym, consider using it. Otherwise, here are some options.
- Use the metonym along with the name of the thing it represents.
- Use only the name of the thing the metonym represents.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use the metonym along with the name of the thing it represents.
- He took the cup in the same way after supper, saying, "This cup is the new covenant in my blood, which is poured out for you. (Luke 22:20 ULB)
- "He took the cup in the same way after supper, saying, "The wine in this cup is the new covenant in my blood, which is poured out for you."
- He took the cup in the same way after supper, saying, "This cup is the new covenant in my blood, which is poured out for you. (Luke 22:20 ULB)
-
Use the name of the thing the metonym represents.
-
The Lord God will give him the throne of his father, David. (Luke 1:32 ULB)
- "The Lord God will give him the kingly authority of his father, David."
- "The Lord God will make him king like his ancestor, King David."
-
who warned you to flee from the wrath to come? (Luke 3:7 ULB)
- "who warned you to flee from God's coming punishment?"
-
To learn about some common metonymies, see Biblical Imagery - Common Metonymies.
Parallelism
This page answers the question: What is parallelism?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
In parallelism two phrases or clauses that are similar in structure or idea are used together. There are different kinds of parallelism. Some of them are the following:
- The second clause or phrase means the same as the first. This is also called synonymous parallelism.
- The second clarifies or strengthens the meaning of the first.
- The second completes what is said in the first.
- The second says something that contrasts with the first, but adds to the same idea.
Parallelism is most commonly found in Old Testament poetry, such as in the books of Psalms and Proverbs. It also occurs in Greek in the New Testament, both in the four gospels and in the apostles' letters.
Synonymous parallelism (the kind in which the two phrases mean the same thing) in the poetry of the original languages has several effects:
- It shows that something is very important by saying it more than once and in more than one way.
- It helps the hearer to think more deeply about the idea by saying it in different ways.
- It makes the language more beautiful and above the ordinary way of speaking.
Reason this is a translation issue
Some languages would not use synonymous parallelism. They would either think it odd that someone said the same thing twice, or they would think that the two phrases must have some difference in meaning. For them it is confusing, rather than beautiful.
Note: We use the term "synonymous parallelism" for long phrases or clauses that have the same meaning. We use the term Doublet for words or very short phrases that mean basically the same thing and are used together.
Examples from the Bible
The second clause or phrase means the same as the first.
Your word is a lamp to my feet and a light for my path. (Psalm 119:105 ULB)
Both parts of the sentence are metaphors saying that God's word teaches people how to live.
You make him to rule over the works of your hands;
you have put all things under his feet (Psalm 8:6 ULB)
Both lines say that God made man the ruler of everything.
The second clarifies or strengthens the meaning of the first.
The eyes of Yahweh are everywhere,
keeping watch over the evil and the good. (Proverbs 15:3 ULB)
The second line tells more specifically what Yahweh watches.
The second completes what is said in the first.
I lift up my voice to Yahweh,
and he answers me from his holy hill. (Psalm 3:4 ULB)
The second line tells what Yahweh does in response to what the person does in the first clause.
The second says something that contrasts with the first, but adds to the same idea.
For Yahweh approves of the way of the righteous,
but the way of the wicked will perish. (Psalm 1:6 ULB)
This contrasts what happens to righteous people with what happens to wicked people.
A gentle answer turns away wrath,
but a harsh word stirs up anger. (Proverbs 15:1 ULB)
This contrasts what happens when someone gives a gentle answer with what happens when someone says something harsh.
Translation Strategies
For most kinds of parallelism, it is good to translate both of the clauses or phrases. For synonymous parallelism, it is good to translate both clauses if people in your language understand that the purpose of saying something twice is to strengthen a single idea. But if your language does not use parallelism in this way, then consider using one of the following translation strategies.
- Combine the ideas of both clauses into one.
- If it appears that the clauses are used together to show that what they say is really true, you could include words that emphasize the truth such as "truly" or "certainly."
- If it appears that the clauses are used together to intensify an idea in them, you could use words like "very," "completely" or "all."
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Combine the ideas of both clauses into one.
-
Until now you have deceived me and told me lies. (Judges 16:13, ULB) - Delilah expressed this idea twice to emphasize that she was very upset.
- "Until now you have deceived me with your lies."
-
Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB) - The phrase "all the paths he takes" is a metaphor for "all he does."
- "Yahweh pays attention to everything a person does."
-
For Yahweh has a lawsuit with his people, and he will fight in court against Israel. (Micah 6:2 ULB) - This parallelism describes one serious disagreement that Yahweh had with one group of people. If this is unclear, the phrases can be combined:
- "For Yahweh has a lawsuit with his people, Israel."
-
-
If it appears that the clauses are used together to show that what they say is really true, you could include words that emphasize the truth such as "truly" or "certainly."
- Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
- "Yahweh truly sees everything a person does."
- Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
-
If it appears that the clauses are used together to intensify an idea in them, you could use words like "very," "completely" or "all."
-
you have deceived me and told me lies. (Judges 16:13 ULB)
- "All you have done is lie to me."
-
Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
- "Yahweh sees absolutely everything that a person does."
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Parallelism with the Same Meaning
This page answers the question: What is parallelism with the same meaning?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Parallelism with the same meaning is a poetic device in which one complex idea is expressed in two or more different ways. Speakers may do this in order to emphasize the idea that is the same in the two phrases. This is also called "synonymous parallelism."
Note: We use the term "parallelism with the same meaning" for long phrases or clauses that have the same meaning. We use the term Doublet for words or very short phrases that mean basically the same thing and are used together.
Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
The first underlined phrase and the second underlined phrase mean the same thing. There are three ideas that are the same between these two phrases. "Sees" corresponds to "watches," "everything ... does" corresponds to "all the paths ... takes," and "a person" corresponds to "he."
Synonymous parallelism in poetry has several effects:
- It shows that something is very important by saying it more than once and in more than one way.
- It helps the hearer to think more deeply about the idea by saying it in different ways.
- It makes the language more beautiful and above the ordinary way of speaking.
Reason this is a Translation Issue
In some languages people do not expect someone to say the same thing twice, even in different ways. They expect that if there are two phrases or two sentences, they must have different meanings. So they do not understand that the repetition of ideas serves to emphasize the idea.
Examples from the Bible
Your word is a lamp to my feet and a light for my path. (Psalm 119:105 ULB)
Both parts of the sentences are metaphors saying that God's word teaches people how to live. The words "lamp" and "light" are similar in meaning because they refer to light, and the words "my feet" and "my path" are related, because they refer to a person walking.
Praise Yahweh, all you nations; exalt him, all you peoples! (Psalm 117:1 ULB)
Both parts of this verse tell people everywhere to praise Yahweh. The words 'Praise' and 'exalt' mean the same thing, 'Yahweh' and 'him' refer to the same person, and 'all you nations' and 'all you peoples' refer to the same people.
For Yahweh has a lawsuit with his people, and he will fight in court against Israel. (Micah 6:2 ULB)
The two parts of this verse say that Yahweh has a serious disagreement with his people, Israel. These are not two different disagreements or two different groups of people.
Translation Strategies
If your language uses parallelism in the same way as the biblical languages, that is, to strengthen a single idea, then it would be appropriate to use it in your translation. But if your language does not use parallelism in this way, then consider using one of the following translation strategies.
- Combine the ideas of both clauses into one.
- If it appears that the clauses are used together to show that what they say is really true, you could include words that emphasize the truth such as "truly" or "certainly."
- If it appears that the clauses are used together to intensify an idea in them, you could use words like "very," "completely" or "all."
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Combine the ideas of both clauses into one.
-
Until now you have deceived me and told me lies. (Judges 16:13, ULB) - Delilah expressed this idea twice to emphasize that she was very upset.
- Until now you have deceived me with your lies.
-
Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB) - The phrase "all the paths he takes" is a metaphor for "all he does."
- Yahweh pays attention to everything a person does.
-
For Yahweh has a lawsuit with his people, and he will fight in court against Israel. (Micah 6:2 ULB) - This parallelism describes one serious disagreement that Yahweh had with one group of people. If this is unclear, the phrases can be combined:
- For Yahweh has a lawsuit with his people, Israel.
-
-
If it appears that the clauses are used together to show that what they say is really true, you could include words that emphasize the truth such as "truly" or "certainly."
- Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
- Yahweh truly sees everything a person does.
- Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
-
If it appears that the clauses are used together to intensify an idea in them, you could use words like "very," "completely" or "all."
-
... you have deceived me and told me lies. (Judges 16:13 ULB)
- All you have done is lie to me.
-
Yahweh sees everything a person does and watches all the paths he takes. (Proverbs 5:21 ULB)
- Yahweh sees absolutely everything that a person does.
-
Personification
This page answers the question: What is personification?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Personification is a figure of speech in which someone speaks of something as if it could do things that animals or people can do. People often do this because it makes it easier to talk about things that we cannot see:
Such as wisdom:
Does not Wisdom call out? (Proverbs 8:1 ULB)
Or sin:
sin crouches at the door (Genesis 4:7 ULB)
People also do this because it is sometimes easier to talk about people's relationships with non-human things, such as wealth, as if they were like relationships between people.
You cannot serve God and wealth. (Matthew 6:24 ULB)
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Some languages do not use personification.
- Some languages use personification only in certain situations.
Examples from the Bible
You cannot serve God and wealth. (Matthew 6:24 ULB)
Jesus speaks of wealth as if it were a master whom people might serve. Loving money and basing one's decisions on it is like serving it as a slave would serve his master.
Does not Wisdom call out? Does not Understanding raise her voice? (Proverbs 8:1 ULB)
The author speaks of wisdom and understanding as if they are a woman who calls out to teach people. This means that they are not something hidden, but something obvious that people should pay attention to.
Translation Strategies
If the personification would be understood clearly, consider using it. If it would not be understood, here are some other ways for translating it.
- Add words or phrases to make it clear.
- Use words such as "like" or "as" to show that the sentences is not to be understood literally.
- Find a way to translate it without the personification.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Add words or phrases to make it clear.
- ... sin crouches at the door (Genesis 4:7 ULB) - God speaks of sin as a wild animal that is waiting for the chance to attack. This shows how dangerous sin is. An additional phrase can be added to make this danger clear.
- ... sin is at your door, waiting to attack you
- ... sin crouches at the door (Genesis 4:7 ULB) - God speaks of sin as a wild animal that is waiting for the chance to attack. This shows how dangerous sin is. An additional phrase can be added to make this danger clear.
-
Use words such as "like" or "as" to show that the sentences is not to be understood literally.
- ... sin crouches at the door (Genesis 4:7 ULB) - This can be translated with the word "as."
- ... sin is crouching at the door, just as a wild animal does waiting to attack a person.
- ... sin crouches at the door (Genesis 4:7 ULB) - This can be translated with the word "as."
-
Find a way to translate it without the personification.
- ... even the winds and the sea obey him (Matthew 8:27 ULB) - The men speak of the "wind and the sea as if they are able to hear" and obey Jesus as people can. This could also be translated without the idea of obedience by speaking of Jesus controlling them.
- He even controls the winds and the sea.
- ... even the winds and the sea obey him (Matthew 8:27 ULB) - The men speak of the "wind and the sea as if they are able to hear" and obey Jesus as people can. This could also be translated without the idea of obedience by speaking of Jesus controlling them.
Note: We have broadened our definition of "personification" to include "zoomorphism" (speaking of other things as if they had animal characteristics) and "anthropomorphism" (speaking of non-human things as if they had human characteristics.)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Predictive Past
This page answers the question: What is the predictive past?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The predictive past is a figure of speech that uses the past tense to refer to things that will happen in the future. This is sometimes done in prophecy to show that the event will certainly happen. It is also called the prophetic perfect.
Therefore my people have gone into captivity for lack of understanding;
their leaders go hungry, and their masses have nothing to drink. (Isaiah 5:13 ULB)
In the example above, the people of Israel had not yet gone into captivity, but God spoke of their going into captivity as if it had already happened because he had decided that they certainly would go into captivity.
Reason this is a translation issue:
Readers who are not aware of the past tense being used in prophecy to refer to future events may find it confusing.
Examples from the Bible
Now all the entrances to Jericho were closed because of the army of Israel. No one went out and no one came in. Yahweh said to Joshua, "See, I have handed over to you Jericho, its king, and its trained soldiers." (Joshua 6:1-2 ULB)
For to us a child has been born, to us a son has been given;
and the rule will be on his shoulder; (Isaiah 9:6 ULB)
In the examples above, God spoke of things that would happen in the future as if they had already happened.
And about these people also Enoch, the seventh in line from Adam, foretold, saying, "Look, the Lord came with tens of thousands of his holy ones, (Jude 1:14 ULB)
Enoch was speaking of something that would happen in the future, but he used the past tense when he said "the Lord came.”
Translation Strategies
If the past tense would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are some other options.
- Use the future tense to refer to future events.
- If it refers to something in the immediate future, use a form that would show that.
- Some languages may use the present tense to show that something will happen very soon.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Use the future tense to refer to future events.
- For to us a child has been born, to us a son has been given; (Isaiah 9:6a ULB)
- "For to us a child will be born, to us a son will be given;
2) If it refers to something that would happen very soon, use a form that shows that.
- Yahweh said to Joshua, "See, I have handed over to you Jericho, its king, and its trained soldiers." (Joshua 6:2 ULB)
- Yahweh said to Joshua, "See, I am about to hand over to you Jericho, its king, and its trained soldiers."
3) Some languages may use the present tense to show that something will happen very soon.
- Yahweh said to Joshua, "See, I have handed over to you Jericho, its king, and its trained soldiers." (Joshua 6:2 ULB)
- Yahweh said to Joshua, "See, I am handing over to you Jericho, its king, and its trained soldiers."
Rhetorical Question
This page answers the question: What are rhetorical questions and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
A rhetorical question is a question that a speaker asks when he is more interested in expressing his attitude about something than in getting information about it. Speakers use rhetorical questions to express deep emotion or to encourage hearers to think deeply about something. The Bible contains many rhetorical questions, often to express surprise, to rebuke or scold the hearer, or to teach. Speakers of some languages use rhetorical questions for other purposes as well.
Description
A rhetorical question is a question that strongly expresses the speaker's attitude toward something. Often the speaker is not looking for information at all, but if he is asking for information, it is not usually the information that the question appears to ask for. The speaker is more interested in expressing his attitude than in getting information.
Those who stood by said, "Is this how you insult God's high priest?" (Acts 23:4 ULB)
The people who asked Paul this question were not asking about his way of insulting God’s high priest. Rather they used theis question to accuse Paul of insulting the high priest.
The Bible contains many rhetorical questions. Some of the purposes of these rhetorical questions are to express attitudes or feelings, to rebuke people, to teach something by reminding people of something they know and encouraging them to apply it to something new, and to introduce something they want to talk about.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Some languages do not use rhetorical questions; for them a question is always a request for information.
- Some languages use rhetorical questions, but for purposes that are more limited or different than in the Bible.
- Because of these differences between languages, some readers might misunderstand the purpose of a rhetorical question in the Bible.
Examples from the Bible
Do you not still rule the kingdom of Israel? (1 Kings 21:7 ULB)
Jezebel used the question above to remind King Ahab of something he already knew: he still ruled the kingdom of Israel. The rhetorical question made her point more strongly than if she had merely stated it, because it forced Ahab to admit the point himself. She did this in order to rebuke him for being unwilling to take over a poor man's property. She was implying that since he was the king of Israel, he had the power to take the man's property.
Will a virgin forget her jewelry, a bride her veils? Yet my people have forgotten me for days without number! (Jeremiah 2:32 ULB)
God used the question above to remind his people of something they already knew: a young woman would never forget her jewelry or a bride forget her veils. He then rebuked his people for forgetting him, who is so much greater than those things.
Why did I not die when I came out from the womb? (Job 3:11 ULB)
Job used the question above to show deep emotion. This rhetorical question expresses how sad he was that he did not die as soon as he was born. He wished that he had not lived.
And why has it happened to me that the mother of my Lord should come to me? (Luke 1:43 ULB)
Elizabeth used the question above to show how surprised and happy she was that the mother of her Lord came to her.
Or what man among you is there who, if his son asks him for a loaf of bread, will give him a stone? (Matthew 7:9 ULB)
Jesus used the question above to remind the people of something they already knew: a good father would never give his son something bad to eat. By introducing this point, Jesus could go on to teach them about God with his next rhetorical question:
Therefore, if you who are evil know how to give good gifts to your children, how much more will your Father from heaven give good things to those who ask him? (Matthew 7:11 ULB)
Jesus used this question to teach the people in an emphatic way that God gives good things to those who ask him.
What is the kingdom of God like, and what can I compare it to? It is like a mustard seed that a man took and threw into his garden... (Luke 13:18-19 ULB)
Jesus used the question above to introduce what he was going to talk about. He was going to compare the kingdom of God to something.
Translation Strategies
In order to translate a rhetorical question accurately, first be sure that the question you are translating truly is a rhetorical question and is not an information question. Ask yourself, "Does the person asking the question already know the answer to the question?" If so, it is a rhetorical question. Or, if no one answers the question, is the one who asked it bothered that he did not get an answer? If not, it is a rhetorical question.
When you are sure that the question is rhetorical, then be sure that you know what the purpose of the rhetorical question is. Is it to encourage or rebuke or shame the hearer? Is it to bring up a new topic? Is it to do something else?
When you know the purpose of the rhetorical question, then think of the most natural way to express that purpose in the target language. It might be as a question, or a statement, or an exclamation.
If using the rhetorical question would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider doing so. If not, here are other options:
- Add the answer after the question.
- Change the rhetorical question to a statement or exclamation.
- Change the rhetorical question to a statement, and then follow it with a short question.
- Change the form of the question so that it communicates in your langauge what the orignal speaker communicated in his.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Add the answer after the question.
-
Will a virgin forget her jewelry, a bride her veils? Yet my people have forgotten me for days without number! (Jeremiah 2:32 ULB)
- Will a virgin forget her jewelry, a bride her veils? Of course not! Yet my people have forgotten me for days without number!
-
Or what man among you is there who, if his son asks him for a loaf of bread, will give him a stone? (Matthew 7:9 ULB)
- Or what man among you is there who, if his son asks him for a loaf of bread, will give him a stone? None of you would do that!
-
-
Change the rhetorical question to a statement or exclamation.
-
What is the kingdom of God like, and what can I compare it to? It is like a mustard seed... (Luke 13:18-19 ULB)
- This is what the kingdom of God is like. It is like a mustard seed..."
-
Is this how you insult God's high priest? (Acts 23:4 ULB)
- You should not insult God's high priest!
-
Why did I not die when I came out from the womb? (Job 3:11 ULB)
- I wish I had died when I came out from the womb!
-
And why has it happened to me that the mother of my Lord should come to me? (Luke 1:43 ULB)
- How wonderful it is that the mother of my Lord has come to me!
-
-
Change the rhetorical question to a statement, and then follow it with a short question.
- Do you not still rule the kingdom of Israel? (1 Kings 21:7 ULB)
- You still rule the kingdom of Israel, do you not?
- Do you not still rule the kingdom of Israel? (1 Kings 21:7 ULB)
-
Change the form of the question so that it communicates in your langauge what the orignal speaker communicated in his.
-
Or what man among you is there who, if his son asks him for a loaf of bread, will give him a stone? (Matthew 7:9 ULB)
- If your son asks you for a loaf of bread, would you give him a stone?
-
Will a virgin forget her jewelry, a bride her veils? Yet my people have forgotten me for days without number! (Jeremiah 2:32 ULB)
- What virgin would forget her jewelry, and what bride would forget her veils? Yet my poeple have forgotten me for days without number
-
Simile
This page answers the question: What is a simile?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
A simile is a comparison of two things that are not normally thought to be similar. One is said to be "like" the other. It focuses on a particular trait the two items have in common, and it includes the words "like," "as" or "than."
Description
A simile is a comparison of two things that are not normally thought to be similar. It focuses on a particular trait the two items have in common, and it includes the words "like," "as" or "than."
When he saw the crowds, he had compassion for them, because they were worried and confused, because they were like sheep without a shepherd. (Matthew 9:36)
Jesus compared the crowds of people to sheep without a shepherd. Sheep grow frightened when they do not have a good shepherd to lead them in safe places. The crowds were like that because they did not have good religious leaders.
See, I send you out as sheep in the midst of wolves, so be as wise as serpents and harmless as doves. (Matthew 10:16 ULB)
Jesus compared his disciples to sheep and their enemies to wolves. Wolves attack sheep. Jesus' enemies would attack his disciples.
For the word of God is living and active and sharper than any two-edged sword. (Hebrews 4:12 ULB)
God's word is compared to a two-edged sword. A two-edged sword is a weapon that can easily cut through a person's flesh. God's word is very effective in showing what is in a person's heart and thoughts.
Purposes of Simile
- A simile can teach about something that is unknown by showing how it is similar to something that is known.
- A simile can emphasize a particular trait, sometimes in a way that gets people's attention.
- Similes help form a picture in the mind or help the reader experience what he is reading about more fully.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- People may not know how the two items are similar.
- People may not be familiar with the item that something is compared to.
Examples from the Bible
Suffer hardship with me, as a good soldier of Christ Jesus. (2 Timothy 2:3 ULB)
In this simile, Paul compares suffering with what soldiers endure, and he encourages Timothy to follow their example.
for as the lightning appears when it flashes from one part of the sky to another part of the sky, so will the Son of Man be in his day. (Luke 17:24 ULB)
This verse does not tell how the Son of Man will be like the lightning. But from the context we can understand from the verses before it that just as lighting flashes suddenly and everyone can see it, the Son of Man will come suddenly and everyone will be able to see him. No one will have to be told about it.
Translation Strategies
If people would understand the correct meaning of a simile, consider using it. If they would not, here are some strategies you can use:
- If people do not know how the two items are alike, tell how they are alike. However, do not do this if the meaning was not clear to the original audience.
- If people are not familiar with the item that something is compared to, use an item from your own culture. Be sure that it is one that could have been used in the cultures of the Bible.
- Simply describe the item without comparing it to another.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If people do not know how the two items are alike, tell how they are alike. However, do not do this if the meaning was not clear to the original audience.
-
See, I send you out as sheep in the midst of wolves (Matthew 10:16 ULB) - This compares the danger that Jesus' disciples would be in with the danger that sheep are in when they are surrounded by wolves.
- See, I send you out among wicked people and you will be in danger from them as sheep are in danger when they are among wolves.
-
For the word of God is living and active and sharper than any two-edged sword. (Hebrews 4:12 ULB)
- For the word of God is living and active and more powerful than a very sharp two-edged sword
-
-
If people are not familiar with the item that something is compared to, use an item from your own culture. Be sure that it is one that could have been used in the cultures of the Bible.
-
See, I send you out as sheep in the midst of wolves, (Matthew 10:16 ULB) - If people do not know what sheep and wolves are, or that wolves kill and eat sheep, you could use some other animal that kills another.
- See, I send you out as chickens in the midst of wild dogs,
-
How often did I long to gather your children together, just as a hen gathers her chickens under her wings, but you did not agree! (Matthew 23:37 ULB)
- How often I wanted to gather your children together, as a mother closely watches over her infants, but you refused!
-
If you have faith even as small as a grain of mustard, (Matthew 17:20)
- If you have faith even as small as a tiny seed,
-
-
Simply describe the item without comparing it to another.
-
See, I send you out as sheep in the midst of wolves, (Matthew 10:16 ULB)
- See, I send you out and people will want to harm you.
-
How often did I long to gather your children together, just as a hen gathers her chickens under her wings, but you did not agree! (Matthew 23:37 ULB)
- How often I wanted to protect you, but you refused!
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Synecdoche
This page answers the question: What does the word synecdoche mean?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Synecdoche is when a speaker uses a part of something to refer to the whole or uses the whole to refer to a part.
My soul exalts the Lord. (Luke 1:46 ULB)
Mary was was very happy about what the Lord was doing, so she said "my soul," which means the inner, emotional part of herself, to refer to her whole self.
the Pharisees said to him, "Look, why are they doing something that is not lawful ...?" (Mark 2:24 ULB)
The Pharisees who were standing there did not all say the same words at the same time. Instead, it is more likely that one man representing the group said those words.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Some readers may understand the words literally.
- Some readers may realize that they are not to understand the words literally, but they may not know what the meaning is.
Example from the Bible
I looked on all the deeds that my hands had accomplished (Ecclesiastes 2:11 ULB)
"My hands" is a synecdoche for the whole person, because clearly the arms and the rest of the body and the mind were also involved in the person's accomplishments.
Translation Strategies
If the synecdoche would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here is another option:
- State specifically what the synecdoche refers to.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
State specifically what the synecdoche refers to.
-
"My soul exalts the Lord." (Luke 1:46 ULB)
- "I exalt the Lord."
-
...the Pharisees said to him (Mark 2:24 ULB)
- ...a representative of the Pharisees said to him ...
-
... I looked on all the deeds that my hands had accomplished ... (Ecclesiastes 2:11 ULB)
- I looked on all the deeds that I had accomplished
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Grammar
Grammar Topics
This page answers the question: What is some basic information about English Grammar?
Grammar has two main parts: words and structure. Structure involves how we put words together to form phrase, clauses, and sentences.
Parts of Speech - All words in a language belong to a category called a part of speech. (see Parts of Speech)
Sentences - When we speak, we organize our thoughts in sentences. A sentence usually has a complete thought about an event or a situation or state of being. (see Sentence Structure)
- Sentences can be statements, questions, commands, or exclamations. (see Exclamations)
- Sentences can have more than one clause. (see Sentence Structure)
- Some languages have both active and passive sentences. (see Active or Passive)
Possession - This shows that there is a relationship between two nouns. In English it is marked with "of" as in "the love of God," or with "'s" as in "God's love," or with a possessive pronoun as in "his love." (see Possession)
Quotations - A quotation is a report of what someone else has said.
- Quotations normally have two parts: Information about who said something and what the person said. (see Quotations and Quote Margins)
- Quotations can be either direct quotes or indirect quotes. (see Direct and Indirect Quotations)
- Quotes can have quotes within them. (see Quotes within Quotes)
- Quotes can be marked to make it easy for readers to understand who said what. (see Quote Markings)
Abstract Nouns
This page answers the question: What are abstract nouns and how do I deal with them in my translation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Abstract nouns are nouns that refer to attitudes, qualities, events, situations, or even to relationships among these ideas. These are things that cannot be seen or touched in a physical sense, such as happiness, weight, injury, unity, friendship, health, and reason. This is a translation issue because some languages may express a certain idea with an abstract noun, while others would need a different way to express it. For example, "What is its weight?" could be expressed as "How much does it weigh?" or "How heavy is it?"
Description
Remember that nouns are words that refer to a person, place, thing, or idea. Abstract Nouns are the nouns that refer to ideas. These can be attitudes, qualities, events, situations, or even relationships among these ideas. These are things that cannot be seen or touched in a physical sense, such as joy, peace, creation, goodness, contentment, justice, truth, freedom, vengeance, slowness, length, and weight.
Using abstract nouns allows people to express thoughts about ideas in fewer words than if they did not have those nouns. It is a way of giving names to actions or qualities so that people can talk about them as though they were things. It is like a short-cut in language. For example, in languages that use abstract nouns, people can say, "I believe in the forgiveness of sin." But if the language did not have the two abstract nouns "forgiveness" and "sin," then they would have to make a longer sentence to express the same meaning. They would have to say, for example, "I believe that God is willing to forgive people after they have sinned," using verb phrases instead of nouns for those ideas.
Reason this is a translation issue
The Bible that you translate from may use abstract nouns to express certain ideas. Your language might not use abstract nouns for some of those ideas; instead, it might use phrases to express those ideas. Those phrases will use other kinds of words such as adjectives, verbs, or adverbs to express the meaning of the abstract noun.
Examples from the Bible
...from childhood you have known the sacred writings ... (2 Timothy 3:15 ULB)
The abstract noun "childhood" refers to when someone is a child.
But godliness with contentment is great gain. (1 Timothy 6:6 ULB)
The abstract nouns "godliness" and "contentment" refer to being godly and content. The abstract noun "gain" refers to something that benefits or helps someone.
Today salvation has come to this house, because he too is a son of Abraham. (Luke 19:9 ULB)
The abstract noun "salvation" here refers to being saved.
The Lord does not move slowly concerning his promises, as some consider slowness to be (2 Peter 3:9 ULB)
The abstract noun "slowness" refers how slowly something is done.
He will bring to light the hidden things of darkness and reveal the purposes of the heart. (1 Corinthians 4:5 ULB)
The abstract noun "purposes" refers to the things that people want to do and the reasons they want to do them.
Translation Strategies
If an abstract noun would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here is another option:
- Reword the sentence with a phrase that expresses the meaning of the abstract noun. Instead of a noun, the new phrase will use a verb, an adverb, or an adjective to express the idea of the abstract noun..
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Reword the sentence with a phrase that expresses the meaning of the abstract noun. Instead of a noun, the new phrase will use a verb, an adverb, or an adjective to express the idea of the abstract noun.
-
... from childhood you have known the sacred writings ... (2 Timothy 3:15 ULB)
- Ever since you were a child you have known the sacred writings.
-
But godliness with contentment is great gain. (1 Timothy 6:6 ULB)
- But being godly and content is very beneficial.
- But we benefit greatly when we are godly and content.
- But we benefit greatly when we honor and obey God and when we are happy with what we have.
-
Today salvation has come to this house, because he too is a son of Abraham. (Luke 19:9 ULB)
- Today the people in this house have been saved…
- Today God has saved the people in this house…
-
The Lord does not move slowly concerning his promises, as some consider slowness to be. (2 Peter 3:9 ULB)
- The Lord does not move slowly concerning his promises, as some consider moving slowly to be.
-
He will bring to light the hidden things of darkness and reveal the purposes of the heart. (1 Corinthians 4:5 ULB)
- He will bring to light the hidden things of darkness and reveal the things that people want to do and the reasons they want to do them.
-
Active or Passive
This page answers the question: What do active and passive mean, and how do I translate passive sentences?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some languages have both active and passive sentences. In active sentences, the subject does the action. In passive sentences, the subject is the one that receives the action. Here are some examples with their subjects underlined:
- ACTIVE: My father built the house in 2010.
- PASSIVE: The house was built in 2010.
Translators whose languages do not have passive sentences will need to know how they can translate passive sentences that they find in the Bible. Other translators will need to decide when to use a passive sentence and when to use the active form.
Description
Some languages have both active and passive forms of sentences.
- In the ACTIVE form, the subject does the action and is always mentioned.
- In the PASSIVE form, the action is done to the subject, and the one who does the action is not always mentioned.
In the examples of active and passive sentences below, we have underlined the subject.
- ACTIVE: My father built the house in 2010.
- PASSIVE: The house was built by my father in 2010.
- PASSIVE: The house was built in 2010. (This does not tell who did the action.)
Reasons this is a translation issue
All languages have active forms. Some languages have passive forms, and some do not. The passive form is not used for the same purposes in all of the languages that have it.
Purposes for the passive
- The speaker is talking about the person or thing the action was done to, not about the person who did the action.
- The speaker does not want to tell who did the action.
- The speaker does not know who did the action.
Translation Principles Regarding the Passive
- Translators whose language does not use passive forms will need to find another way to express the idea.
- Translators whose language has passive forms will need to understand why the passive is used in a particular sentence in the Bible and decide whether or not to use a passive form for that purpose in his translation of the sentence.
Examples from the Bible
And their shooters shot at your soldiers from off the wall, and some of the king's servants were killed, and your servant Uriah the Hittite was killed too. (2 Samuel 11:24 ULB)
This means that the enemy's shooters shot and killed some of the king's servants, including Uriah. The point is what happened to the king's servants and Uriah, not who shot them. The purpose of the passive form here is to keep the focus on the king's servants and Uriah.
In the morning when the men of the town got up, the altar of Baal was broken down … (Judges 6:28 ULB)
The men of the town saw what had happened to the altar of Baal, but they did not know who broke it down. The purpose of the passive form here is to communicate this event from the perspective of the men of the town.
It would be better for him if a millstone were put around his neck and he were thrown into the sea (Luke 17:2 ULB)
This describes a situation in which a person ends up in the sea with a millstone around his neck. The purpose of the passive form here is to keep the focus on what happens to this person. Who does these things to the person is not important.
Translation Strategies
If you decide that it is better to translate without a passive form, here are some strategies you might consider.
- Use the same verb in an active sentence and tell who or what did the action. If you do this, try to keep the focus on the person receiving the action.
- Use the same verb in an active sentence, and do not tell who or what did the action. Instead, use a generic expression like "they" or "people" or "someone."
- Use a different verb.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use the same verb in an active sentence and tell who did the action. If you do this, try to keep the focus on the person receiving the action.
- A loaf of bread was given him every day from the street of the bakers. (Jeremiah 37:21 ULB)
- The king's servants gave Jeremiah a loaf of bread every day from the street of the bakers.
- A loaf of bread was given him every day from the street of the bakers. (Jeremiah 37:21 ULB)
-
Use the same verb in an active sentence, and do not tell who did the action. Instead, use a generic expression like "they" or "people" or "someone."
- It would be better for him if a millstone were put around his neck and he were thrown into the sea. (Luke 17:2 ULB)
- It would be better for him if they were to put a millstone around his neck and throw him into the sea.
- It would be better for him if someone were to put a heavy stone around his neck and throw him into the sea.
- It would be better for him if a millstone were put around his neck and he were thrown into the sea. (Luke 17:2 ULB)
-
Use a different verb in an active sentence.
- A loaf of bread was given him every day from the street of the bakers. (Jeremiah 37:21 ULB)
- He received a loaf of bread every day from the street of the bakers.
- A loaf of bread was given him every day from the street of the bakers. (Jeremiah 37:21 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Distinguishing versus Informing or Reminding
This page answers the question: When a phrase is used with a noun, what is the difference between phrases that distinguish the noun from others and phrases that simply inform or remind?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
In some languages, phrases that modify a noun can be used with the noun for two different purposes. They can either distinguish the noun from other similar items, or they can give more information about the noun. That information could be new to the reader, or a reminder about something the reader might already know. Other languages use modifying phrases with a noun only for distinguishing the noun from other similar things. When people who speak these languages hear a modifying phrase with a noun, they assume that its function is to distinguish one item from another similar item.
Some languages use a comma to mark the difference between making a distinction between similar items and gving more information about an item. Without the comma, the sentence below communicates that it is making a distinction:
- Mary gave some of the food to her sister who was very thankful.
- If her sister was usually thankful, the phrase "who was thankful" could distinguish this sister of Mary's from another sister who was not usually thankful.
With the comma, the sentence is giving more information:
- Mary gave some of the food to her sister, who was very thankful.
- This same phrase can be used give us more information about Mary's sister. It tells us about how Mary's sister responded when Mary gave her the food. In this case it does not distinguish one sister from another sister.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Many source languages of the Bible use phrases that modify a noun both for distinguishing the noun from another similar item and also for giving more information about the noun. The translator must be careful to understand which meaning the author intended in each case.
- Some languages use phrases that modify a noun only for distinguishing the noun from another similar item. When translating a phrase that is used for giving more information, people who speak these languages will need to separate the phrase from the noun. Otherwise, people who read it or hear it will think that the phrase is meant to distinguish the noun from other similar items.
Examples from the Bible
Examples of words and phrases that are used to distinguish one item from other possible items: These usually do not cause a problem in translation.
… The curtain is to separate the holy place from the most holy place. (Exodus 26:33 ULB)
The words "holy" and "most holy" distinguish two different places from each other and from any other place.
A foolish son is a grief to his father, and bitterness to the woman who bore him. (Proverbs 17:25 ULB)
The phrase "who bore him" distinguishes which woman the son is bitterness to. He is not bitterness to all women, but to his mother.
Examples of words and phrases that are used to give added information or a reminder about an item: These are a translation issue for languages that do not use these.
... for your righteous judgments are good. (Psalm 119:39 ULB)
The word "righteous" simply reminds us that God's judgments are righteous. It does not distinguish his righteous judgements from his unrighteous judgements, because all of his judgments are righteous.
Can Sarah, who is ninety years old, bear a son? - (Genesis 17:17-18 ULB)
The phrase "who is ninety years old" is the reason that Abraham did not think that Sarah could bear a son. He was not distinguishing one woman named Sarah from another woman named Sarah who was a different age, and he was not telling anyone something new about her age. He simply did not think that a woman who was that old could bear a child.
I will wipe away mankind whom I have created from the surface of the earth. (Genesis 6:7 ULB)
The phrase "whom I have created" is a reminder of the relationship between God and mankind. It is the reason God had the right to wipe away mankind. There is not another mankind that God did not create.
Translation Strategies
If people would understand the purpose of a phrase with a noun, then consider keeping the phrase and the noun together. For languages that use words or phrases with a noun only to distinguish one item from another, here are some strategies for translating phrases that are used to inform or remind.
- Put the information in another part of the sentence and add words that show its purpose.
- Use one of your language's ways for expressing that this is just added information. It may be by adding a small word, or by changing the way the voice sounds. Sometimes changes in the voice can be shown with punctuation marks, such as parentheses or commas.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Put the information in another part of the sentence and add words that show its purpose.
-
I hate those who serve worthless idols (Psalm 31:6 ULB) - By saying "worthless idols," David was commenting about all idols and giving his reason for hating those who serve them. He was not distinguishing worthless idols from valuable idols.
- Because idols are worthless, I hate those who serve them.
-
... for your righteous judgments are good. (Psalm 119:39 ULB)
- ... for your judgments are good because they are righteous.
-
Can Sarah, who is ninety years old, bear a son? (Genesis 17:17-18 ULB) - The phrase "who is ninety years old" is a reminder of Sarah's age. It tells why Abraham was asking the question. He did not expect that a woman who was that old could bear a child.
- Can Sarah bear a son even when she is ninety years old?
-
I will call on Yahweh, who is worthy to be praised (2 Samuel 22:4 ULB) - There is only one Yahweh. The phrase "who is worthy to be praised" gives a reason for calling on Yahweh.
- I will call on Yahweh, because he is worthy to be praised
-
-
Use one of your language's ways for expressing that this is just added information.
- You are my Son, whom I love. I am pleased with you. (Luke 3:22 ULB)
- You are my Son. I love you and I am pleased with you.
- Receiving my love, you are my Son. I am pleased with you.
- You are my Son, whom I love. I am pleased with you. (Luke 3:22 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Double Negatives
This page answers the question: What are double negatives?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
A double negative occurs when a clause has two words that each express the meaning of "not." Double negatives mean very different things in different languages. To translate sentences that have double negatives accurately and clearly, you need to know what a double negative means in the Bible and how to express this idea in your language.
Description
Negative words are words that have in them the meaning "not." Examples are "no," "not," "none," "no one," "nothing," "nowhere," "never," "nor," "neither," and "without." Also, some words have prefixes or suffixes that mean "not" such as the underlined parts of these words: "unhappy," "impossible," and "useless."
A double negative occurs when a sentence has two words that each express the meaning of "not."
It is not that we do not have authority... (2 Thessalonians 3:9 ULB)
And this better confidence did not happen without the taking of an oath, ... (Hebrews 7:20 ULB.)
Be sure of this—wicked people will not go unpunished (Proverbs 11:21 ULB)
Reason this is a translation issue
Double negatives mean very different things in different languages.
- In some languages, such as Spanish, a double negative emphasizes the negative. The following Spanish sentence No ví a nadie is literally, "I did not see no one." It has both the word 'no' next to the verb and 'nadie,' which means "no one." The two negatives are seen as in agreement with each other, and the sentence means, "I did not see anyone."
- In some languages, a second negative cancels the first one, creating a positive sentence. So, "He is not unintelligent" means "He is intelligent."
- In some languages the double negative creates a positive sentence, but it is a weak statement. So, "He is not unintelligent" means, "He is somewhat intelligent."
- In some languages, such as the languages of the Bible, the double negative can create a positive sentence, and often strengthens the statement. So, "He is not unintelligent" can mean "He is intelligent" or "He is very intelligent."
To translate sentences with double negatives accurately and clearly in your language, you need to know both what a double negative means in the Bible and how to express the same idea in your language.
Examples from the Bible
... so that they may not be unfruitful. (Titus 3:14 ULB)
This means "so that they will be fruitful."
All things were made through him and without him there was not one thing made that has been made. (John 1:3 ULB)
By using a double negative, John emphasized that the Son of God created absolutely everything.
Translation Strategies
If double negatives are natural and are used to express the positive in your language, consider using them. Otherwise, you could consider these strategies:
- If the purpose of a double negative in the Bible is simply to make a positive statement, and if it would not do that in your language, remove the two negatives so that it is positive.
- If the purpose of a double negative in the Bible is to make a strong positive statement, and if it would not do that in your language, remove the two negatives and put in a strengthening word or phrase such as "very" or "surely."
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If the purpose of a double negative in the Bible is simply to make a positive statement, and if it would not do that in your language, remove the two negatives so that it is positive.
-
For we do not have a high priest who cannot feel sympathy for our weaknesses. (Hebrews 4:15 ULB)
- "For we have a high priest who can feel sympathy for our weaknesses."
-
... so that they may not be unfruitful. (Titus 3:14 ULB)
- "... so that they may be fruitful."
-
-
If the purpose of a double negative in the Bible is to make a strong positive statement, and if it would not do that in your language, remove the two negatives and put in a strengthening word or phrase such as "very" or "surely."
-
Be sure of this—wicked people will not go unpunished ... (Proverbs 11:21 ULB)
- "Be sure of this—wicked people will certainly be punished ..."
-
All things were made through him and without him there was not one thing made that has been made. (John 1:3 ULB)
- "All things were made through him. He made absolutely everything that has been made."
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Ellipsis
This page answers the question: What is ellipsis?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Ellipsis is what happens when a speaker or writer leaves one or more words out of a sentence because he knows that the hearer or reader will understand the meaning of the sentence and fill in the words in his mind when he hears or reads the words that are there. The information that is omitted has usually already been stated in a preceding sentence or phrase.
... the wicked will not stand in the judgment, nor sinners in the assembly of the righteous. (Psalm 1:5)
This is ellipsis because "sinners in the assembly of the righteous" is not a complete sentence. The speaker assumes that the hearer will understand what it is that sinners will not do in the assembly of the righteous by filling in the action from the previous clause.
Reason this is a translation issue
Readers who see incomplete sentences or phrases may not know what the missing information is if they do not use ellipsis in their language.
Examples from the Bible
... when the blind man was near, Jesus asked him, "What do you want me to do for you?" He said, "Lord, that I might receive my sight." (Luke 18:40-41 ULB)
The man answered in an incomplete sentence because he wanted to be polite and not directly ask Jesus for healing. He knew that Jesus would understand that the only way he could receive his sight would be for Jesus to heal him.
He makes Lebanon skip like a calf and Sirion like a young ox. (Psalm 29:6 ULB)
The writer wants his words to be few and to make good poetry. He did not say that Yahweh makes Sirion skip like a young ox because he knew that his readers could fill in the information themselves.
Translation Strategies
If ellipsis would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here is another option:
- Add the missing words to the incomplete phrase or sentence.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Add the missing words to the incomplete phrase or sentence.
-
... the wicked will not stand in the judgment, nor sinners in the assembly of the righteous. (Psalm 1:5)
- ... the wicked will not stand in the judgment, and sinners will not stand in the assembly of the righteous
-
... when the blind man was near, Jesus asked him, "What do you want me to do for you?" He said, "Lord, that I might receive my sight." (Luke 18:40-41)
- ... when the blind man was near, Jesus asked him, "What do you want me to do for you?" He said, "Lord, I want you to heal me that I might receive my sight."
-
He makes Lebanon skip like a calf and Sirion like a young ox. (Psalm 29:6)
- He makes Lebanon skip like a calf, and he makes Sirion skip like a young ox.
-
Forms of You
This page answers the question: What are the different forms of you?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Singular, Dual, and Plural
Some languages have more than one word for "you" based on how many people the word "you" refers to. The singular form refers to one person, and the plural form refers to more than one person. Some languages also have a dual form which refers to two people, and some have other forms that refer to three or four people.
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_younum.
Sometimes in the Bible a speaker uses a singular form of "you" even though he is speaking to a crowd.
Formal and Informal
Some languages have more than one form of "you" based on the relationship between the speaker and the person he is talking to. People use the formal form of "you" when speaking to someone who is older, or has higher authority, or is someone they do not know very well. People use the informal form when speaking to someone who is not older, or does not have higher authority, or is a family member or close friend.
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_youform.
For help with translating these, we suggest you read:
Forms of 'You' - Dual/Plural
This page answers the question: How do I know if the word 'you' is dual or plural?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some languages have a singular form of "you" for when the word "you" refers to just one person, and a plural form for when the word "you" refers to more than one person. Some languages also have a dual form of "you" for when the word "you" refers to only two people. Translators who speak one of these languages will always need to know what the speaker meant so they can choose the right word for "you" in their language. Other languages, such as English, have only one form, which people use regardless of how many people it refers to.
The Bible was first written in the Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek languages. These languages all have a singular form of "you" and a plural form of "you." When we read the Bible in those languages, the pronouns and verb forms show us whether the word "you" refers to one person or more than one person. However, they do not show us whether it refers to only two people or more than two people. When the pronouns do not show us how many people the word "you" refers to, we need to look at the context to see how many people the speaker was speaking to.
Reasons this is a Translation Issue
- Translators who speak a language that has distinct singular, dual, and plural forms of "you" will always need to know what the speaker meant so they can choose the right word for "you" in their language.
- Many languages also have different forms of the verb depending on whether the subject is singular or plural. So even if there is no pronoun meaning "you," translators of these languages will need to know if the speaker was referring to one person or more than one.
Often the context will make it clear whether the word "you" refers to one person or more than one. If you look at the other pronouns in the sentence, they will help you know how many people the speaker was addressing.
Examples from the Bible
James and John, the sons of Zebedee, came up to him and said, "Teacher, we want you to do for us whatever we ask you." He [Jesus] said to them, "What do you want me to do for you?" (Mark 10:35-36 ULB)
Jesus is asking the two, James and John, what they want him to do for them. If the target language has a dual form of "you," use that. If the target language does not have a dual form, then the plural form would be appropriate.
… and Jesus sent out two of his disciples and said to them, "Go into the village opposite us. As soon as you enter it, you will find a colt that has never been ridden. Untie it and bring it to me. (Mark 11:1-2 ULB)
The context makes it clear that Jesus is addressing two people. If the target language has a dual form of "you," use that. If the target language does not have a dual form, then the plural form would be appropriate.
James, a servant of God and of the Lord Jesus Christ, to the twelve tribes of the Dispersion, greetings. Consider it all joy, my brothers, when you experience various troubles, knowing that the testing of your faith works endurance. (James 1:1-3 ULB)
James wrote this letter to many people, so the word "you" refers to many people. If the target language has a plural form of "you," it would be best to use it here.
Strategies for finding out how many people "you" refers to
- Look at the notes to see if they tell whether "you" refers to one person or more than one person.
- Look at the UDB to see if it says anything that would show you whether the word "you" refers to one person or more than one person.
- If you have a Bible that is written in a language that distinguishes "you" singular from "you" plural, see which form of "you" that Bible has in that sentence.
- Look at the context to see who the speaker was talking to and who responded.
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_youdual.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Forms of 'You' - Singular
This page answers the question: How do I know if the word 'you' is singular?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some languages have a singular form of "you" for when the word "you" refers to just one person, and a plural form for when the word "you" refers to more than one person. Translators who speak one of these languages will always need to know what the speaker meant so they can choose the right word for "you" in their language. Other languages, such as English, have only one form, which people use regardless of how many people it refers to.
The Bible was first written in the Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek languages. These languages all have both a singular form of "you" and a plural form of "you." When we read the Bible in those languages, the pronouns and verb forms show us whether the word "you" refers to one person or more than one. When we read the Bible in a language that does not have different forms of you, we need to look at the context to see how many people the speaker was speaking to.
Reason this is a Translation Issue
- Translators who speak a language that has distinct singular and plural forms of "you" will always need to know what the speaker meant so they can choose the right word for "you" in their language.
- Many languages also have different forms of the verb depending on whether the subject is singular or plural. So even if there is no pronoun meaning "you", translators of these languages will need to know if the speaker was referring to one person or more than one.
Often the context will make it clear whether the word "you" refers to one person or more than one. If you look at the other pronouns in the sentence, they will help you know the number of people the speaker was speaking to. Sometimes Greek and Hebrew speakers used "you" singular even though they were speaking to a group of people. See Forms of 'You' - Singular to a Crowd
Examples from the Bible
The ruler said, "All these things I have obeyed from the time I was a youth." When Jesus heard that, he said to him, "One thing you still lack. You must sell all that you have and distribute it to the poor, and you will have treasure in heaven—and come, follow me." (Luke 18:21, 22 ULB)
The ruler was speaking about just himself when he said "I." This shows us that when Jesus said "you" he was referring only to the ruler. So languages that have singular and plural forms of "you" would have the singular form here.
The angel said to him, "Dress yourself and put on your sandals." Peter did so. The angel said to him, "Put on your outer garment and follow me." So Peter followed the angel and went out. (Acts 12:8, ULB)
The context makes it clear that the angel was speaking to one person and that only one person did what the the angel commanded. So languages that have singular and plural forms of "you" would have the singular form here for "yourself" and "your". Also, if verbs have different forms for singular and plural subjects, the verbs "dress" and "put on" will need the form for "you" singular.
To Titus, a true son in our common faith. ... For this purpose I left you in Crete, that you might set in order things not yet complete, and ordain elders in every city as I directed you. … But you, say what agrees with healthy doctrine. (Titus 1:4,5; 2:1 ULB)
Paul wrote this letter to one person, Titus. Most of the time the word "you" in this letter refers only to Titus.
Strategies for finding out how many people "you" refers to
- Look at the notes to see if they tell whether "you" refers to one person or more than one person.
- Look at the UDB to see if it says anything that would show you whether the word "you" refers to one person or more than one person.
- If you have a Bible that is written in a language that distinguishes "you" singular from "you" plural, see which form of "you" that Bible has in that sentence.
- Look at the context to see how many people the speaker was talking to and who responded.
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_younum.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Generic Noun Phrases
This page answers the question: What are generic noun phrases and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Generic noun phrases refer to people or things in general rather than to specific individuals or things. This happens frequently in proverbs, because proverbs tell about things that are true about people in general.
Can a man walk on hot coals without scorching his feet?
So is the man who goes into his neighbor's wife;
the one who has relations with her will not go unpunished. (Proverbs 6:28 ULB)
The underlined phrases above do not refer to a specific man. They refer to any man who does these things.
Reason this is a translation issue
Different languages have different ways of showing that noun phrases refer to something in general. Translators should refer to these general ideas in ways that are natural in their language.
Examples from the Bible
The one who does what is right is kept away from trouble and it comes upon the wicked instead. (Proverbs 11:8 ULB)
The underlined phrases above do not refer to any specific people but to anyone who does what is right or anyone who is wicked.
People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
This does not refer to a particular man, but to any person who refuses to sell grain.
Yahweh gives favor to a good man, but he condemns a man who makes evil plans. (Proverbs 12:2 ULB)
The phrase "a good man" does not refer to a particular man, but to any person who is good. The phrase "a man who makes evil plans" does not refer to a particular man, but to any person who makes evil plans.
Translation Strategies
If your language can use the same wording as in the ULB to refer to people or things in general rather than to specific individuals or things, consider using the same wording. Here are some strategies you might use.
- Use the word "the" in the noun phrase.
- Use the word "a" in the noun phrase.
- Use the word "any", as in "any person" or "anyone."
- Use the plural form, as in "people."
- Use any other way that is natural in your language.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use the word "the" in the noun phrase.
- Yahweh gives favor to a good man, but he condemns a man who makes evil plans. (Proverbs 12:2 ULB)
- "Yahweh gives favor to the good man, but he condemns the man who makes evil plans." (Proverbs 12:2)
- Yahweh gives favor to a good man, but he condemns a man who makes evil plans. (Proverbs 12:2 ULB)
-
Use the word "a" in the noun phrase.
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
- "People curse a man who refuses to sell them grain"
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
-
Use the word "any, as in "any person" or "anyone."
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
- "People curse any man who refuses to sell them grain."
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
-
Use the plural form, as in "people" (or in this sentence, "men").
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
- "People curse men who refuse to sell them grain"
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
-
Use any other way that is natural in your language.
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
- "People curse whoever refuses to sell them grain."
- People curse the man who refuses to sell them grain. (Proverbs 11:26 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Go and Come
This page answers the question: What do I do if the word "go" or "come" is confusing in a certain sentence?
Description
Different languages have different ways of determining whether to use the words "go" or "come" and whether to use the words "take" or "bring" when talking about motion. For example, when saying that they are approaching a person who has called them, English speakers say "I'm coming," while Spanish speakers say "I'm going." You will need to translate the words "go" and "come" (and also "take" and "bring") in a way that your readers will understand which direction people are moving in.
Reason this is a translation issue
Different languages have different ways of talking about motion. The biblical languages or your source language may use the words "go" and "come" or "take" and "bring" differently than your language uses them. If these words are not translated in the way that is natural in your language, your readers may be confused about which direction people are moving.
Examples from the Bible
Yahweh said to Noah, "Come, you and all your household, into the ark (Genesis 7:1 ULB)
In some languages, this would lead people to think that Yahweh was in the ark.
But you will be free from my oath if you come to my relatives and they will not give her to you. Then you will be free from my oath. (Genesis 24:41 ULB)
Abraham was speaking to his servant. Abraham's relatives lived far away, from where he and his servant were standing and he wanted his servant to go to them, not come toward Abraham.
When you have come to the land that Yahweh your God gives you, and when you take possession of it and begin to live in it ... (Deuteronomy 17:14 ULB)
Moses is speaking to the people in the wilderness. They had not yet gone into the land that God was giving them. In some languages, it would make more sense to say, "When you have gone into the land..."
Joseph and Mary brought him up to the temple in Jerusalem to present him to the Lord. (Luke 1:22 ULB)
In some languages, it might make more sense to say that Joseph and Mary took or carried Jesus to the temple.
Behold, there came a man named Jairus, and he was one of the leaders of the synagogue. Jairus fell down at Jesus' feet and implored him to come to his house, (Luke 8:41 ULB)
The man was not at his house when he spoke to Jesus. He wanted Jesus to go with him to his house.
Some time after this, his wife Elizabeth became pregnant, but she did not go out in public for five months. (Luke 1:24 UDB)
In some languages, it might make more sense to say that Elizabeth did not come out in public.
Translation Strategies
If the word used in the ULB would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are other strategies.
- Use the word "go," "come," "take," or "bring" that would be natural in your language.
- Use another word that expresses the right meaning.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use the word "go," "come," "take," or "bring" that would be natural in your language.
-
But you will be free from my oath if you come to my relatives and they will not give her to you. (Genesis 24:41 ULB)
- But you will be free from my oath if you go to my relatives and they will not give her to you.
-
Some time after this, his wife Elizabeth became pregnant, but she did not go out in public for five months. (Luke 1:24 UDB)
- Some time after this, his wife Elizabeth became pregnant, but she did not come out in public for five months.
-
-
Use another word that expresses the right meaning.
-
When you have come to the land that Yahweh your God gives you, and when you take possession of it and begin to live in it ... (Deuteronomy 17:14 ULB)
- "When you have arrived in the land that Yahweh your God gives you, and when you take possession of it and begin to live in it ..."
-
Yahweh said to Noah, "Come, you and all your household, into the ark ... (Genesis 7:1 ULB)
- "Yahweh said to Noah, "Enter, you and all your household, into the ark ..."
-
Some time after this, his wife Elizabeth became pregnant, but she did not go out in public for five months. (Luke 1:24 UDB)
- Some time after this, his wife Elizabeth became pregnant, but she did not appear in public for five months.
-
Nominal Adjectives
This page answers the question: How do I translate adjectives that act like nouns?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
In some languages an adjective can be used to refer to a class of things that the adjective describes. When it does, it acts like a noun. For example, the word "rich" is an adjective. Here are two sentences that show that "rich" is an adjective.
... The rich man had huge numbers of flocks and herds ... (2 Samuel 12:2 ULB)
The adjective "rich" comes before the word "man" and describes "man."
He will not be rich; his wealth will not last ... (Job 15:29 ULB)
The adjective "rich" comes after the verb "be" and describes "He."
Here is a sentence that shows that "rich" can also function as a noun.
…the rich must not give more than the half shekel, and the poor must not give less. (Exodus 30:15 ULB)
In Exodus 30:15, the word "rich" acts as a noun in the phrase "the rich," and it refers to rich people. The word "poor" also acts as a noun and refers to poor people.
Reason this is a translation issue
- Many times in the Bible adjectives are used as nouns to describe a group of people.
- Some languages do not use adjectives in this way.
- Readers of these languages may think that the text is talking about one particular person when it is really talking about the group of people whom the adjective describes.
Examples from the Bible
The scepter of wickedness must not rule in the land of the righteous. (Psalms 125:3 ULB)
"The righteous" here are people who are righteous, not one particular righteous person.
Blessed are the meek (Matthew 5:5 ULB)
"The meek" here are all people who are meek, not one particular meek person.
Translation Strategies
If your language uses adjectives as nouns to refer to a class of people, consider using the adjectives in this way. If it would sound strange, or if the meaning would be unclear or wrong, here is another option:
- Use the adjective with a plural form of the noun that the adjective describes.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use the adjective with a plural form of the noun that the adjective describes.
-
The scepter of wickedness must not rule in the land of the righteous. (Psalms 125:3 ULB)
- The scepter of wickedness must not rule in the land of righteous people.
-
Blessed are the meek ... (Matthew 5:5 ULB)
- Blessed are people who are meek ...
-
Order of Events
This page answers the question: Why are the events not listed in the order they happened, and how do I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
In the Bible, events are not always told in the order in which they occurred. Sometimes the author wanted to discuss something that happened at an earlier time than the event that he just talked about. This can be confusing to the reader.
Reason this is a translation issue: Readers might think that the events happened in the order that they are told. It is important to help them understand the correct order of events.
Examples from the Bible
But then Herod ... had John locked up in prison. Now it came about, while all the people were being baptized by John, that Jesus also was baptized. (Luke 3:20-21 ULB)
This could sound like John baptized Jesus after John was locked up in prison, but John baptized Jesus before John was locked up in prison.
Just as Joshua had said to the people, the seven priests carried the seven trumpets of rams horns before Yahweh, as they advanced, they gave a blast on the trumpets… But Joshua commanded the people, saying, "Do not shout. No sound must leave your mouths until the day I tell you to shout. Only then must you shout." (Joshua 6:8-10 ULB)
This could sound like Joshua gave the order not to shout after the army had already started their march, but he had given that order before they started marching.
Who is worthy to open the scroll and break its seals? (Revelation 5:2 ULB)
This sounds like a person must first open the scroll and then break its seals, but the seals that lock the scroll must be broken before the scroll can be unrolled.
Translation Strategies
- If your language uses phrases or time words to show that an event happened before one that was already mentioned, consider using one of them.
- If your language uses verb tense or aspect to show that an event happened before one that was already mentioned, consider using that. (See: the section on Aspect on Verbs)
- If your language prefers to tell events in the order that they occurred, consider reordering the events so they they are in that order. This may require putting two or more verses together (like 5-6). (See: Verse Bridges)
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If your language uses phrases, time words or tenses to show that an event happened before the one just mentioned, consider using one of them.
-
20 But then Herod ... had John locked up in prison. 21 Now it came about, while all the people were being baptized by John, that Jesus also was baptized. (Luke 3:20-21 ULB)
- 20 But then Herod ... had John locked up in prison. 21 Before John was put in prison, while all the people were being baptized by John, Jesus also was baptized.
-
Who is worthy to open the scroll and break its seals? (Revelation 5:2 ULB)
- Who is worthy to open the scroll after breaking its seals?
-
-
If your language uses verb tense or aspect to show that an event happened before one that was already mentioned, consider using that.
- 8 Just as Joshua had said to the people, the seven priests carried the seven trumpets of rams' horns before Yahweh, as they advanced, they gave a blast on the trumpets...10 But Joshua commanded the people, saying, "Do not shout. No sound must leave your mouths until the day I tell you to shout. Only then must you shout." (Joshua 6:8-10 ULB)
- 8 Just as Joshua had said to the people, the seven priests carried the seven trumpets of rams horns before Yahweh, as they advanced, they gave a blast on the trumpets...10 But Joshua had commanded the people, saying, "Do not shout. No sound must leave your mouths until the day I tell you to shout. Only then must you shout.
- 8 Just as Joshua had said to the people, the seven priests carried the seven trumpets of rams' horns before Yahweh, as they advanced, they gave a blast on the trumpets...10 But Joshua commanded the people, saying, "Do not shout. No sound must leave your mouths until the day I tell you to shout. Only then must you shout." (Joshua 6:8-10 ULB)
-
If your language prefers to tell events in the order that they occur, consider reordering the events. This may require putting two or more verses together (like 5-6).
-
8 Just as Joshua had said to the people, the seven priests carried the seven trumpets of rams horns before Yahweh, as they advanced, they gave a blast on the trumpets...10 But Joshua commanded the people, saying, "Do not shout. No sound must leave your mouths until the day I tell you to shout. Only then must you shout." (Joshua 6:8-10 ULB)
- 8-10 Joshua commanded the people, saying, "Do not shout. No sound must leave your mouths until the day I tell you to shout. Only then must you shout." Then just as Joshua had said to the people, the seven priests carried the seven trumpets of rams horns before Yahweh, as they advanced, they gave a blast on the trumpets ...
-
Who is worthy to open the scroll and break its seals? (Revelation 5:2 ULB)
- Who is worthy to break the seals and open the scroll?
-
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_events.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Parts of Speech
This page answers the question: What are some of the parts of speech in English?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Parts of speech are categories of words. The different categories of words have different functions in a sentence. All languages have parts of speech, and all words in a language belong to a part of speech. Most languages have these basic parts of speech, with some variations, and some languages have more categories than this. This is not an exhaustive list of parts of speech, but it covers the basic categories.
VERBS are words that express either an action (such as come, go, eat) or a state-of-being (such as is, are, was). More detailed information can be found on Verbs.
NOUNS are words that represent a person, place, thing, or idea. Common nouns are generic, that is, they do not refer to any specific entity (man, city, country). Names, or proper nouns, refer to a specific entity (Peter, Jerusalem, Egypt). (For more information see) How to Translate Names.
PRONOUNS take the place of nouns and include such words as he, she, it, you, they, and we. More detailed pages on pronouns can be found on Pronouns.
CONJUNCTIONS are words that join phrases or sentences. Examples include and, or, but, for, yet, nor. Some conjunctions are used in pairs: both/and; either/or; neither/nor; not only/but also. More information about these can be found on Connecting Words
PREPOSITIONS are words that begin phrases which connect a noun or verb with more detail about that noun or verb. For example, "The girl ran to her father." Here the phrase with the preposition "to" tells the direction of the girl's running (the action) in relation to her father. Another example is, "The crowd around Jesus grew in numbers." The phrase with the preposition around tells the location of the crowd in relation to Jesus. Some examples of prepositions are to, from, in, out, on, off, with, without, above, below, before, after, behind, in front of, among, through, beyond, among.
ARTICLES are words that are used with nouns to show whether or not the speaker is referring to something that his listener should be able to identify. In English these words are: "a", an, the. The words a and an mean the same thing. If a speaker says "a dog, he does not expect his listener to know which dog he is talking about; this might be the first time he says anything about a dog. If a speaker says the dog, he is usually referring to a specific dog, and he expects his listener to know which dog he is talking about. English speakers also use the to show that they are talking about something in general. For example, they can say "The elephant is a large animal" and refer to elephants in general, not a specific elephant. More information about this can be found on Generic Noun Phrases.
ADJECTIVES are words that describe nouns and express such things as quantity, size, color, and age. Some examples are: many, big, blue, old, smart, tired. Sometimes people use adjectives to give some information about something, and sometimes people use them to distinguish one item from another. For example, in my elderly father the adjective elderly simply tells something about my father. But in my eldest sister the word eldest distinguishes that sister from any other older sisters I might have. More information about this can be found on Distinguishing versus Informing or Reminding.
ADVERBS are words that describe verbs or adjectives and tell such things as how, when, where, why, and to what extent. Many English adverbs end in ly. Some examples of adverbs: slowly, later, far, intentionally, very.
Possession
This page answers the question: What is possession and how can I translate phrases that have it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
In common English, "possession" refers to having something, or to something that a person has. In English that grammatical relationship is shown with of, or an apostrophe and the letter s, or a possessive pronoun.
- the house of my grandfather
- my grandfather's house
- his house
Possession is used in Hebrew, Greek, and English for a variety of situations. Here are a few common situations that it is used for.
- Ownership - Someone owns something.
- My clothes - The clothes that I own
- Social relationship - Someone has some kind of social relationship with another.
- my mother - the woman who gave birth to me, or the woman who cared for me
- my teacher - the person who teaches me
- Contents - Something has something in it.
- a bag of potatoes - a bag that has potatoes in it, or a bag that is full of potatoes
- Part and whole: One thing is part of another.
- my head - the head that is part of my body
- the roof of a house - the roof that is part of a house
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Translators need to understand the relationship between two ideas represented by the two nouns when one possesses the other.
- Some languages do not use possession for all of the situations that your source text Bible might use it for.
Examples from the Bible
Ownership - In the example below, the son owned the money.
… the younger son … wasted his money with wildly extravagant living. (Luke 15:13)
Social Relationship - In the example below, the disciples were people who learned from John.
Then the disciples of John came to him …, (Matthew 9:14 ULB)
Material - In the example below, the material used for making the crowns was gold.
On their heads were something like crowns of gold (Revelation 9:7)
Contents - In the example below, the cup has water in it.
Whoever gives you a cup of water to drink … will not lose his reward. (Mark 9:41 ULB)
Part of a whole - In the example below, the door was a part of the palace.
But Uriah slept at the door of the king's palace (2 Samuel 11:9 ULB)
Part of a group - In the example below, "us" refers to the whole group and "each one" refers to the individual members.
To each one of us has been given a gift (Ephesians 4:7 ULB)
Events and Possession
Sometimes one or both of the nouns is an abstract noun that refers to an event or action. In the examples below, the abstract nouns are in bold print. These are just some of the relationships that are possible between two nouns when one of them refers to an event.
Subject - Sometimes the word after "of" tells who would do the action named by the first noun. In the example below, John baptized people.
The baptism of John, was it from heaven or from men? Answer me." (Mark 11:30)
In the example below, Christ loves us.
Who will separate us from the love of Christ? (Romans 3:35)
Object - Sometimes the word after "of" tells who or what something would happen to. In the example below, people love money.
For the love of money is a root of all kinds of evil. (1 Timothy 6:10 ULB)
Instrument - Sometimes the word after "of" tells how something would happen. In the example below, God would punish people by sending enemies to attack them with swords.
then be afraid of the sword, because wrath brings the punishment of the sword (Job 19:29 ULB)
Representation - In the example below, John was baptizing people who were repenting of their sins. They were being baptized to show that they were repenting. Their baptism represented their repentance.
As John came, he was baptizing in the wilderness and was preaching a baptism of repentance for the forgiveness of sins. (Mark 1:4 ULB)
Strategies for learning what the relationship is between the two nouns
- Read the surrounding verses to see if they help you to understand the relationship between the two nouns.
- Read the verse in the UDB. Sometimes it shows the relationship clearly.
- See what the notes say about it.
Translation Strategies
If possession would be a natural way to show a particular relationship between two nouns, consider using it. If it would be strange or hard to understand, consider these.
- Use an adjective to show that one describes the other.
- Use a verb to show how the two are related.
- If one of the nouns refers to an event, translate it as a verb.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use an adjective to show that one describes the other. The adjective below is in bold print.
- On their heads were something like crowns of gold (Revelation 9:7)
- "On their heads were gold crowns"
- On their heads were something like crowns of gold (Revelation 9:7)
-
Use a verb to show how the two are related. In the example below, the added verb is in bold.
-
... Whoever gives you a cup of water to drink ... will not lose his reward. (Mark 9:41 ULB)
- ... Whoever gives you a cup that has water in it to drink ... will not lose his reward.
-
Wealth is worthless on the day of wrath (Proverbs 11:4 ULB)
- Wealth is worthless on the day when God shows his wrath.
- Wealth is worthless on the day when God punishes people because of his wrath.
-
-
If one of the nouns refers to an event, translate it as a verb. In the example below, that verb is in bold.
-
Notice that I am not speaking to your children, who have not known or seen the punishment of Yahweh your God, (Deuteronomy 11:2 ULB)
- Notice that I am not speaking to your children who have not known or seen how Yahweh your God punished the people of Egypt.
-
You will only observe and see the punishment of the wicked. (Psalms 91:8 ULB)
- You will only observe and see how Yahweh punishes the wicked.
-
... you will receive the gift of the Holy Spirit. (Acts 2:38 ULB)
- ... you will receive the Holy Spirit, whom God will give to you.
-
Verbs
This page answers the question: What are verbs and what kinds of things are associated with them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Verbs are words that refer to an action or event or that is used in describing or identifying things.
Examples The verbs in the examples below are underlined.
- John ran. ("Run" is an action.)
- John ate a banana. ("Eat" is an action.)
- John saw Mark. ("See" is an event.)
- John died. ("Die" is an event.)
- John is tall. (The phrase "is tall" describes John. The word "is" is a verb that links "John" with "tall.")
- John looks handsome. (The phrase "is handsome" describes John. The word "looks" here is a verb that links "John" with "handsome.")
- John is my brother. (The phrase "is my brother" identifies John.)
People or Things Associated with a Verb
A verb usually says something about someone or something. All of the example sentences above say something about John. "John" is the subject of those sentences. In English the subject usually comes before the verb.
Sometimes there is another person or thing associated with the verb. In the examples below, the underlined word is the verb, and the phrase in bold print is the object. In English the object usually comes after the verb.
- He ate lunch.
- He sang a song.
- He read a book.
- He saw the book.
Some verbs never have an object.
- The sun rose at six o'clock.
- John slept well.
- John fell yesterday.
For many verbs in English, it is alright to leave out the object when the object is not important in the sentence.
- He never eats at night.
- He sings all the time.
- He reads well.
- He cannot see.
In some languages, a verb that needs an object must always take one, even if the object is not very important. People who speak those languages might say the sentences above like this.
- He never eats food at night.
- He sings songs all the time.
- He reads words well.
- He cannot see anything.
Subject and Object Marking on Verbs
In some languages, the verb may be a little bit different depending on the persons or things associated with it. For example, English speakers sometimes put "s" at the end of the verb when the subject is just one person. In other languages marking on the verb may show whether the subject is "I," "you," or "he"; singular, dual, or plural; male or female, or human or non-human.
- They eat bananas every day. (The subject "they" is more than one person.)
- John eats bananas every day. (The subject "John" is one person.)
Time and Tense
When we tell about an event, we usually tell whether it is in the past, the present, or the future. Sometimes we do this with words like "yesterday," "now," or "tomorrow."
In some languages the verb may be a little bit different depending on the time associated with it. This kind of marking on a verb is called tense. English speakers sometimes put "ed" at the end of the verb when the event happened in the past.
- Sometimes Mary cooks meat.
- Yesterday Mary cooked meat. (She did this in the past.)
In some languages speakers might add a word to tell something about the time. English speakers use the word "will" when the verb refers to something in the future.
- Tomorrow Mary will cook meat.
Aspect
When we tell about an event, sometimes we want to show how the event progressed over a period of time, or how the event relates to another event. This is aspect. English speakers sometimes use the verbs "is" or "has" and add "s," "ing," or "ed" to the end of the verb in order to show how the event relates to another event or to the present time.
- Mary cooks meat every day. (This tell about something Mary often does.)
- Mary is cooking the meat. (This tells about something Mary is in the process of doing right now.)
- Mary cooked the meat, and John came home. (This simply tells about things that Mary and John did.)
- While Mary was cooking the meat, John came home. (This tells about something Mary was in the process of doing when John came home)
- Mary has cooked the meat, and she wants us to come eat it. (This tells about something Mary did that is still relevant now.)
- Mary had cooked the meat by the time Mark came home. (This tells about something that Mary completed in the past before something else happened.)
Next we recommend you learn about:
When Masculine Words Include Women
This page answers the question: How do I translate "brother" or "he" when it could refer to anyone, male or female?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
In some parts of the Bible, the words "men", "brothers" and "sons" refer only to men. In other parts of the Bible, those words include both men and women. When the writer meant both men and women, translators need to translate it in a way that does not limit the meaning to men.
Description
In some languages a word that normally refers to men can also be used in a more general way to refer to both men and women. For example, the Bible sometimes says 'brothers' when it refers to both brothers and sisters.
Also in some languages, the masculine pronouns "he" and "him" can be used in a more general way for any person if it is not important whether the person is a man or a woman. In the example below, the pronoun is "his", but it is not limited to males.
A wise child makes his father rejoice
but a foolish child brings grief to his mother. (Proverbs 10:1 ULB)
Reason this is a translation issue
- In some cultures words like "man," "brother," and "son" can only be used to refer to men. If those words are used in a translation in a more general way, people will think that what is being said does not apply to women.
- In some cultures, the masculine pronouns "he" and "him" can only refer to men. If a masculine pronoun is used, people will think that what is said does not apply to women.
Translation Principles
When a statement applies to both men and women, translate it in such a way that people will be able to understand that it applies to both.
Examples from the Bible
We want you to know, brothers, about the grace of God that has been given to the churches of Macedonia. (2 Corinthians 8:1 ULB)
This verse is addressing the believers in Corinth, not only men, but men and women.
Then said Jesus to his disciples, "If anyone wants to follow me, he must deny himself, take up his cross, and follow me." (Matthew 16:24-26 ULB)
Jesus was not speaking only of men, but of men and women.
Caution: Sometimes masculine words are used specifically to refer to men. Do not use words that would lead people to think that they include women. The underlined words below are specifically about men.
Moses said, 'If a man dies, having no children, his brother must marry his wife and have a child for his brother.' (Mark 22:24 ULB)
Translation Strategies
If people would understand that that masculine words like "man," "brother," and "he" can include women, then consider using them. Otherwise, here are some ways for translating those words when they include women.
- Use a noun that can be used for both men and women.
- Use a word that refers to men and a word that refers to women.
- Use pronouns that can be used for both men and women.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use nouns that can be used for both men and women.
- The wise man dies just like the fool dies. (Ecclesiastes 2:16 ULB)
- "The wise person dies just like the fool dies."
- "Wise people die just like fools die."
- The wise man dies just like the fool dies. (Ecclesiastes 2:16 ULB)
-
Use a word that refers to men and a word that refers to women.
- For we do not want you to be ignorant, brothers, about the troubles we had in Asia. (2 Corinthians 1:8) - Paul was writing this letter to both men and women.
- "For we do not want you to be ignorant, brothers and sisters, about the troubles we had in Asia." (2 Corinthians 1:8)
- For we do not want you to be ignorant, brothers, about the troubles we had in Asia. (2 Corinthians 1:8) - Paul was writing this letter to both men and women.
-
Use pronouns that can be used for both men and women.
- If anyone wants to follow me, he must deny himself, take up his cross, and follow me." (Matthew 16:24 ULB) - English speakers can change the masculine singular pronouns, "he," "himself," and "his" to plural pronouns that do not mark gender, "they," "themselves," and "their" in order to show that it applies to all people, not just men.
- "If people want to follow me, they must deny themselves, take up their cross, and follow me."
- If anyone wants to follow me, he must deny himself, take up his cross, and follow me." (Matthew 16:24 ULB) - English speakers can change the masculine singular pronouns, "he," "himself," and "his" to plural pronouns that do not mark gender, "they," "themselves," and "their" in order to show that it applies to all people, not just men.
Word Order
This page answers the question: What does "word order" mean?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Most languages have a normal way of ordering the parts of a sentence. It is not the same in all languages. Translators need to know what the normal word order is in their language.
The Main Parts of a Sentence
Most sentences have three basic important parts: subject, object, and verb. Subjects and objects are usually nouns (i.e., a person, place, thing, or idea) or pronouns. Verbs show action or a state of being.
Subject
The subject is usually what the sentence is about. It usually performs some action or is being described. A subject may be active; it does something, such as sing, or work, or teach.
- Peter sings the song well.
A subject may have something done to it.
- Peter was fed good food.
A subject can be described or it can be in a state, such as being happy, sad, or angry.
- He is tall.
- The boy is happy.
Object
The object is often the thing that the subject does something to.
- Peter hit the ball.
- Peter read a book.
- Peter sang the song well.
- Peter ate good food.
Verb
The verb shows an action or a state of being.
- Peter sings the song well.
- Peter is singing.
- Peter is tall.
Preferred Word Order
All languages have a preferred word order. The examples below show the order of the subject, object, and verb in "Peter hit the ball" for some languages. In some languages, such as English, the order is Subject-Verb-Object.
- Peter hit the ball.
In some languages the order is Subject-Object-Verb.
- Peter the ball hit.
In some languages the order is Verb-Subject-Object.
- Hit Peter the ball.
Changes in Word Order
Word order can change if the sentence:
- is a question or command
- describes a state of being (He is happy. He is tall.)
- expresses a condition, such as with the the word "if"
- has a location
- has a time element
- is in a poem
Word order can also change
- if there is some kind of emphasis on a certain part of the sentence
- if the sentence is really about something other than the subject
Translation Principles
- Know which word order is preferred in your language.
- Use your language's preferred word order unless there is some reason in your language to change it.
- Translate the sentence so that the meaning is accurate and clear and so that it sounds natural.
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_order.
Pronouns
Pronouns
This page answers the question: What are pronouns and what kinds of pronouns are in some languages?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Pronouns are words that people use in place of a noun to refer to someone or something. Some examples are I, you, he, it, this, that, himself, someone. The most common type of pronoun is personal.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to people or things and show if the speaker is referring to himself, the person he is speaking to, or someone or something else. The following are kinds of information that personal pronouns may give. Other types of pronouns may give some of this information, as well.
Person
- First Person - The speaker and possibly others (I, we)
- Second Person - The person or people that the speaker is talking to and possibly others (you)
- Third Person - Someone or something other than the speaker and those he is talking to (he, she, it, they)
Number
- Singular - one (I, you, he, she, it)
- Plural - more than one (we, you, they)
- Dual - two (Some languages have pronouns for specifically two people or two things.)
Gender
- Masculine - he
- Feminine - she
- Neuter - it
Relationship to other words in the sentence
- Subject of the verb: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Object of the verb or preposition: me, you, him, her, it, us, them
- Possessor with a noun: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Possessor without a noun: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
Other Types of pronouns
Reflexive Pronouns refer to another noun or pronoun in the same sentence: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
- John saw himself in the mirror. - The word "himself" refers to John.
Interrogative Pronouns are used to make a question that needs more than just a yes or no for an answer: who, whom, whose, what, where, when, why, how
- Who built the house?
Relative Pronouns mark a relative clause. They tell more about a noun in the main part of the sentence: that, which, who, whom, where, when
- I saw the house that John built. The clause "that John built" tells which house I saw.
- I saw the man who built the house. The clause "who built the house" tells which man I saw.
Demonstrative Pronouns are used to draw attention to someone or something and to show distance from the speaker or something else: this, these, that, those.
- Have you seen this here?
- Who is that over there?
Indefinite pronouns are used when no particular noun is being referred to: any, anyone, someone, anything, something, some. Sometimes a personal pronoun is used in a generic way to do this: you, they, he or it.
- He does not want to talk to anyone.
- Someone fixed it, but I do not know who.
- They say that you should not wake a sleeping dog.
In the last example, "they" and "you" just refer to people in general.
First, Second, or Third Person
This page answers the question: What are first, second, and third person, and how do I translate when a third person form does not refer to the third person?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Normally a speaker refers to himself as "I" and the person he is speaking to as "you." Sometimes in the Bible a speaker referred to himself or to the person he was speaking to with a phrase other than "I" or "you."
Description
- First person - This is how a speaker normally refers to himself. English uses the pronouns "I" and "we." (Also: me, my, mine; us, our, ours)
- Second person - This is how a speaker normally refers to the person or people he is speaking to. English uses the pronoun "you." (Also: your, yours)
- Third person - This is how a speaker refers to someone else. English uses the pronouns "he," "she," "it" and "they." (Also: him, his, her, hers, its; them, their, theirs) Noun phrases like "the man" or "the woman" are also third person.
Reason this is a Translation Issue
Sometimes in the Bible a speaker used the third person to refer to himself or to the people he was speaking to. Readers might think that the speaker was referring to someone else. They might not understand that he meant "I" or "you."
Examples from the Bible
Sometimes people used the third person instead of "I" or "me" to refer to themselves.
But David said to Saul, "Your servant used to keep his father's sheep." (1 Samuel 17:34 ULB)
David referred to himself in the third person as "your servant" and "his." He was calling himself Saul's servant in order to show his humility before Saul.
Then Yahweh answered Job out of a fierce storm and said,
"… Do you have an arm like God's? Can you thunder with a voice like him? (Job 40:6, 9 ULB)
God referred to himself in the third person with the words "God's" and "him." He did this to emphasize that he is God, and he is powerful.
Sometimes people use the third person instead of "you" or "your" to refer to the person or people they are speaking to.
Abraham answered and said, "Look what I have done, taking it upon myself to speak to my Lord, even though I am only dust and ashes! (Genesis 18:27 ULB)
Abraham was speaking to the Lord, and referred to the Lord as "My Lord" rather than as "you." He did this to show his humility before God.
So also my heavenly Father will do to you, if each of you does not forgive his brother from your heart. (Matthew 18:35 ULB)
After saying "each of you," Jesus used the third person "his" instead of "your."
Translation Strategies
If using the third person to mean "I" or "you" would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are some other options.
- Use the third person phrase along with the pronoun "I" or "you."
- Simply use the first person ("I") or second person ("you") instead of the third person.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Use the third person phrase along with the pronoun "I" or "you."
- But David said to Saul, "Your servant used to keep his father's sheep." (1 Samuel 17:34)
- But David said to Saul, "I, your servant, used to keep my father's sheep."
- But David said to Saul, "Your servant used to keep his father's sheep." (1 Samuel 17:34)
-
Simply use the first person ("I") or second person ("you") instead of the third person.
-
Then Yahweh answered Job out of a fierce storm and said, "… Do you have an arm like God's? Can you thunder with a voice like him? (Job 40:6, 9 ULB)
- Then Yahweh answered Job out of a fierce storm and said, "… Do you have an arm like mine? Can you thunder with a voice like me?"
-
So also my heavenly Father will do to you, if each of you does not forgive his brother from your heart. (Matthew 18:35 ULB)
- So also my heavenly Father will do to you, if each of you does not forgive your brother from your heart.
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Exclusive and Inclusive "We"
This page answers the question: What is exclusive and inclusive "we"?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some languages have more than one form of "we:" an inclusive form that means "I and you" and an exclusive form that means "I and someone else but not you." The exclusive form excludes the person being spoken to. The inclusive form includes the person being spoken to and possibly others. This is also true for "us," "our," "ours," and "ourselves." Some languages have inclusive forms and exclusive forms for each of these. Translators whose language has separate exclusive and inclusive forms for these words will need to understand what the speaker meant so that they can decide which form to use.
See the pictures. The people on the right are the people that the speaker is talking to. The yellow highlight shows who the inclusive "we" and the exclusive "we" refer to.


Reason this is a translation issue
The Bible was first written in the Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek languages. Like English, these languages do not have separate exclusive and inclusive forms for "we." Translators whose language has separate exclusive and inclusive forms of "we" will need to understand what the speaker meant so that they can decide which form of "we" to use.
Examples from the Bible
They said, “We have no more than five loaves of bread and two fish, unless we went and bought food for all this crowd of people.” (Luke 9:13 ULB)
In the first clause, the disciples are telling Jesus how much food they have among them, so this "we" could be the inclusive form or the exclusive form. In the second clause, the disciples are talking about some of them going to buy food, so that "we" would be the exclusive form, since Jesus would not go to buy food.
we have seen, and bear witness, and declare to you the eternal life, which was with the Father, and was manifested to us (1 John 1:2 ULB)
John is telling people who have not seen Jesus what he and the other apostles have seen. So languages that have exclusive forms of "we" and "us" would use the exclusive forms in this verse.
… the shepherds said one to each other, "Let us now go to Bethlehem, and see this thing that has happened, which the Lord has made known to us." (Luke 2:15 ULB)
The shepherds were speaking to one another. When they said "us," they were including the people they were speaking to - one another.
Now it happened on one of those days that Jesus and his disciples entered into a boat, and he said to them, "Let us go over to the other side of the lake." Then they set sail. (Luke 8:22 ULB)
When Jesus said "us," he was referring to himself and to the disciples he was speaking to, so this would be the inclusive form.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Forms of "You" - Formal or Informal
This page answers the question: What are formal and informal "you"?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
(You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_youform.)
Description
Some languages make a distinction between the formal form of "you" and the informal form of "you." This page is primarily for people whose language makes this distinction.
In some cultures people use the formal "you" when speaking to someone who is older or in authority, and they use the informal "you" when speaking to someone who is their own age or younger or who has less authority. In other cultures, people use the formal "you" when speaking to strangers or people they do not know well, and the informal "you" when speaking with family members and close friends.
Reasons this is a Translation Issue
- The Bible was written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. These languages do not have formal and informal forms of "you."
- English and many other source languages do not have formal and informal forms of "you."
- Translators who use a source text in a language that does have formal and informal forms of "you" will need to understand how those forms are used in that language. The rules in that language may not be exactly the same as the rules in the translator's language.
- Translators will need to understand the relationship between two speakers in order to choose the appropriate form in their language.
Translation Principles
- Understand the relationship between a speaker and the person or people he is speaking to.
- Understand the speaker's attitude toward the person he is speaking to.
- Choose the form in your language that is appropriate for that relationship and attitude.
Examples from the Bible
Yahweh God called to the man and said to him, "Where are you?" (Genesis 3:9 ULB)
God is in authority over the man, so languages that have formal and informal forms of "you" would probably use the informal form here.
So, it seemed good to me also, having investigated everything accurately from the beginning, to write it down for you in order, most excellent Theophilus. I want you to know the certainty of the things that you were taught. (Luke 1:3-4 ULB)
Luke called Theophilus "most excellent." This shows us that Theophilus was probably a high official to whom Luke was showing great respect. Speakers of languages that have a formal form of "you" would probably use that form here.
Heavenly Father, sanctify your name. (Matthew 6:9 ULB)
This is part of a prayer that Jesus taught his disciples. Some cultures would use the formal "you" because God is in authority. Other cultures would use the informal "you" because God is our Father.
Translation Strategies
Translators whose language has formal and informal forms of "you" will need to understand the relationship between two speakers in order to choose the appropriate form of "you" in their language.
Deciding whether to use the Formal or Informal "You"
-
Pay attention to the relationships between the speakers.
- Is one speaker in authority over the other?
- Is one speaker older than the other?
- Are the speakers family members, relatives, friends, strangers, or enemies?
-
If you have a Bible in a language that has formal and informal forms of "you," see what forms it uses. Remember, though, that the rules in that language might be different than the rules in your language.
Translation Strategies Applied
English does not have formal and informal forms of "you", so we cannot show in English how to translate using formal and informal forms of "you." Please see the examples and discussion above.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Singular Pronouns that Refer to Groups
This page answers the question: How do I translate singular pronouns that refer to groups of people?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The Bible was written in Hebrew, Aramaic and Greek. These languages have a singular form of "you" for when the word "you" refers to just one person, and a plural form for when the word "you" refers to more than one person. However sometimes speakers in the Bible used the singular form of "you" even though they were speaking to a group of people. This is not obvious when you read the Bible in English, because English does not have distinct forms for "you" singular and "you" plural. But you may see this if you read a Bible in a language that does have distinct forms.
Also, speakers and writers of the Old Testament often referred to groups of people with the singular pronoun "he," rather than with the plural pronoun "they."
Reason this is a Translation Issue
- For many languages, a translator who reads a Bible with a general form of "you" will need to know whether the speaker was speaking to one person or to more than one.
- In some languages it might be confusing if a speaker uses a singular pronoun when speaking to or about more than one person.
Examples from the Bible
1Take heed that you do not do your acts of righteousness before people to be seen by them, or else you will have no reward from your Father who is in heaven. 2So when you give alms, do not sound a trumpet before yourself as the hypocrites do in the synagogues and in the streets, so that they may have the praise of people. Truly I say to you, they have received their reward. (Matthew 6:1,2 ULB)
Jesus said this to a crowd. He used "you" plural in verse 1, and "you" singular in the first sentence of verse 2. Then in the last sentence he used the plural again.
God spoke all these words: "I am Yahweh, your God, who brought you out of the land of Egypt, out of the house of slavery. You must have no other gods before me." (Exodus 20:1-3 ULB)
God said this to all the people of Israel. He had taken them all out of Egypt and he wanted them all to obey him, but he used the singular form of you here when speaking to them.
This is what Yahweh says,
"For three sins of Edom,
even for four,
I will not turn away punishment,
because he pursued his brother with the sword
and cast off all pity.
His anger raged continually,
and his wrath lasted forever." (Amos 1:11 ULB)
Yahweh said these things about the nation of Edom, not about only one person.
Translation Strategies
If the singular form of the pronoun would be natural when referring to a group of people, consider using it.
- Whether you can use it may depend on who the speaker is and who the people are that he is talking about or talking to.
-
It may also depend on what the speaker is saying.
-
If the singular form of the pronoun would not be natural when referring to a group of people, or if the readers would be confused by it, use the plural form of the pronoun.
Translation Strategies Applied
- If the singular form of the pronoun would not be natural when referring to a group of people, or if the readers would be confused by it, use the plural form of the pronoun.
This is what Yahweh says,
"For three sins of Edom,
even for four,
I will not turn away punishment,
because he pursued his brother with the sword
and cast off all pity.
His anger raged continually,
and his wrath lasted forever." (Amos 1:11 ULB)
This is what Yahweh says, "For three sins of Edom, even for four, I will not turn away punishment, because they pursued their brothers with the sword and cast off all pity. Their anger raged continually, and their wrath lasted forever."
Next we recommend you learn about:
Reflexive Pronouns
This page answers the question: What are reflexive pronouns?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
All languages have ways of showing that the same person fills two different roles in a sentence. English does this by using Reflexive pronouns. These are pronouns that refer to someone or something that has already been mentioned in a sentence. In English the reflexive pronouns are: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves. Other languages may have other ways to show this.
Reason this is a translation issue
- Languages have different ways of showing that the same person fills two different roles in a sentence. For those languages, translators will need to know how to translate the English reflexive pronouns.
- The reflexive pronouns in English also have other functions.
Uses of Reflexive Pronouns
- To show that the same person or things fills two different roles in a sentence
- To emphasize a person or thing in the sentence
- To show that someone did something alone
- To show that someone or something was alone
Examples from the Bible
Reflexive pronouns are used to show the same person or thing fills two different roles in a sentence.
If I should testify about myself alone, my testimony would not be true. (John 5:31 ULB)
Now the Passover of the Jews was near, and many went up to Jerusalem out of the country before the Passover in order to purify themselves. (John 11:55 ULB)
Reflexive pronouns are used to emphasize a person or thing in the sentence.
Jesus himself was not baptizing, but his disciples were (John 4:2 ULB)
So they left the crowd, taking Jesus with them, since he was already in the boat. Other boats were also with him. And a violent windstorm arose and the waves were breaking into the boat so that the boat was already full. But Jesus himself was in the stern, asleep on a cushion. (Mark 4:36-38 ULB)
Reflexive pronouns are used to show that someone did something alone.
When Jesus realized that they were about to come and seize him by force to make him king, he withdrew again up the mountain by himself. (John 6:15 ULB)
Reflexive pronouns are used to show that someone or something was alone.
He saw the linen cloths lying there and the cloth that had been on his head. It was not lying with the linen cloths but was rolled up in its place by itself. (John 20:6-7 ULB)
Translation Strategies
If a reflexive pronoun would have the same function in your language, consider using it. If not, here are some other strategies.
- In some languages people put something on the verb to show that the object of the verb is the same as the subject.
- In some languages people emphasize a certain person or thing by referring to it in a special place in the sentence.
- In some languages people emphasize a certain person or thing by adding something to that word or putting another word with it.
- In some languages people show that someone did something alone by using a word like "alone."
- In some languages people show that something was alone by using a phrase that tells about where it was.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
In some languages people put something on the verb to show that the object of the verb is the same as the subject.
-
If I should testify about myself alone, my testimony would not be true. (John 5:31)
- "If I should self-testify alone, my testimony would not be true."
-
Now the Passover of the Jews was near, and many went up to Jerusalem out of the country before the Passover in order to purify themselves. (John 11:55)
- "Now the Passover of the Jews was near, and many went up to Jerusalem out of the country before the Passover in order to self-purify."
-
-
In some languages people emphasize a certain person or thing by referring to it in a special place in the sentence.
-
He himself took our sickness and bore our diseases. (Matthew 8:17 ULB)
- "It was he who took our sickness and bore our diseases."
-
Jesus himself was not baptizing, but his disciples were. (John 4:2)
- "It was not Jesus who was baptizing, but his disciples were."
-
-
In some languages people emphasize a certain person or thing by adding something to that word or putting another word with it. English adds the reflexive pronoun.
- Now Jesus said this to test Philip, for he himself knew what he was going to do. (John 6:6)
-
In some languages people show that someone did something alone by using a word like "alone."
- When Jesus realized that they were about to come and seize him by force to make him king, he withdrew again up the mountain by himself. (John 6:15)
- "When Jesus realized that they were about to come and seize him by force to make him king, he withdrew again alone up the mountain."
- When Jesus realized that they were about to come and seize him by force to make him king, he withdrew again up the mountain by himself. (John 6:15)
-
In some languages people show that something was alone by using a phrase that tells about where it was.
- He saw the linen cloths lying there and the cloth that had been on his head. It was not lying with the linen cloths but was rolled up in its place by itself. (John 20:6-7 ULB)
- "He saw the linen cloths lying there and the cloth that had been on his head. It was not lying with the linen cloths but was rolled up and lying in it's own place."
- He saw the linen cloths lying there and the cloth that had been on his head. It was not lying with the linen cloths but was rolled up in its place by itself. (John 20:6-7 ULB)
Pronouns - When to Use Them
This page answers the question: How do I decide whether or not to use a pronoun?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
When we talk or write, we use pronouns to refer to people or things without always having to repeat the noun or name. Usually the first time we refer to someone in a story, we use a descriptive phrase or a name. The next time we might refer to that person with a simple noun or by name. After that we might refer to him simply with a pronoun, as long as we think that our listeners will be able to understand easily to whom the pronoun refers.
Now there was a Pharisee whose name was Nicodemus, a member of the Jewish Council. This man came to Jesus ... Jesus replied to him (John 3:1-3 ULB)
In John 3, Nicodemus is first referred to with noun phrases and his name. Then he is referred to with the noun phrase "this man." Then he is referred to with the pronoun "him."
Each language has its rules and exceptions to this usual way of referring to people and things.
- In some languages the first time something is referred to in a paragraph or chapter, it is referred to with a noun rather than a pronoun.
- The main character is the person whom a story is about. In some languages, after a main character is introduced in a story, he is usually referred to with a pronoun. Some languages have special pronouns that refer only to the main character.
- In some languages, marking on the verb helps people know who the subject is. (see Verbs) In some of these languages, listeners rely on this marking to help them understand who the subject is, and speakers use a pronoun, noun phrase, or name only when they want to emphasize or clarify who the subject is.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- If translators use a pronoun at the wrong time for their language, readers might not know who the writer is talking about.
- If translators too frequently refer to a main character by name, listeners of some languages might not realize that the person is a main character, or they might think that there is a new character with the same name.
- If translators use pronouns, nouns, or names at the wrong time, people might think that there is some special emphasis on the person or thing it refers to.
Examples from the Bible
The example below occurs at the beginning of a chapter. In some languages it might not be clear whom the pronouns refer to.
Again Jesus walked into the synagogue, and a man with a withered hand was there. They watched him to see if he would heal him on the Sabbath. (Mark 3:1-2 ULB)
In the example below, two men are named in the first sentence. It might not be clear whom "he" in the second sentence refers to.
Now after some days, King Agrippa and Bernice arrived at Caesarea to pay an official visit to Festus. After he had been there for many days, Festus presented Paul's case to the king... (Acts 25:13-14 ULB)
Jesus is the main character of the book of Matthew, but in the verses below he is referred to four times by name. This may lead speakers of some languages to think that Jesus is not the main character. Or it might lead them to think that there is more than one person named Jesus in this story. Or it might lead them to think that there is some kind of emphasis on him, even though there is no emphasis.
At that time Jesus went on the Sabbath day through the grainfields. His disciples were hungry and began to pluck heads of grain and eat them. But when the Pharisees saw that, they said to Jesus, "See, your disciples do what is unlawful to do on the Sabbath." But Jesus said to them, "Have you never read what David did, when he was hungry, and the men who were with him? ..." Then Jesus left from there and went into their synagogue. (Matthew 12:1-9 ULB)
Translation Strategies
- If it would not be clear to your readers whom or what a pronoun refers to, use a noun or name.
- If repeating a noun or name would lead people to think that a main character is not a main character, or that the writer is talking about more than one person with that name, or that there is some kind of emphasis on someone when there is no emphasis, use a pronoun instead.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If it would not be clear to your readers whom or what a pronoun refers to, use a noun or name.
- Again Jesus walked into the synagogue, and a man with a withered hand was there. They watched him to see if he would heal him on the Sabbath. (Mark 3:1-2 ULB)
- Again Jesus walked into the synagogue, and a man with a withered hand was there. Some Pharisees watched Jesus to see if he would heal the man on the Sabbath. (Mark 3:1-2 UDB)
- Again Jesus walked into the synagogue, and a man with a withered hand was there. They watched him to see if he would heal him on the Sabbath. (Mark 3:1-2 ULB)
-
If repeating a noun or name would lead people to think that a main character is not a main character, or that the writer is talking about more than one person with that name, or that there is some kind of emphasis on someone when there is no emphasis, use a pronoun instead.
At that time Jesus went on the Sabbath day through the grain fields. His disciples were hungry and began to pluck heads of grain and eat them. But when the Pharisees saw that, they said to Jesus , "See, your disciples do what is unlawful to do on the Sabbath."
But Jesus said to them, "Have you never read what David did, when he was hungry, and the men who were with him? ...
Then Jesus left from there and went into their synagogue. (Matthew 12:1-9 ULB)
May be translated as:
At that time Jesus went on the Sabbath day through the grain fields. His disciples were hungry and began to pluck heads of grain and eat them. But when the Pharisees saw that, they said to him, "See, your disciples do what is unlawful to do on the Sabbath.
But he said to them, "Have you never read what David did, when he was hungry, and the men who were with him? ...
Then he left from there and went into their synagogue.
Sentences
Sentence Structure
This page answers the question: What are the parts of a sentence?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The simplest sentence structure in English includes a subject and an action word:
- The boy ran.
Subject
The subject is who or what the sentence is about. In these examples, the subject is underlined:
- The boy is running.
- He is running.
Subjects are typically noun phrases or pronouns. (see Parts of Speach) In the examples above, "the boy" is a noun phrase that has the noun "boy," and "he" is a pronoun.
When the sentence is a command, in many languages it does not have a subject pronoun. People understand that the subject is "you."
- Close the door.
Predicate
The predicate is the part of a sentence that tells something about the subject. It usually has a verb. (See: Verbs) In the sentences below, the subjects are "the man" and "he." The predicates are underlined and the verbs are in bold.
- The man is strong.
- He worked hard.
- He made a garden.
Compound Sentences
A sentence can be made up of more than one sentence. Each of the two lines below has a subject and a predicate and is a full sentence.
- He planted the yams.
- His wife planted the corn.
The compound sentence below contains the two sentences above. In English, compound sentences are joined with a conjunction such as "and," "but," or "or."
- He planted the yams and his wife planted the corn.
Clauses
Sentences can also have clauses and other phrases. Clauses are like sentences because they have a subject and a predicate, but they do not normally occur by themselves. Here are some examples of clauses. The subjects are in bold, and the predicates are underlined.
- when the corn was ready
- after she picked it
- because it tasted so good
Sentences can have many clauses, and so they can become long and complex. But each sentence has to have at least one independent clause, that is, a clause that can be a sentence all by itself. The other clauses that cannot be sentences by themselves are called the dependent clauses. Dependent clauses depend on the independent clause to complete their meaning. The dependent clauses are underlined in the sentences below.
- When the corn was ready, she picked it.
- After she picked it, she carried it home and cooked it.
- Then she and her husband ate it all, because it tasted so good.
The following phrases can each be a whole sentence. They are the independent clauses from the sentences above.
- She picked it.
- She carried it home and cooked it.
- Then she and her husband ate it all.
Relative Clauses
In some languages, clauses can be used with a noun that is part of a sentence. These are called relative clauses.
In the sentence below, "the corn that was ready" is part of the predicate of the whole sentence. The relative clause "that was ready" is used with the noun "corn" to tell which corn she picked.
- His wife picked the corn that was ready.
In the sentence below "her mother, who was very annoyed" is part of the predicate of the whole sentence. The relative clause "who was very annoyed" is used with the noun "mother" to tell how her mother felt when she did not get any corn.
- She did not give any corn to her mother, who was very annoyed.
Translation Issues
- Languages have different orders for the parts of a sentence. (See: //add Information Structure page//)
- Some languages do not have relative clauses, or they use them in a limited way. (see Distinguishing versus Informing or Reminding)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Information Structure
This page answers the question: How do languages arrange the parts of a sentence?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Different languages arrange the parts of the sentence in different ways. In English, a sentence normally has the subject first, then the verb, then the object, then other modifiers, like this:
Peter painted his house yesterday.
Many other languages normally put these things in a different order, such as:
Painted yesterday Peter his house.
Although all languages have a normal order for parts of a sentence, this order can change depending on what information the speaker or writer considers to be the most important. Suppose that someone is answering the question, "What did Peter paint yesterday?" The person asking the question already knows all of the information in our sentence above except for the object: "his house." Therefore, that becomes the most important part of the information, and a person answering in English might say:
His house is what Peter painted (yesterday).
This puts the most important information first, which is normal for English. Many other languages would normally put the most important information last. In the flow of a text, the most important information is usually what the writer considers to be new information for the reader. In some languages the new information comes first, and in others it comes last.
Reasons this is a translation Issue
- Different languages arrange the parts of a sentence in different ways. If a translator copies the order of the parts of a sentence from the source, it may not make sense in his language.
- Different languages put important or new information in different places in the sentence. If a translator keeps the important or new information in the same place that it had in the source language, it may be confusing or give the wrong message in his language.
Examples from the Bible
They all ate until they were satisfied. (Mark 6:42 ULB)
The parts of this sentence were in a different order in the original Greek source language. They were like this:
- And they ate all and they were satisfied.
In English, this means that the people ate everything. But the next verse says that they took up twelve baskets full of leftover pieces of food. In order for this to not be so confusing, the translators of the ULB put the parts of the sentence in the right order for English.
Now the day was about to come to an end, and the twelve came to him and said, "Send the crowd away that they may go into the surrounding villages and countryside to find lodging and food, because we are here in an isolated place." (Luke 9:12 ULB)
In this verse, what the disciples say to Jesus puts the important information first - that he should send the crowd away. But in languages that put the important information last, people would understand that the reason that they give - being in an isolated place - is the most important part of their message to Jesus. They might then think that the disciples are afraid of the spirits in that place, and that sending the people to buy food is a way to protect them from the spirits. That is the wrong message.
Woe to you, when all men speak well of you, for that is how their ancestors treated the false prophets. (Luke 6:26 ULB)
In this verse, the most important part of the information is first - that "woe" is coming on the people for what they are doing. The reason that supports that warning comes last. This could be confusing for people who expect the important information to come last.
Translation Strategies
- Study how your language arranges the parts of a sentence, and use that order in your translation.
- Study where your language puts the new or important information, and rearrange the order of information so that it follows the way it is done in your language.
Translation Strategies Applied
-
Study how your language arranges the parts of a sentence, and use that order in your translation.
-
And he went out from there and came to the hometown his, and they followed him the disciples his. (Mark 6:1)
This is the verse in the original Greek order. The ULB has put this into the normal order for English:
And he went out from there and came into his hometown, and his disciples followed him. (Mark 6:1 ULB)
- Study where your language puts the new or important information, and rearrange the order of information so that it follows the way it is done in your language.
Now the day was about to come to an end, and the twelve came to him and said, "Send the crowd away that they may go into the surrounding villages and countryside to find lodging and food, because we are here in an isolated place." (Luke 9:12 ULB)
If your language puts the important information last, you can change the order of the verse:
- Now the day was about to come to an end, and the twelve came to him and said, "Because we are here in an isolated place, send the crowd away that they may go into the surrounding villages and countryside to find lodging and food."
Woe to you, when all men speak well of you, for that is how their ancestors treated the false prophets. (Luke 6:26 ULB)
If your language puts the important information last, you can change the order of the verse:
- When all men speak well of you, which is just as people's ancestors treated the false prophets, then woe to you!
Next we recommend you learn about:
Sentence Types
This page answers the question: What are the different types of sentences and what are they used for?
Description
A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. The basic types of sentences are listed below with the functions they are mainly used for.
- Statements - These are mainly used to give information. 'This is a fact.'
- Questions - These are mainly used to ask for information. 'Do you know him?'
- Imperative Sentences - These are mainly used to express a desire or requirement that someone do something. 'Pick that up.'
- Exclamations - These are mainly used to express a strong feeling. 'Ouch, that hurt!'
Reasons this is a translation Issue
- Languages have different ways of using sentence types to express particular functions.
- Most languages use these sentence types for more than one function.
- Each sentence in the Bible belongs to a certain sentence type and has a certain function, but some languages would not use that type of sentence for that function.
Examples from the Bible
The examples below show each of these types used for their main functions.
Statements
In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth. (Genesis 1:1 ULB)
Statements can also have other functions. (see Statements - Other Uses)
Questions
The speakers below used these questions to get information, and the people they were speaking to answered their questions.
Jesus said to them, "Do you believe that I can do this?" They said to him, "Yes, Lord." (Matthew 9:28 ULB)
The jailer...said, "Sirs, what must I do to be saved?" They said, "Believe in the Lord Jesus, and you will be saved, you and your house." (Acts 16:29-31 ULB)
Questions can also have other functions. (see Rhetorical Question)
Imperative Sentences
There are different kinds of imperative sentences: commands, instructions, suggestions, invitations, requests, and wishes.
With a command, the speaker uses his authority and tells someone to do something.
Rise up, Balak, and hear. Listen to me, you son of Zippor. (Numbers 23:18 ULB)
With an instruction, the speaker tells someone how to do something.
...but if you want to enter into life, keep the commandments. ... If you wish to be perfect, go, sell what you have, and give it to the poor, and you will have treasure in heaven. (Matthew 19:17, 21 ULB)
With a suggestion, the speaker tells someone something to do or not do that he thinks might help that person. In the example below, it is best for both blind men if they do not try to lead each other.
A blind man should not try to lead another blind man. If he did, they both would fall into a hole! ( Luke 6:39 UDB)
Speakers may intend to be part of the group that does what is suggested. In Genesis 11, the people were saying that it would be good for them all to make bricks together.
They said to one another, "Come, let us make bricks and bake them thoroughly." (Genesis 11:3 ULB)
With an invitation, the speaker uses politeness or friendliness to suggest that someone do something if he wants. This is usually something that the speaker thinks the listener will enjoy.
Come with us and we will do you good. (Numbers 10:29)
With a request, the speaker uses politeness to say that he wants someone to do something. This may include the word 'please' to make it clear that it is a request and not a command. This is usually something that would benefit the speaker.
Give us today our daily bread. (Matthew 6:11 ULB)
Please excuse me. (Luke 14:18 ULB)
With a wish a person expresses what they want to happen. In English they often start with the word "may" or "let."
In Genesis 28, Isaac told Jacob what he wanted God to do for him.
May God Almighty bless you, make you fruitful and multiply you. (Genesis 28:3 ULB)
In Genesis 9, Noah said what he wanted to happen to Canaan.
Cursed be Canaan. May he be a servant to his brothers' servants. (Genesis 9:25 ULB)
In Genesis 21, Hagar expressed her strong desire not to see her son die, and then she moved away so that she would not see him die.
Let me not look upon the death of the child. (Genesis 21:16 ULB)
Imperative sentences also have other functions. (see Imperatives - Other Uses)
Exclamations
Exclamations express strong feeling. In the ULB and UDB, they usually have an exclamation mark (!) at the end.
Save us, Lord; we are about to die! (Matthew 8:25 ULB)
(See Exclamations for other ways that exclamations are shown and ways to translate them.)
Translation Strategies
- Use your language's ways of showing that a sentence has a particular function.
-
When a sentence in the Bible has a sentence type that your language would not use for the sentence's function, see the pages below for translation strategies.
Statements - Other Uses
This page answers the question: What other uses are there for statements?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Normally statements are used to give information. But sometimes they are used in the Bible for other functions.
Reason this is a translation issue
Some languages would not use a statement for some of the functions that statements are used for in the Bible.
Examples from the Bible
Statements are normally used to give information. All of the sentences in John 1:6-8 below are statements, and their function is to give information.
There was a man who was sent from God, whose name was John. He came as a witness to testify about the light, that all might believe through him. John was not the light, but came that he might testify about the light. (John 1:6-8 ULB)
A statement can also be used as a command to tell someone what to do. In the examples below, the high priest used statements with the verb "will" to tell people what to do.
He commanded them, saying, "This is what you must do. A third of you who come on the Sabbath will keep watch over the king's house, and a third will be at the Sur Gate, and a third at the gate behind the guardhouse." (2 Kings 11:5 ULB)
A statement can also be used to give instructions. The speaker below was not just telling Joseph about something Joseph would do in the future; he was telling Joseph what he needed to do.
She will give birth to a son, and you will call his name Jesus, for he will save his people from their sins. (Matthew 1:21 ULB)
A statement can also be used to make a request. The man with leprosy was not just saying what Jesus was able to do. He was also asking Jesus to heal him.
Behold, a leper came to him and bowed before him, saying, "Lord, if you are willing, you can make me clean." (Matthew 8:2 ULB)
A statement can also be used to perform something. By telling Adam that the ground was cursed because of him, God actually cursed it.
... cursed is the ground because of you; (Genesis 3:17 ULB)
By telling a man that his sins were forgiven, Jesus forgave the man's sins.
Seeing their faith, Jesus said to the paralyzed man, "Son, your sins are forgiven." (Luke 2:5 ULB)
Translation Strategies
- If the function of a statement would not be understood correctly in your language, use a sentence type that would express that function.
- If the function of a statement would not be understood correctly in your language, add a sentence type that would express that function.
- If the function of a statement would not be understood correctly in your language, use a verb form that would express that function.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If the function of a statement would not be understood correctly in your language, use a sentence type that would express that function.
- She will give birth to a son, and you will call his name Jesus, for he will save his people from their sins. (Matthew 1:21 ULB) The phrase "you will call his name Jesus" is an instruction. It can be translated using the sentence type of a normal instruction.
- She will give birth to a son. Name him Jesus, because he will save his people from their sins.
- She will give birth to a son, and you will call his name Jesus, for he will save his people from their sins. (Matthew 1:21 ULB) The phrase "you will call his name Jesus" is an instruction. It can be translated using the sentence type of a normal instruction.
-
If the function of a statement would not be understood correctly in your language, add a sentence type that would express that function.
- Lord, if you are willing, you can make me clean. (Matthew 8:2 ULB) The function of "you can make me clean" is to make a request. In addition to the statement, a request can be added.
- Lord, if you are willing, you can make me clean. Please do so.
- Lord, if you are willing, please make me clean. I know you can do so.
- Lord, if you are willing, you can make me clean. (Matthew 8:2 ULB) The function of "you can make me clean" is to make a request. In addition to the statement, a request can be added.
-
If the function of a statement would not be understood correctly in your language, use a verb form that would express that function.
-
She will give birth to a son, and you will call his name Jesus, for he will save his people from their sins. (Matthew 1:21 ULB)
- She will give birth to a son, and you must call his name Jesus, for he will save his people from their sins.
-
Son, your sins are forgiven. Luke 2:5 ULB)
- Son, I forgive your sins.
- Son, God has forgiven your sins.
-
Imperatives - Other Uses
This page answers the question: What other uses are there for imperative sentences in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Imperative sentences are mainly used to express a desire or requirement that someone do something. Sometimes imperative sentences in the Bible have other uses.
Reason this is a translation issue
Some languages would not use an imperative sentence for some of the functions that they are used for in the Bible.
Examples from the Bible
Speakers often use imperative sentences to tell or ask their listeners to do something. In Genesis 2, God spoke to Isaac and told him not to go to Egypt but to live where God would tell him to live.
Now Yahweh appeared to him and said, "Do not go down to Egypt; live in the land that I tell you to live in. (Genesis 26:2 ULB)
Sometimes imperative sentences in the Bible have other uses.
Imperatives that make things happen
God can make things happen by commanding that they happen. Jesus healed a man by commanding that the man be healed. The man could not do anything to obey the command, but Jesus caused him to be healed by commanding it. ("Be clean" means "Be healed.")
"I am willing. Be clean." Immediately he was cleansed of his leprosy. (Matthew 8:3 ULB)
In Genesis 1, God commanded that there should be light, and by commanding it, he caused it to exist. Some languages, such as the Hebrew of the Bible, have commands that are in the third person. English does not do that, and so it must turn the third-person command into a general second-person command, as in the ULB:
God said, "Let there be light," and there was light. (Genesis 1:3 ULB)
Languages that have third-person commands can follow the original Hebrew, which translates into English as something like, "light must be."
Imperatives that function as blessings
In the Bible, God blesses people by using imperatives. This indicates what his will is for them.
God blessed them and said to them, "Be fruitful, and multiply. Fill the earth, and subdue it. Have dominion over the fish of the sea, over the birds of the sky, and over every living thing that moves upon the earth."
Imperatives that function as conditions
An imperative sentence can also be used to tell the condition under which something will happen. The proverbs mainly tell about life and things that often happen. The purpose of Proverbs 4:6 below is not primarily to give a command, but to teach what people can expect to happen if they love wisdom.
... do not abandon wisdom and she will watch over you; love her and she will keep you safe. (Proverbs 4:6 ULB)
The purpose of Proverbs 22:6 below is teach what people can expect to happen if they teach their children the way they should go.
Teach a child the way he should go, and when he is old he will not turn away from that instruction. (Proverbs 22:6 ULB)
Translation Strategies
- If people would not use an imperative sentence for one of the functions in the Bible, try using a statement instead.
- If people would not understand that a sentence is used to cause something to happen, add a connecting word like "so" to show that what happened was a result of what was said.
- If people would not use a command as a condition, translate it as a statement with the words "if" and "then."
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If people would not use an imperative sentence for one of the functions in the Bible, try using a statement instead.
-
Be clean. (Matthew 8:3 ULB)
- "You are now clean."
- "I now cleanse you."
-
God said, "Let there be light," and there was light. (Genesis 1:3 ULB)
- God said, "There is now light" and there was light.
-
God blessed them and said to them, "Be fruitful, and multiply. Fill the earth, and subdue it. Have dominion over the fish of the sea, over the birds of the sky, and over every living thing that moves upon the earth." (Genesis 1:3 ULB)
- God blessed them and said to them, "My will for you is that you be fruitful, and multiply. Fill the earth, and subdue it. I want you to have dominion over the fish of the sea, over the birds of the sky, and over every living thing that moves upon the earth."
-
-
If people would not understand that a sentence is used to cause something to happen, add a connecting word like "so" to show that what happened was a result of what was said.
- God said, "Let there be light," and there was light. (Genesis 1:3 ULB)
- God said, 'Let there be light,' so there was light.
- God said, "Light must be;" as a result, there was light.
- God said, "Let there be light," and there was light. (Genesis 1:3 ULB)
-
If people would not use a command as a condition, translate it as a statement with the words "if" and "then."
Teach a child the way he should go,
and when he is old he will not turn away from that instruction. (Proverbs 22:6 ULB)
Translated as:
"If you teach a child the way he should go,
then when he is old he will not turn away from that instruction."
Exclamations
This page answers the question: What are ways of translating exclamations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Exclamations are words or sentences that show strong feeling such as surprise, joy, fear, or anger. In the ULB and UDB, they usually have an exclamation mark (!) at the end. The mark shows that it is an exclamation. The situation and the meaning of what the people say helps us understand what feelings they were expressing. In the example below from Matthew 8, the speakers were terribly afraid. In the example from Matthew 9, the speakers were amazed, because something happened that they had never seen before.
Save us, Lord; we are about to die! (Matthew 8:25 ULB)
When the demon had been driven out, the mute man spoke. The crowds were astonished and said, "This has never been seen before in Israel!" (Matthew 9:33 ULB)
Reason this is a translation issue
Languages have different ways of showing that a sentence communicates strong emotion.
Examples from the Bible
Some exclamations have a word that shows feeling. The sentences below have "Oh" and "Ah." The word "oh" here shows the speaker's amazement.
Oh, the depth of the riches both of the wisdom and the knowledge of God! (Romans 11:33 ULB)
The word "Ah" below shows that Gideon was very frightened.
Gideon understood that this was the angel of Yahweh. Gideon said, "Ah, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!" (Judges 6:22 ULB)
Some exclamations start with a question word such as "how" or "why," even though they are not questions. The sentence below shows that the speaker is amazed at how unsearchable God's judgments are.
How unsearchable are his judgments, and his ways beyond discovering! (Romans 11:33 ULB)
Some exclamations in the Bible do not have a main verb. The exclamation below shows that the speaker is disgusted with the person he is speaking to.
You worthless person! (Matthew 5:22 ULB)
Translation Strategies
- If an exclamation in your language needs a verb, add one. Often a good verb is "is" or "are."
- Use an exclamation word from your language that shows the strong feeling.
- Translate the exclamation word with a sentence that shows the feeling.
- Use a word that emphasizes the part of the sentence that brings about the strong feeling.
- If the strong feeling is not clear in the target language, then tell how the person felt.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If an exclamation in your language needs a verb, add one. Often a good verb is "is" or "are."
-
You worthless person! (Matthew 5:22 ULB)
- "You are such a worthless person!"
-
Oh, the depth of the riches both of the wisdom and the knowledge of God! (Romans 11:33 ULB)
- "Oh, the riches of the wisdom and the knowledge of God are so deep!"
-
-
Use an exclamation word from your language that shows the strong feeling. The word "wow" below shows that they were astonished. The expression "Oh no" shows that something terrible or frightening has happened.
-
They were absolutely astonished, saying, "He has done everything well. He even makes the deaf to hear and the mute to speak." (Mark 7:36 ULB)
- "They were absolutely astonished, saying, "Wow! He has done everything well. He even makes the deaf to hear and the mute to speak." "
-
Ah, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face! (Judges 6:22 ULB)
- "Oh no, Lord Yahweh! I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!"
-
-
Translate the exclamation word with a sentence that shows the feeling.
- Ah, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face! (Judges 6:22 ULB)
- Lord Yahweh, what will happen to me? For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!"
- Help, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!
- Ah, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face! (Judges 6:22 ULB)
-
Use a word that emphasizes the part of the sentence that brings about the strong feeling.
- How unsearchable are his judgments, and his ways beyond discovering! (Romans 11:33 ULB)
- "His judgements are so unsearchable and his ways are far beyond discovering!"
- How unsearchable are his judgments, and his ways beyond discovering! (Romans 11:33 ULB)
-
If the strong feeling is not clear in the target language, then tell how the person felt.
- Gideon understood that this was the angel of Yahweh. Gideon said, "Ah, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!" (Judges 6:22 ULB)
- "Gideon understood that this was the angel of Yahweh. He was terrified and said, "Ah, Lord Yahweh! I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!" (Judges 6:22 ULB)
- Gideon understood that this was the angel of Yahweh. Gideon said, "Ah, Lord Yahweh! For I have seen the angel of Yahweh face to face!" (Judges 6:22 ULB)
Quotes
Quotations and Quote Margins
This page answers the question: What are quote margins and where should I put them?
Description
When saying that someone said something, we often tell who spoke, whom they spoke to, and what they said. The information about who spoke and whom they spoke to is called the quote margin. What the person said is the quotation. (This is also called a quote.) In some languages the quote margin may come first, last, or even in between two parts of the quotation.
The quote margins are underlined below.
- She said, "The food is ready. Come and eat."
- "The food is ready. Come and eat," she said.
- "The food is ready," she said. "Come and eat."
Also in some languages, the quote margin may have more than one verb meaning "said."
But his mother answered and said, "No, instead he will be called John." (Luke 1:60 ULB)
When writing that someone said something, some languages put the quote (what was said) in quotation marks called inverted commas (" "). Some languages use other symbols around the quotation, such as these angle quote marks (« »), or something else.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Translators need to put the quote margin where it is most clear and natural in their language.
- Translators need to decide whether they want the quote margin to have one or two verbs meaning "said."
- Translators need to decide which marks to use around the quotation.
Examples from the Bible
Quote margin before the quote
Zechariah said to the angel, "How will I know this will happen? For I am an old man, and my wife also is very old." (Luke 1:18 ULB)
Then some tax collectors also came to be baptized, and they said to him, "Teacher, what must we do?" (Luke 3:12 ULB)
He said to them, "Do not collect more money than you are supposed to." (Luke 3:13 ULB)
Quote margin after the quote
Yahweh relented concerning this. "It will not happen," he said. (Amos 7:3 ULB)
Quote margin between two parts of the quote
"I will hide my face from them," he said, "and I will see what their end will be; for they are a perverse generation, children who are unfaithful." (Deuteronomy 32:20 ULB)
"Therefore, those who can," he said, "should go there with us. If there is something wrong with the man, you should accuse him." (Acts 25:5 ULB)
"For look, days are coming"—this is Yahweh's declaration—"when I will restore the fortunes of my people, Israel" (Jeremiah 30:3 ULB)
Translation Strategies
- Decide where to put the quote margin.
- Decide whether to use one or two words meaning "said."
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Decide where to put the quote margin.
- "Therefore, those who can," he said, "should go there with us. If there is something wrong with the man, you should accuse him." (Acts 25:5 ULB)
- He said, "Therefore, those who can should go there with us. If there is something wrong with the man, you should accuse him."
- "Therefore, those who can should go there with us. If there is something wrong with the man, you should accuse him," he said.
- "Therefore, those who can should go there with us," he said. "If there is something wrong with the man, you should accuse him."
- "Therefore, those who can," he said, "should go there with us. If there is something wrong with the man, you should accuse him." (Acts 25:5 ULB)
-
Decide whether to use one or two words meaning "said."
- But his mother answered and said, "No, instead he will be called John." (Luke 1:60 ULB)
- But his mother replied, "No, instead he will be called John."
- But his mother said, "No, instead he will be called John."
- But his mother answered like this, "No, instead he will be called John," she said.
- But his mother answered and said, "No, instead he will be called John." (Luke 1:60 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Direct and Indirect Quotations
This page answers the question: What are direct and indirect quotations?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
There are two kinds of quotations: direct quotation and indirect quotation.
A direct quotation occurs when someone reports what another person said from the viewpoint of that original speaker. People usually expect that this kind of quotation will represent the original speaker's exact words. In the example below, John would have said "I" when referring to himself, so the narrator, who is reporting John's words, uses the word "I" in the quotation to refer to John. To show that these are John's exact words, many languages put the words between quotation marks:"".
- John said, "I do not know at what time I will arrive."
An indirect quotation occurs when a speaker reports what someone else said, but in this case, the speaker is reporting it from his own point of view instead of from the original person's point of view. This kind of quotation usually features changes in pronouns, and it often features changes in time, in word choices, and in length. In the example below, the narrator refers to John as "he" in the quotation and uses the word "would," to replace the future tense indicated by "will."
- John said that he did not know at what time he would arrive.
Why this is a translation issue
In some languages, reported speech can be expressed by either direct or indirect quotations. In other languages, it is more natural to use one rather than the other, or there is a certain meaning implied by using one rather than the other. So for each quotation, translators need to decide whether it is best to translate it as a direct quotation or an indirect quotation.
Examples from the Bible
The verses in the examples below contain both direct and indirect quotations. In the explanation below the verse, we have underlined the quotations.
He instructed him to tell no one, but told him, "Go on your way, and show yourself to the priest and offer a sacrifice for your cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them." (Luke 5:14 ULB)
- Indirect quote: He instructed him to tell no one,
- Direct quote: but told him, "Go on your way, and show yourself to the priest…"
Being asked by the Pharisees when the kingdom of God would come, Jesus answered them and said, "The kingdom of God is not something that can be observed. Neither will they say, 'Look here!' or, 'Look there!' because the kingdom of God is among you." (Luke 17:20-21 ULB)
- Indirect quote: Being asked by the Pharisees when the kingdom of God would come,
- Direct quote: Jesus answered them and said, "The kingdom of God is not something that can be observed. Neither will they say, 'Look here!' or, 'Look there!' because the kingdom of God is among you."
- Direct quotes: Neither will they say, 'Look here!' or, 'Look there!'
Translation Strategies
If the kind of quote used in the source text would work well in your language, consider using it. If the kind of quote used in that context is not natural for your language, follow these strategies.
- If a direct quote would not work well in your language, change it to an indirect quote.
- If an indirect quote would not work well in your language, change it to a direct quote.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If a direct quote would not work well in your language, change it to an indirect quote.
- He instructed him to tell no one, but told him, "Go on your way, and show yourself to the priest and offer a sacrifice for your cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them." (Luke 5:14 ULB)
- He instructed him to tell no one, but to go on his way, and to show himself to the priest and to offer a sacrifice for his cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them."
- He instructed him to tell no one, but told him, "Go on your way, and show yourself to the priest and offer a sacrifice for your cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them." (Luke 5:14 ULB)
-
If an indirect quote would not work well in your language, change it to a direct quote.
- He instructed him, to tell no one, but told him, "Go on your way, and show yourself to the priest and offer a sacrifice for your cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them." (Luke 5:14 ULB)
- He instructed him, "Tell no one. Just go on your way, and show yourself to the priest and offer a sacrifice for your cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them."
- He instructed him, to tell no one, but told him, "Go on your way, and show yourself to the priest and offer a sacrifice for your cleansing, according to what Moses commanded, for a testimony to them." (Luke 5:14 ULB)
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_quotations.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Quote Markings
This page answers the question: How can quotes be marked, especially when there are quotes within quotes?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some languages use quotation marks to mark off direct quotes from the rest of the text. English uses the mark " before and after a quote.
- John said, "I do not know when I will arrive."
Quotation marks are not used with indirect quotes.
- John said that he did not know when he would arrive.
When there are many layers of quotes inside of quotes, it might be hard for readers to understand who is saying what. Alternating two kinds of quote marks can help careful readers to keep track of them. In English the outermost quote has double quote marks, and the next quote inside has single marks. The next quote inside of that has double quote marks.
- Mary said, "John said, 'I do not know when I will arrive.' "
- Bob said, "Mary said, 'John said, "I do not know when I will arrive." ' "
Some languages use other kinds of quotation marks: Here are some examples: ‚ ' „ " ‹ › « » ⁊ — .
Examples from the Bible
The examples below show the kind of quote marking used in the ULB.
A quotation with only one layer
A first layer direct quote has double quote marks around it.
So the king replied, "That is Elijah the Tishbite." (2 Kings 1:8 ULB)
Quotations with two layers
A second layer direct quote has single quote marks around it. We have underlined it and the phrase for you to see it clearly.
They asked him, "Who is the man that said to you, 'Pick up your bed and walk'?" (John 5:12 ULB)
… he sent two of the disciples, saying, "Go into the next village. As you enter, you will find a colt that has never been ridden. Untie it and bring it to me. If any one asks you, 'Why are you untying it?' say, 'The Lord has need of it.' " (Luke 19:29-31 ULB)
A quotation with three layers
A third layer direct quote has double quote marks around it. We have underlined it for you to see it clearly.
Abraham said, "Because I thought, 'Surely there is no fear of God in this place, and they will kill me because of my wife.' Besides, she is indeed my sister, the daughter of my father, but not the daughter of my mother; and she became my wife. When God caused me to leave my father's house and travel from place to place, I said to her, 'You must show me this faithfulness as my wife: At every place where we go, say about me, "He is my brother." ' " (Genesis 20:10-13 ULB)
A quotation with four layers
A fourth layer direct quote has single quote marks around it. We have underlined it for you to see it clearly.
They said to him, "A man came to meet us who said to us, 'Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, "Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' " ' " (2 Kings 1:5-6 ULB)
Quote Marking Strategies
Here are some ways you may be able to help readers see where each quote starts and ends so they can more easily know who said what.
- Alternate two kinds of quote marks to show layers of direct quotation. English alternates double quote marks and single quote marks.
- Translate one or some of the quotes as indirect quotes in order to use fewer quote marks, since indirect quotes do not need them. (see Direct and Indirect Quotations)
- If a quotation is very long and has many layers of quotation in it, indent the main overall quote, and use quote marks only for the direct quotes inside of it.
Examples of Quote Marking Strategies Applied
- Alternate two kinds of quote marks to show layers of direct quotation as shown in the ULB text below.
They said to him, "A man came to meet us who said to us, 'Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, "Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' " ' " (2 Kings 1:6 ULB)
- Translate one or some of the quotes as indirect quotes in order to use fewer quote marks, since indirect quotes do not need them. In English the word "that" can introduce an indirect quote. In the example below, everything after the word "that" is an indirect quote of what the messengers said to the king. Within that indirect quote, there are some direct quotes marked with " and '.
They said to him, "A man came to meet us who said to us, 'Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, "Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' " ' " (2 Kings 1:6 ULB)
-
They told him that a man came to meet them who said to them, "Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, 'Yahweh says this: "Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die." ' "
-
If a quotation is very long and has many layers of quotation in it, indent the main overall quote, and use quote marks only for the direct quotes inside of it.
They said to him, "A man came to meet us who said to us, 'Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, "Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' " ' " (2 Kings 1:6 ULB)
- They said to him,
- A man came to meet us who said to us, "Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, 'Yahweh says this: "Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die." ' "
Next we recommend you learn about:
Quotes Within Quotes
This page answers the question: What is a quote within a quote, and how can I help the readers understand who is saying what?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
A quotation may have a quote within it, and quotes that are inside of other quotes can also have quotes within them. When a quote has quotes within it, we can talk about it having layers of quotation, and each of the quotes is a layer. When there are many layers of quotes inside of quotes, it can be hard for listeners and readers to know who is saying what. Some languages use a combination of direct quotes and indirect quotes to make it easier.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- When there is a quote within a quote, the listener needs to know who the pronouns refer to. For example if a quote that is inside a quote has the word "I," the listener needs to know whether "I" refers to the speaker of the inner quote or the outer quote.
- Some languages make this clear by using different kinds of quotes when there are quotes within quotes. They may use direct quotes for some and indirect quotes for others.
- Some languages do not use indirect quotes.
Examples from the Bible
A quotation with only one layer
But Paul said, "I was born a Roman citizen." (Acts 22:28 ULB)
Quotations with two layers
Jesus answered and said to them, "Be careful that no one leads you astray. For many will come in my name. They will say, 'I am the Christ,' and will lead many astray." Matthew 24:4-5 ULB
The outermost layer is what Jesus said to his disciples. The second layer is what other people will say.
Jesus answered, "You say that I am a king." (John 18:37 ULB)
The outermost layer is what Jesus said to Pilate. The second layer is what Pilate said about Jesus.
A quotation with three layers
Abraham said, "... I said to her, 'You must show me this faithfulness as my wife: At every place where we go, say about me, "He is my brother." ' " (Genesis 20:10-13 ULB)
The outermost layer is what Abraham said to Abimelech. The second layer is what Abraham had told his wife. The third layer is what he wanted his wife to say. (We have underlined the third layer.)
A quotation with four layers
They said to him, "A man came to meet us who said to us, 'Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, "Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' " ' " (2 Kings 1:6 ULB)
The outermost layer is what the messengers said to the king. The second layer is what the man who had met the messengers told them. The third is what that man wanted the messengers to say to the king. The fourth is what Yahweh said. (We have underlined the fourth layer.)
Translation Strategies
Some languages use only direct quotes. Other languages use a combination of direct quotes and indirect quotes. In those languages it might sound strange and perhaps even be confusing if there are many layers of direct quotes.
- Translate all of the quotes as direct quotes.
- Translate one or some of the quotes as indirect quotes. (see Direct and Indirect Quotations)
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Translate all of the quotes as direct quotes. In the example below we have underlined the indirect quotes in the ULB and the quotes that we have changed to direct quotes below it.
- Festus presented Paul's case to the king; he said, "A certain man was left behind here by Felix as a prisoner. ...I was puzzled about how to investigate this matter, and I asked him if he would go to Jerusalem to be judged there about these things. But when Paul called to be kept under guard for the Emperor's decision, I ordered him to be kept until I send him to Caesar." (Acts 25:14-21 ULB)
- Festus presented Paul's case to the king; he said, "A certain man was left behind here by Felix as a prisoner. ...I was puzzled about how to investigate this matter, and I asked him, 'Will you go to Jerusalem to be judged there about these things?' But when Paul said, 'I want to be kept under guard for the Emperor's decision,' I told the guard, 'Keep him under guard until I send him to Caesar.'"
- Festus presented Paul's case to the king; he said, "A certain man was left behind here by Felix as a prisoner. ...I was puzzled about how to investigate this matter, and I asked him if he would go to Jerusalem to be judged there about these things. But when Paul called to be kept under guard for the Emperor's decision, I ordered him to be kept until I send him to Caesar." (Acts 25:14-21 ULB)
-
Translate one or some of the quotes as indirect quotes. In English the word "that" can come before indirect quotes. It is underlined in the examples below. The pronouns that changed because of the indirect quote are also underlined.
-
Then Yahweh spoke to Moses and said, "I have heard the grumbling of the Israelites. Tell them, 'At twilight you will eat meat, and in the morning you will be filled with bread. Then you will know that I am Yahweh your God.' " (Exodus 16:11-12 ULB)
- Then Yahweh spoke to Moses and said, "I have heard the grumbling of the Israelites. Tell them that at twilight they will eat meat, and in the morning they will be filled with bread. Then they will know that I am Yahweh their God."
-
They said to him, "A man came to meet us who said to us, 'Go back to the king who sent you, and say to him, "Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' " ' " (2 Kings 1:6 ULB)
- They told him that a man had come to meet them who said to them, "Go back to the king who sent you, and tell him that Yahweh says this: 'Is it because there is no God in Israel that you sent men to consult with Baal Zebub, the god of Ekron? Therefore you will not come down from the bed to which you have gone up; instead, you will certainly die.' "
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Writing Styles (Discourse)
Types of Writing
This page answers the question: What are the different types of writing and the issues involved?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
There are different kinds or types of writing, and each type of writing has its own purpose. Because these purposes are different, the different kinds of writing are organized in different ways. They use different verbs, different kinds of sentences, and refer to the people and things that they write about in different ways. These differences help the reader to quickly know the purpose of the writing, and they work to communicate the author's meaning in the best way.
Types of Writing
The following are four basic types of writing that exist in every language. Each type of writing has a different purpose.
- Narrative or Parable - tells a story or event
- Explanatory - explains facts or teaches principles
- Procedural - tells how to do something
- Argumentative - tries to persuade someone to do something
Why This Is a Translation Issue
Every language has its own way of organizing these different types of writing. The translator must understand the type of writing that he is translating, understand how it is organized in the source language, and also know how his language organizes this kind of writing. He must put the writing into the form that his language uses for that type of writing so that people will understand it correctly. In every translation, the way that words, sentences, and paragraphs are arranged will affect how people will understand the message.
Writing Styles
The following are ways of writing that may combine with the four basic types above. These writing styles often present challenges in translation.
- Poetry - expresses ideas and feelings in a beautiful way
- Proverbs - briefly teaches a truth or wisdom
- Symbolic Language - uses symbols to represent things and events
- Symbolic Prophecy - uses symbolic language to show what will happen in the future
- Hypothetical Situations - tells about what would happen if something were real or expresses an emotion about something that is not real
Discourse Features
The differences between the different types of writing in a language can be called their discourse features. The purpose of a particular text will influence what kinds of discourse features are used. For example, in a narrative, discourse features would include:
- Telling about events that happen before and after other events
- Introducing people in the story
- Introducing new events in the story
- Conversation and the use of quotes
- Referring to people and things with nouns or pronouns
Languages have different ways of using these different discourse features. The translator will need to study the way his language does each of these things, so that his translation communicates the right message in a clear and natural way. Other types of writing have other discourse features.
Specific discourse issues
- Introduction of a New Event - Phrases like "One day" or "It came about that" or "This is how it happened" or "Sometime after that" signal to the reader that a new event is about to be told.
- Introduction of New and Old Participants - Languages have ways of introducing new people and of referring to those people again.
- Background Information - An author may use background information for several reasons: 1) to add interest to the story, 2) to provide information that is important for understanding the story or 3) to explain why something in the story is important.
- Pronouns - When to Use Them - Languages have patterns for how frequently to use pronouns. If that pattern is not followed, wrong meaning can result.
- End of Story - Stories can end with various kinds of information. Languages have different ways of showing how that information is related to the story.
- Quotations and Quote Margins - Languages have different ways of reporting what someone said.
- Connecting Words - Languages have patterns for how to use connecting words (such as "and," "but," or "then").
Next we recommend you learn about:
- Background Information
- Connecting Words
- Introduction of a New Event
- Introduction of New and Old Participants
- Order of Events
- Poetry
- Proverbs
- Quotations and Quote Margins
- Symbolic Language
Background Information
This page answers the question: What is background information, and how can I show that some information is background information?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
When people tell a story, they normally tell the events in the order that they happened. This sequence of events makes up the storyline. The storyline is full of action verbs that move the story along in time. But sometimes a writer may take a break from the storyline and give some information to help his listeners understand the story better. This type of information is called background information. The background information might be about things that happened before the events he has already told about, or it might explain something in the story, or it might be about something that would happen much later in the story.
Example - The underlined sentences in the story below are all background information.
Peter and John went on a hunting trip because their village was going to have a a feast the next day. Peter was the best hunter in the village. He once killed three wild pigs in one day! They walked for hours through low bushes until they heard a wild pig. The pig ran, but they managed to shoot the pig and kill it. Then they tied up its legs with some rope they had brought with them, and carried it home on a pole. When they brought it to the village, Peter's cousin saw the pig and realized that it was his own pig. Peter had mistakenly killed his cousin's pig.
Background information often tells about something that had happened earlier or something that would happen much later. Examples of these are "their village was going to have a feast the next day" and "He once killed three wild pigs in one day," "that they had brought with them," and "Peter had mistakenly killed his cousins's pig.
Often background information uses "be" verbs like "was" and "were", rather than action verbs. Examples of these are "Peter was the best hunter in the village" and "it was his own pig."
Background information can also be marked with words that tell the reader that this information is not part of the event line of the story. In this story, some of these words are "because," "once," and "had."
A writer may use background information
- To help their listeners be interested in the story
- To help their listeners understand something in the story
- To help the listeners understand why something is important in the story
- To tell the setting of a story
- Setting includes:
- where the story takes place
- when the story takes place
- who is present when the story begins
- what is happening when the story begins
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Languages have different ways of marking background information and storyline information.
- Translators need to know the order of the events in the Bible, which information is background information, and which is storyline information.
- Translators will need to translate the story in a way that marks the background information in a way that their own readers will understand the order of events, which information is background information, and which is storyline information.
Examples from the Bible
Hagar gave birth to Abram's son, and Abram named his son, whom Hagar bore, Ishmael. Abram was eighty-six years old when Hagar bore Ishmael to Abram. (Genesis 16:16 ULB)
The first sentence tells about two events. Hagar gave birth and Abraham named his son. The second sentence is background information about how old Abram was when those things happened.
Now Jesus himself, when he began to teach, was about thirty years of age. He was the son (as was supposed) of Joseph, the son of Heli. (Luke 3:23 ULB)
The verses before this tell about when Jesus was baptized. This sentence introduces background information about Jesus' age and ancestors. The story starts up again in chapter 4 where it tells about Jesus going to the wilderness.
Now it happened on a Sabbath that Jesus was going through the grain fields and his disciples were picking the heads of grain, rubbing them between their hands, and eating the grain. But some of the Pharisees said... (Luke 6:1-2a ULB)
These verses give the setting of the story. The events took place in a grain field on the Sabbath day. Jesus, his disciples, and some Pharisees were there, and Jesus' disciples were picking heads of grain and eating them. The main action in the story starts with the sentence, "But some of the Pharisees said."
Translation Strategies
To keep translations clear and natural you will need to study how people tell stories in your language. Observe how your language marks background information. You may need to write down some stories in order to study this. Observe what kind of verbs your language uses for background information and what kinds of words or other markers signal that something is background information. Do these same things when you translate, so that your translation is clear and natural and people can understand it easily.
- Use your language's way of showing that certain information is background information.
- Reorder the information so that earlier events are mentioned first. (This is not always possible when the background information is very long.)
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Use your language's way of showing that certain information is background information. The examples below explain how this was done in the ULB English translations.
-
Now Jesus himself, when he began to teach, was about thirty years of age. He was the son (as was supposed) of Joseph, the son of Heli. (Luke 3:23 ULB) English uses the word "now" to show that there is some kind of change in the story. The verb "was" shows that it is background information.
-
With many other exhortations also, he preached good news to the people. John also rebuked Herod the tetrarch for marrying his brother's wife, Herodias, and for all the other evil things that Herod had done. But then Herod did another very evil thing. He had John locked up in prison. (Luke 3:18-20 ULB) The underlined phrases happened before John rebuked Herod. In English, the helping verb "had" in "had done" shows that Herod did those things before John rebuked him.
2) Reorder the information so that earlier events are mentioned first.
-
Hagar gave birth to Abram's son, and Abram named his son, whom Hagar bore, Ishmael. Abram was eighty-six years old when Hagar bore Ishmael to Abram. (Genesis 16:16 ULB)
- "When Abram was eighty-six years old, Hagar gave birth to his son, and Abram named his son Ishmael."
-
John also rebuked Herod the tetrarch for marrying his brother's wife, Herodias, and for all the other evil things that Herod had done. But then Herod did another very evil thing. He had John locked up in prison. (Luke 3:18-20) - The translation below reorders John's rebuke and Herod's actions.
- "Now Herod the tetrarch married his brother's wife, Herodias, and he did many other evil things, so John rebuked him. But then Herod did another very evil thing. He had John locked up in prison."
Next we recommend you learn about:
Connecting Words
This page answers the question: What are connecting words for, and how do I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Connecting words show how thoughts are related to other thoughts. They are also called conjunctions. This page is about connecting words that connect statements and groups of statements to others. Some examples of connecting words are: and, but, for, so, therefore, now, if, if only, since, then, when, while, whenever, because, yet, unless.
- It was raining, so I opened my umbrella.
- It was raining, but I did not have an umbrella. So I got very wet.
Sometimes people might not use a connecting word because they expect the readers to understand the relationship between the thoughts because of the context.
- It was raining. I did not have an umbrella. I got very wet.
Reason this is a translation issue
- Translators need to understand the meaning of a connecting word in the Bible and the relationship between the thoughts it is connecting.
- Each language has its own ways of showing how thoughts are related.
- Translators need to know how to help their readers understand the relationship between the thoughts in a way that is natural in their language.
Translation Principles
- Translators need to translate in a way that readers can understand the same relationship between thoughts that the original readers would have understood.
- Whether or not a connecting word is used is not as important as readers being able to understand the relationship between the ideas.
Examples from the Bible
I did not immediately consult with flesh and blood, nor did I go up to Jerusalem to those who had become apostles before me, but instead I went to Arabia and then returned to Damascus. Then after three years I went up to Jerusalem to visit Cephas, and I stayed with him fifteen days. (Galatians 1:16-18 ULB)
The word "but" introduces something that contrasts with what was said before. The contrast here is between what Paul did not do with what he did do. Here the word "then" introduces something Paul did after he returned to Damascus.
Therefore whoever breaks the least one of these commandments and teaches others to do so, will be called least in the kingdom of heaven. But whoever keeps them and teaches them will be called great in the kingdom of heaven. (Matthew 5:19 ULB)
The word "Therefore" links this section with the section before it, signalling that the section that came before gave the reason for this section. "Therefore" usually links sections larger than one sentence. The word "and" links only two actions within the same sentence, that of breaking commandments and teaching others. In this verse the word "But" contrasts what one group of people will be called in God's kingdom with what another group of people will be called.
We do not place a stumbling block in front of anyone, for we do not wish our ministry to be brought into disrepute. Instead, we prove ourselves by all our actions, that we are God's servants. (2 Corinthians 6:3-4 ULB)
Here the word "for" connects what follows as the reason for what came before; the reason that Paul does not place stumbling blocks is that he does not want his ministry brought into disrepute. "Instead" contrasts what Paul does (proving by his actions that he is God's servant) with what he said he does not do (placing stumbling blocks).
Translation Strategies
If the way the relationship between thoughts is shown in the ULB would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, then consider using it. If not, here are some other options.
- Use a connecting word (even if the ULB does not use one).
- Do not use a connecting word if it would be odd to use one and people would understand the right relationship between the thoughts without it.
- Use a different connecting word.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Use a connecting word (even if the ULB does not use one).
- Jesus said to them, "Come after me, and I will make you become fishers of men." Immediately they left the nets and went after him. (Mark 1:17-18 ULB) - They followed Jesus because he told them to. Some translators may want to mark this with "so."
- Jesus said to them, "Come after me, and I will make you become fishers of men." So immediately they left the nets and went after him.
2) Do not use a connecting word if it would be odd to use one and people would understand the right relationship between the thoughts without it.
- Therefore whoever breaks the least one of these commandments and teaches others to do so, will be called least in the kingdom of heaven. But whoever keeps them and teaches them will be called great in the kingdom of heaven. (Matthew 5:19 ULB) -
Some languages would prefer not to use connecting words here, because the meaning is clear without them and using them would be unnatural. They might translate like this:
-
Therefore whoever breaks the least one of these commandments, teaching others to do so as well, will be called least in the kingdom of heaven. Whoever keeps them and teaches them will be called great in the kingdom of heaven.
-
I did not immediately consult with flesh and blood, nor did I go up to Jerusalem to those who had become apostles before me, but instead I went to Arabia and then returned to Damascus. Then after three years I went up to Jerusalem to visit Cephas, and I stayed with him fifteen days. (Galatians 1:16-18 ULB) -
Some languages might not need the words "but" or "then" here.
- I did not immediately consult with flesh and blood, nor did I go up to Jerusalem to those who had become apostles before me. Instead I went to Arabia and then returned to Damascus. After three years I went up to Jerusalem to visit Cephas, and I stayed with him fifteen days.
3) Use a different connecting word.
-
Therefore whoever breaks the least one of these commandments and teaches others to do so, will be called least in the kingdom of heaven. But whoever keeps them and teaches them will be called great in the kingdom of heaven. (Matthew 5:19 ULB) Instead of a word like "therefore," a language might need a phrase to indicate that there was a section before it that gave the reason for the section that follows. Also, the word "but" is used here because of the contrast between the two groups of people. But in some languages, the word "but" would show that what comes after it is surprising because of what came before it. So "and" might be clearer for those languages.
- Because of that, whoever breaks the least one of these commandments and teaches others to do so, will be called least in the kingdom of heaven. And whoever keeps them and teaches them will be called great in the kingdom of heaven.
-
Since the captain could not tell anything because of all the noise, he ordered that Paul be brought into the fortress. (Acts 21:34 ULB) - Instead of starting the first part of the sentence with "since," some translators might prefer to start the second part of the sentence with "so" to show the same relationship.
- "The captain could not tell anything because of all the noise, so he ordered that Paul be brought into the fortress."
End of Story
This page answers the question: What kinds of information are given at the end of a story?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
There are different types of information that may be given at the end of a story. Often this is background information. This background information is different from the actions that make up the main part of the story. A book of the Bible is often made up of many smaller stories that are part of the larger story of the book itself. For example, the story of Jesus' birth is a smaller story in the larger story of the book of Luke. Each of these stories, whether large or small, can have background information at the end of it.
Different purposes for end of story information
- To summarize the story
- To give a comment about what happened in the story
- To connect a smaller story to the larger story it is a part of
- To tell the reader what happens to a specific character after the main part of the story ends
- To tell on-going action that continues after the main part of the story ends
- To tell what happens after the story as a result of the events that happened in the story itself
Reasons this is a translation issue
Different languages have different ways of presenting these kinds of information. If translators do not use their language's ways of doing this, readers may not know these things:
- That this information is ending the story
- What the purpose of the information is
- How the information is related to the story
Principles of translation
- Translate the particular kind of information at the end of a story the way your language expresses that kind of information.
- Translate it so that people will understand how it relates to the story it is part of.
- If possible, translate the end of the story in a way that people will know where that story ends and the next begins.
Examples from the Bible
- To summarize the story
Then the rest of the men should follow, some on planks, and some on other things from the ship. In this way it happened that all of us came safely to land. (Acts 27:44 ULB)
- To give a comment about what happened in the story
Many who practiced magical arts brought their books together and burned them in the sight of everyone. When they counted the value of them, it was fifty thousand pieces of silver. So the word of the Lord spread very widely in powerful ways. (Acts 19:19-20 ULB)
- To tell the reader what happens to a specific character after the main part of the story ends
Mary said,"My soul praises the Lord, and my spirit has rejoiced in God my savior..." Mary stayed with Elizabeth about three months and then returned to her house. (Luke 1:46-47, 56 ULB)
- To tell on-going action that continues after the main part of the story ends
All who heard it were amazed at what was spoken to them by the shepherds. But Mary kept thinking about all the things she had heard, treasuring them in her heart. (Luke 2:18-19 ULB)
- To tell what happens after the story as a result of the events that happened in the story itself
"Woe to you teachers of Jewish laws, because you have taken away the key of knowledge; you do not enter in yourselves, and you hinder those who are entering." After Jesus left there, the scribes and the Pharisees opposed him and argued with him about many things, trying to trap him in his own words. (Luke 11:52-54 ULB)
Hypothetical Situations
This page answers the question: What is a hypothetical situation?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
"If the sun stopped shining…", "What if the sun stopped shining…", "Suppose the sun stopped shining…", "If only the sun had not stopped shining." We use such expressions to set up hypothetical situations, imagining what might have happened or what could happen in the future but probably will not. We also use them to express regret or wishes. These occur often in the Bible. We need to translate them in a way that people will know that the event did not actually happen, and that they will understand why the event was imagined.
Description
Hypothetical situations are situations that are not real. They can be in the past, present, or future. Hypothetical situations in the past and present have not happened, and ones in the future are not expected to happen.
People sometimes tell about conditions and what would happen if those conditions were met, but they know that these things have not happened or probably will not happen. (The conditions are the phrase that start with "if.")
- If he had known about the party, he would have come to it. (But he did not come.)
- If he knew about the party, he would be here. (But he is not here.)
- If he knew about the party, he would come to it. (But he probably will not come.)
People sometimes express wishes about things that have not happened or that are not expected to happen.
- I wish he had come.
- I wish he were here.
- I wish he would come.
People sometimes express regrets about things that have not happened or that are not expected to happen.
- If only he had come.
- If only he were here.
- If only he would come.
Reason this is a translation issue
- Translators need to recognize the different kinds of hypothetical situations in the Bible.
- Translators need to know their own language's ways of talking about different kinds of hypothetical situations.
Examples from the Bible
- Hypothetical situations in the past
"Woe to you, Chorazin! Woe to you, Bethsaida! If the mighty deeds had been done in Tyre and Sidon which were done in you, they would have repented long ago in sackcloth and ashes." (Matthew 11:21 ULB)
Here in Matthew 11:21 Jesus said that if the people living in the ancient cities of Tyre and Sidon had been able to see the miracles that he performed, they would have repented long ago. The people of Tyre and Sidon did not actually see his miracles and repent. He said this to rebuke the people of Chorazin and Bethsaida who had seen his miracles yet did not repent.
Martha then said to Jesus, "Lord, if you had been here, my brother would not have died." (John 11:21 ULB)
Martha said this to express her wish that Jesus had come sooner. But Jesus did not come sooner, and her brother did die.
- Hypothetical situations in the present
Also, no man puts new wine into old wineskins. If he did that, the new wine would burst the skins, and the wine would be spilled, and the wineskins would be destroyed. (Luke 5:37 ULB)
Jesus told about what would happen if a person were to put new wine into old wineskins. But no one would do that. He used this imaginary situation as an example to show that there are times when it is unwise to mix new things with old things. He did this so that people could understand why his disciples were not fasting as people traditionally did.
Jesus said to them, "What man would there be among you, who, if he had just one sheep, and if this sheep fell into a deep hole on the Sabbath, would not grasp hold of it and lift it out? (Matthew 12:11 ULB)
Jesus asked the religious leaders what they would do on the Sabbath if one of their sheep fell into a hole. He was not saying that their sheep would fall into a hole. He used this imaginary situation to show them that they were wrong to judge him for healing people on the Sabbath.
- Hypothetical situation in the future
Unless those days are shortened, no flesh would be saved; but for the sake of the elect, those days will be shortened. (Matthew 24:22 ULB)
Jesus was talking about a future time when very bad things would happen. He told what would happen if those days of trouble were to last a long time. He did this to show about how bad those days will be - so bad that if they lasted a long time, no one would be saved. But then he clarified that God will shorten those days of trouble, so that the elect (those he has chosen) will be saved.
- Expressing emotion about a hypothetical situation
Regrets and wishes are very similar.
The Israelites said to them, "If only we had died by Yahweh's hand in the land of Egypt when we were sitting by the pots of meat and were eating bread to the full. For you have brought us out into this wilderness to kill our whole community with hunger." (Exodus 16:3 ULB)
Here the Israelites were afraid they would have to suffer and die of hunger in the wilderness, and so they wished that they had stayed in Egypt and died there with full stomachs. They were complaining, expressing regret that this had not happened.
I know what you have done, and that you are neither cold nor hot. I wish that you were either cold or hot! (Revelation 3:15 ULB)
Jesus wished that the people were either hot or cold, but they are neither. He was rebuking them, expressing anger at this.
Translation Strategies
Know how people speaking your language show:
- that something could have happened, but did not.
- that something could be true now, but is not.
- that something could happen in the future, but will not unless something changes.
- that they wish for something, but it does not happen.
- that they regret that something did not happen.
Use your language's ways of showing these kinds of things.
You may also want to watch the video at http://ufw.io/figs_hypo.
Introduction of a New Event
This page answers the question: How do we introduce a new event in a story?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
When people tell a story, they tell about an event or a series of events. Often they put certain information at the beginning of the story, such as who the story is about, when it happened, and where it happened. This information that the writer gives before the events of the story begin is called the setting of the story. Some new events in a story also have a setting because they might involve new people, new times, and new places. In some languages people also tell if they saw the event or heard about it from someone else.
When your people tell about events, what information do they give at the beginning? Is there a certain order that they put it in? In your translation, you will need to follow the way your language introduces new information at the beginning of a story or a new event rather than the way the source language did that. In this way your translation will sound natural and communicate clearly in your language.
Examples from the Bible
In the days of Herod, king of Judea, there was a certain priest named Zechariah, from the division of Abijah. His wife was from the daughters of Aaron, and her name was Elizabeth. (Luke 1:5 ULB)
The verses above introduce a story about Zechariah. The first underlined phrase tells when it happened, and the next two underlined phrases introduce the main people. The next two verses go on to explain that Zechariah and Elizabeth were old and did not have any children. All of this is the setting. Then the phrase "One day" in Luke 1:8 helps to introduce the first event in this story:
One day while Zechariah was performing his duties as a priest before God in the order of his division, the priests followed their custom and chose him by lot to enter the temple of the Lord and burn incense. (Luke 1:8-9 ULB)
The birth of Jesus Christ happened in the following way. His mother Mary was engaged to marry Joseph, but before they came together, she was found to be pregnant by the Holy Spirit. (Matthew 1:18 ULB)
The underlined sentence above makes it explicit that a story about Jesus is being introduced. The story will tell about how the birth of Jesus happened.
After Jesus was born in Bethlehem of Judea in the days of Herod the king, learned men from the east arrived in Jerusalem saying,... (Matthew 2:1 ULB)
The underlined phrase above shows that the events concerning the learned men happened after Jesus was born.
In those days John the Baptist came preaching in the wilderness of Judea saying, … (Matthew 3:1-22 ULB)
The underlined phrase above shows that John the Baptist came preaching around the time of the previous events. It is probably very general and refers to when Jesus lived in Nazareth.
Then Jesus came from Galilee to the Jordan River to be baptized by John. (Matthew 3:13 ULB)
The word "then" shows that Jesus came to the Jordan River some time after the events in the previous verses.
Now there was a Pharisee whose name was Nicodemus, a member of the Jewish Council. This man came to Jesus at night time (John 3:1-2 ULB)
The author first introduced the new person and then told about what he did and when he did it. In some languages it might be more natural to tell about the time first.
6Noah was six hundred years old when the flood came upon the earth. 7Noah, his sons, his wife, and his sons' wives went into the ark together because of the waters of the flood. (Genesis 7:6-7 ULB)
Verse 6 is a summary of the events that happen in the rest of chapter 7. Chapter 6 already told about how God told Noah that there would be a flood, and how Noah prepared for it. Chapter 7 verse 6 introduces the part of the story that tells about Noah and his family and the animals going into the ship, the rain starting, and the rain flooding the earth. Some languages might need to make it clear that this verse simply introduces the event, or move this verse after verse 7. Verse 6 is not one of the events of the story. The people went into the ship before the flood came.
Translation Strategies
If the information given at the beginning of a new event is clear and natural to your readers, consider translating it as it is in the ULB or UDB. If not, consider one of these strategies.
- Put the information that introduces the event in the order that your people put it.
- If readers would expect certain information but it is not in the Bible, consider using an indefinite word or phrase to fill in that information, such as: "another time" or "someone."
- If the introduction is a summary of the whole event, use your language's way of showing that it is a summary.
- If it would be strange in the target language to give a summary of the event at the beginning, show that the event would actually happen later in the story.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Put the information that introduces the event in the order that your people put it.
-
Now there was a Pharisee whose name was Nicodemus, a member of the Jewish Council. This man came to Jesus at night time and said to him ... (John 3:1,2)
- There was a man whose name was Nicodemus. He was a Pharisee and a member of the Jewish Council. One night he came to Jesus and said…
- One night a man named Nicodemus, who was a Pharisee and a member of the Jewish Council, came to Jesus and said ...
-
As he passed by, he saw Levi the son of Alpheus, who was sitting at the tax collecting place, and he said to him ... (Mark 2:14 ULB)
- As he passed by, Levi the son of Alpheus was sitting at the tax collecting place. Jesus saw him and and said to him ...
- As he passed by, there was a man sitting at the tax collecting place. His name was Levi, and he was the son of Alpheus. Jesus saw him and said to him ...
- As he passed by, there was a tax collector sitting at the tax collecting place. His name was Levi, and he was the son of Alpheus. Jesus saw him and said to him ...
-
-
If readers would expect certain information but it is not in the Bible, consider using an indefinite word or phrase such as: another time, someone.
-
Noah was six hundred years old when the flood came upon the earth. (Genesis 7:6 ULB) - If people expect to be told something about when the new event happened, the phrase "after that" can help them see that it happened after the events already mentioned.
- After that, when Noah was six hundred years old, the flood came upon the earth.
-
Again he began to teach beside the lake. (Mark 4:1 ULB) - In chapter 3 Jesus was teaching at someone's house. Readers may need to be told that this new event happened at another time, or that Jesus actually went to the lake.
- Another time Jesus began to teach people again beside the lake.
- Jesus went to the lake and began to teach people again there.
-
-
If the introduction is a summary of the whole event, use your language's way of showing that it is a summary.
- Noah was six hundred years old when the flood came upon the earth. (Genesis 7:6 ULB)
- Now this is what happened when Noah was six hundred years old and the flood came upon the earth.
- This part tells about what happened when the flood came upon the earth. It happened when Noah was six hundred years old.
- Noah was six hundred years old when the flood came upon the earth. (Genesis 7:6 ULB)
-
If it would be strange in the target language to give a summary of the event at the beginning, show that the event would actually happen later in the story.
- Noah was six hundred years old when the flood came upon the earth. Noah, his sons, his wife, and his sons' wives went into the ark together because of the waters of the flood. (Genesis 7:6-7 ULB)
- Now this is what happened when Noah was six hundred years old. Noah, his sons, his wife, and his sons' wives went into the ark together because God had said that the waters of the flood would come.
- Noah was six hundred years old when the flood came upon the earth. Noah, his sons, his wife, and his sons' wives went into the ark together because of the waters of the flood. (Genesis 7:6-7 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Introduction of New and Old Participants
This page answers the question: Why cannot the readers of my translation understand who the author was writing about?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The first time that people or things are mentioned in a story, they are new participants. After that, whenever they are mentioned, they are old participants.
Now there was a Pharisee whose name was Nicodemus... This man came to Jesus at night time... Jesus replied to him (John 3:1)
The first underlined phrase introduces Nicodemus as a new participant. He is then referred to as "This man" and "him" when he is an old participant.
Reason this is a translation issue
In order to make your translation clear and natural, it is necessary to refer to the participants in such a way that people will know if they are new participants or participants that they have already read about. Different languages have different ways of doing this. You must follow the way that your language does this, not the way that the source language does this.
Examples from the Bible
New Participants
Often the most important new participant is introduced with a phrase that says that he existed, such as "There was a man" in the example below. The phrase "There was" tells us that this man existed. The word "a" in "a man" tells us that the author is speaking about him for the first time. The rest of the sentence tells where this man was from, who is family was, and what his name was.
There was a man from Zorah, of the family of the Danites, whose name was Manoah. (Judges 13:2 ULB)
A new participant who is not the most important one is often introduced in relation to the more important person who was already introduced. In the example below, Manoah's wife is simply referred to as "his wife." This phrase shows her relationship to him.
There was a man from Zorah, of the family of the Danites, whose name was Manoah. His wife was not able to become pregnant and so she had not given birth. (Judges 13:2 ULB)
Sometimes a new participant is introduced simply by name because the author assumes that the readers know who the person is. In the first verse of 1 Kings, the author assumes that his readers know who King David is, so there is no need to explain who he is.
When King David was very old, they covered him with blankets, but he could not keep warm. (1 Kings 1:1 ULB)
Old Participants
A person who has already been brought into the story can be referred to with a pronoun after that. In the example below, Manoah is referred to with the pronoun "his," and his wife is referred to with the pronoun "she".
His wife was not able to become pregnant and so she had not given birth. (Judges 13:2 ULB)
Old participants can also be referred to in other ways, depending on what is happening in the story. In the example below, the story is about bearing a son, and Manoah's wife is referred to with the noun phrase "the woman."
The angel of Yahweh appeared to the woman and said to her, (Judges 13:3 ULB)
If the old participant has not been mentioned for a while, or if there could be confusion between participants, the author may use the participant's name again. In the example below, Manoah is referred to with his name, which the author has not used since verse 2.
Then Manoah prayed to Yahweh... (Judges 13:8 ULB)
Some languages have something on the verb that tells something about the subject. In some of those languages people do not always use noun phrases or pronouns for old participants when they are the subject of the sentence. The marker on the verb gives enough information for the listener to understand who the subject is. (see Verbs)
Translation Strategies
- If the participant is new, use one of your language's ways of introducing new participants.
- If it is not clear to whom a pronoun refers, use a noun phrase or name.
- If an old participant is referred to by name or a noun phrase, and people wonder if this is another new participant, try using a pronoun instead. If a pronoun is not needed because people would understand it clearly from the context, then leave out the pronoun.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If the participant is new, use one of your language's ways of introducing new participants.
- Joseph, a Levite, a man from Cyprus, was given the name Barnabas by the apostles (that is, being interpreted, Son of encouragement). (Acts 4:36-37 ULB) - Starting the sentence with Joseph's name when he has not been introduced yet might be confusing in some languages.
- There was a man from Cyprus who was a Levite. His name was Joseph, and he was given the name Barnabas by the apostles (that is, being interpreted, Son of encouragement).
- There was a Levite from Cyprus whose name was Joseph. The apostles gave him the name Barnabas, which means Son of encouragement.
- Joseph, a Levite, a man from Cyprus, was given the name Barnabas by the apostles (that is, being interpreted, Son of encouragement). (Acts 4:36-37 ULB) - Starting the sentence with Joseph's name when he has not been introduced yet might be confusing in some languages.
-
If it is not clear who a pronoun refers to, use a noun phrase or name.
- It happened when he finished praying in a certain place, that one of his disciples said, "Lord, teach us to pray just as John taught his disciples." (Luke 11:1 ULB) - Since this is the first verse in a chapter, readers might wonder who "he" refers to.
- It happened when Jesus finished praying in a certain place, that one of his disciples said, "Lord, teach us to pray just as John taught his disciples.
- It happened when he finished praying in a certain place, that one of his disciples said, "Lord, teach us to pray just as John taught his disciples." (Luke 11:1 ULB) - Since this is the first verse in a chapter, readers might wonder who "he" refers to.
-
If an old participant is referred to by name or a noun phrase, and people wonder if this is another new participant, try using a pronoun instead. If a pronoun is not needed because people would understand it clearly from the context, then leave out the pronoun.
- Joseph's master took Joseph and put him in prison, in the place where all the king's prisoners were put, and Joseph stayed there. (Genesis 39:20 ULB) - Since Joseph is the main person in the story, some languages might find it unnatural or confusing to use his name so much. They might prefer a pronoun.
- Joseph's master took him and put him in prison, in the place where all the king's prisoners were put, and he stayed there in the prison.
- Joseph's master took Joseph and put him in prison, in the place where all the king's prisoners were put, and Joseph stayed there. (Genesis 39:20 ULB) - Since Joseph is the main person in the story, some languages might find it unnatural or confusing to use his name so much. They might prefer a pronoun.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Parables
This page answers the question: What is a parable?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
A parable is a short story that makes truth easy to understand and hard to forget.
Description
A parable is a short story that is told to teach a truth. Though the events in a parable could happen, they did not actually happen. They are told only to teach a truth. Parables rarely contain the names of specific people. (This may help you identify what is a parable and what is an account of a real event.) Parables often have figures of speech such as simile and metaphor.
Then he also told them a parable. "Can a blind person guide another blind person? If he did, they would both fall into a pit, would they not?" (Luke 6:39 ULB)
This parable teaches that if a person does not have spiritual understanding, he cannot help someone else to understand spiritual things.
Examples from the Bible
Neither do people light a lamp and put it under a basket, but rather, on the lampstand, and it shines for everyone in the house. Let your light shine before people in such a way that they see your good deeds and praise your Father who is in heaven. (Matthew 5:15-16 ULB)
This parable teaches us not to hide the way we live for God from other people.
Then Jesus presented another parable to them. He said, "The kingdom of heaven is like a mustard seed which a man took and sowed in his field. This seed is indeed the smallest of all other seeds. But when it has grown, it is greater than the garden plants and becomes a tree, so that the birds of the air come and nest in its branches." (Matthew 13:31-32 ULB)
This parable teaches that the kingdom of God may seem small at first, but it will grow and spread throughout the world.
Translation Strategies
- If a parable is hard to understand because it has unknown things in it, you can replace the unknown things with things that people in your culture know. However, be careful to keep the teaching the same. (See: Translate Unknowns)
- If the teaching of the parable is unclear, consider telling a little about what it teaches in the introduction, such as "Jesus told this story about being generous."
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If a parable is hard to understand because it has unknown things in it, you can replace the unknown things with things that people in your culture know. However, be careful to keep the teaching the same.
-
Jesus said to them, "Do you bring a lamp inside the house to put it under a basket, or under the bed? You bring it in and you put it on a lampstand". (Mark 4:21 ULB) - If people do not know what a lampstand is, you could substitute something else that people put a light on so it can give light to the house.
- Jesus said to them, "Do you bring a lamp inside the house to put it under a basket, or under the bed? You bring it in and you put it on a high shelf.
-
Then Jesus presented another parable to them. He said, "The kingdom of heaven is like a mustard seed which a man took and sowed in his field. This seed is indeed the smallest of all other seeds. But when it has grown, it is greater than the garden plants and becomes a tree, so that the birds of the air come and nest in its branches." (Matthew 13:31-32 ULB) - To sow seeds means to toss them so that they scatter on the ground. If people are not familiar with sowing, you can substitute planting.
- Then Jesus presented another parable to them. He said, "The kingdom of heaven is like a mustard seed which a man took and planted in his field. This seed is indeed the smallest of all other seeds. But when it has grown, it is greater than the garden plants and becomes a tree, so that the birds of the air come and nest in its branches."
-
-
If the teaching of the parable is unclear, consider telling a little about what it teaches in the introduction, such as "Jesus told this story about being generous."
-
Jesus said to them, "Do you bring a lamp inside the house to put it under a basket, or under the bed? You bring it in and you put it on a lampstand". (Mark 4:21 ULB)
- Jesus told them a parable about why they should witness openly. "Do you bring a lamp inside the house to put it under a basket, or under the bed? You bring it in and you put it on a lampstand." (Mark 4:21 ULB)
-
Then Jesus presented another parable to them. He said, "The kingdom of heaven is like a mustard seed which a man took and sowed in his field. This seed is indeed the smallest of all other seeds. But when it has grown, it is greater than the garden plants and becomes a tree, so that the birds of the air come and nest in its branches." (Matthew 13:31-32 ULB)
- Then Jesus presented another parable to them about how the Kingdom of God grows. He said, "The kingdom of heaven is like a mustard seed which a man took and sowed in his field. This seed is indeed the smallest of all other seeds. But when it has grown, it is greater than the garden plants and becomes a tree, so that the birds of the air come and nest in its branches."
-
Poetry
This page answers the question: What is poetry and how do I translate it into my language?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Poetry is one of the ways that people use the words and sounds of their language to make their speech and writing more beautiful and to express strong emotion. Through poetry, people can communicate deeper emotion than they can through simple non-poetic forms. Poetry gives more weight and elegance to statements of truth, such as proverbs, and is also easier to remember than ordinary speech.
Some things commonly found in poetry
- Many figures of speech such as Apostrophe.
- Parallel lines (see Parallelism and Parallelism with the Same Meaning)
- Repetition of some or all of a line
- Praise him, all his angels; praise him, all his angel armies. Praise him, sun and moon; praise him, all you shining stars. (Psalm 148:2-3 ULB)
- Lines of similar length.
- Love is patient and kind; love does not envy or boast; it is not arrogant or rude. (1 Corinthians 13:4 ULB)
- The same sound used at the end or at the beginning of two or more lines
- "Twinkle, twinkle little star. How I wonder what you are." (from an English rhyme)
- The same sound repeated many times
- "Peter, Peter, pumpkin eater" (from an English rhyme)
- Old words and expressions
- Dramatic imagery
- Different use of grammar - including:
- incomplete sentences
- lack of connective words
Some places to look for poetry in your language
- Songs, particularly old songs or songs used in children's games
- Religious ceremony or chants of priests or witch doctors
- Prayers, blessings, and curses
- Old legends
Elegant or fancy speech
Elegant or fancy speech is similar to poetry in that it uses beautiful language, but it does not use all of the language's features of poetry, and it does not use them as much as poetry does. Popular speakers in the language often use elegant speech, and this is probably the easiest source of text to study to find out what makes speech elegant in your language.
Reasons this is a translation issue:
- Different languages use poetry for different things. If a poetic form would not communicate the same meaning in your language you may need to write it without the poetry.
- In some languages, using poetry for a particular part of the Bible would make it much more powerful.
Examples from the Bible
The Bible uses poetry for songs, teaching, and prophecy. Almost all of the books of the Old Testament have poetry in them and many of the books are completely poetry.
for you saw my affliction;
you knew the distress of my soul. (Psalm 31:7 ULB)
This example of Parallelism with the Same Meaning has two lines that mean the same thing.
Yahweh, judge the nations;
vindicate me, Yahweh, because I am righteous and innocent, Most High.
This example of parallelism shows the contrast between what David wants God to do to him and what he wants God to do to the unrighteous nations. (see Parallelism)
Keep your servant also from arrogant sins;
let them not rule over me. (Psalm 19:13 ULB)
This example of personification speaks of sins as if they could rule over a person. (see Personification)
Oh, give thanks to Yahweh; for he is good, for his covenant faithfulness endures forever.
Oh, give thanks to the God of gods, for his covenant faithfulness endures forever.
Oh, give thanks to the Lord of lords, for his covenant faithfulness endures forever. (Psalm 136:1-3 ULB)
This example repeats the phrases "give thanks" and "his covenant faithfulness endures forever."
Translation Strategies
If the style of poetry that is used in the source text would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider using it. If not, here are some other ways of translating it.
- Translate the poetry using one of your styles of poetry.
- Translate the poetry using your style of elegant speech.
- Translate the poetry using your style of ordinary speech.
If you use poetry it may be more beautiful.
If you use ordinary speech it may be more clear.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
Blessed is the man who does not walk in the advice of the wicked,
or stand in the pathway with sinners,
or sit in the assembly of mockers.
But his delight is in the law of Yahweh,
and on his law he meditates day and night. (Psalm 1:1,2 ULB)
The following are examples of how people might translate Psalm 1:1,2.
1) Translate the poetry using one of your styles of poetry. (The style in this example has words that sound similar at the end of each line.)
"Happy is the person not encouraged to sin
Disrespect for God he will not begin
To those who laugh at God, he is no kin.
God is his constant delight
He does what God says is right
He thinks of it all day and night
2) Translate the poetry using your style of elegant speech.
- This is the kind of person who is truly blessed: the one who does not follow the advice of wicked people, or stop along the road to speak with sinners, or join the gathering of those who mock God. Rather he takes great joy in Yahweh's law, and he meditates on it day and night.
3) Translate the poetry using your style of ordinary speech.
- The people who do not listen to the advice of bad people are really happy. They do not spend time with people who continually do evil things or with those who do not respect God. They love to obey Yahweh's law, and they think about it all the time.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Proverbs
This page answers the question: What are proverbs, and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Proverbs are short sayings that give wisdom or teach a truth. People enjoy proverbs because they give a lot of wisdom in few words. Proverbs in the Bible often use metaphor and parallelism.
Hatred stirs up conflicts,
but love covers over all offenses. (Proverbs 10:12 ULB)
Another example from Proverbs.
Look at the ant, you lazy person, consider her ways, and be wise.
It has no commander, officer, or ruler,
yet it prepares its food in the summer,
and during the harvest it stores up what it will eat. (Proverbs 6:6-8 ULB)
Reason this is a translation issue
Each language has its own ways of saying proverbs. There are many proverbs in the Bible. They need to be translated in the way that people say proverbs in your language, so that people recognize them as proverbs and understand what they teach.
Examples from the Bible
A good name is to be chosen over great riches,
and favor is better than silver and gold. (Proverbs 22:1 ULB)
This means that it is better to be a good person and to have a good reputation than it is to have a lot of money.
Like vinegar on the teeth and smoke in the eyes,
so is the sluggard to those who send him. (Proverbs 10:26 ULB)
This means that a lazy person is very annoying to those who send him to do something.
The way of Yahweh protects those who have integrity,
but it is destruction for the wicked. (Proverbs 10:29 ULB)
This means that Yahweh protects people who do what is right, but he destroys those who are wicked.
Translation Strategies
If translating a proverb literally would be natural and give the right meaning in your language, consider doing that. If not, here are some options:
- Find out how people say proverbs in your language, and use one of those ways.
- If certain objects in the proverb are not known to many people in your language group, consider replacing them with objects that people know and that function in the same way in your language.
- Substitute a proverb in your language that has the same teaching as the proverb in the Bible.
- Give the same teaching but not in a form of a proverb.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Find out how people say proverbs in your language, and use one of those ways.
- A good name is to be chosen over great riches,
and favor is better than silver and gold. (Proverbs 22:1 ULB)
Here are some ideas for ways that people might say a proverb in their language.
- It is better to have a good name than to have great riches, and to be favored by people than to have silver and gold.
- Wise people choose a good name over great riches, and favor over silver and gold.
- Try to have a good reputation rather than great riches.
- Will riches really help you? I would rather have a good reputation.
2) If certain objects in the proverb are not known to many people in your language group, consider replacing them with objects that people know and that function in the same way in your language.
- Like snow in summer or rain in harvest,
so a fool does not deserve honor. (Proverbs 26:1 ULB)
- It is not natural for a cold wind to blow in the hot season or for it to rain in the harvest season; And it is not natural to honor a foolish person.
3) Substitute a proverb in your language that has the same teaching as the proverb in the Bible.
- Do not boast about tomorrow (Proverbs 27:1 ULB)
- Do not count your chickens before they hatch.
4) Give the same teaching but not in a form of a proverb.
- A generation that curses their father and does not bless their mother,
that is a generation that is pure in their own eyes,
but they are not washed of their filth. (Proverbs 30:11-12 ULB)
- People who do not respect their parents think that they are righteous, and they do not turn away from their sin.
Symbolic Language
This page answers the question: What is symbolic language and how do I translate it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Symbolic language in speech and writing is the use of symbols to represent other things and events. In the Bible it occurs most in prophecy and poetry, especially in visions and dreams about things that will happen in the future. Though people may not immediately know the meaning of a symbol, it is important to keep the symbol in the translation.
Eat this scroll, then go speak to the house of Israel." (Ezekiel 3:1 ULB)
This was in a dream. Eating the scroll is a symbol of reading and understanding well what was written on the scroll, and accepting these words from God into himself.
Purposes of symbolism
- One purpose of symbolism is to help people understand the importance or severity of an event by putting it in other, very dramatic terms.
- Another purpose of symbolism is to tell some people about something while hiding the true meaning from others who do not understand the symbolism.
Reason this is a translation issue
People who read the Bible today may find it hard to recognize that the language is symbolic, and they may not know what the symbol stands for.
Translation Principles
- When symbolic language is used, it is important to keep the symbol in the translation.
- It is also important not to explain the symbol more than the original speaker or writer did, since he may not have wanted everyone living then to be able to understand it easily.
Examples from the Bible
After this I saw in my dream at night a fourth animal, terrifying, frightening, and very strong. It had large iron teeth; it devoured, broke in pieces, and trampled underfoot what was left. It was different from the other animals, and it had ten horns. (Daniel 7:7 ULB)
The meaning of the underlined symbols is explained in Daniel 7:23-24 as shown below. The animals represent kingdoms, iron teeth represent a powerful army, and the horns represent powerful leaders.
This is what that person said, 'As for the fourth animal, it will be a fourth kingdom on earth that will be different from all the other kingdoms. It will devour the whole earth, and it will trample it down and break it into pieces. As for the ten horns, out of this kingdom ten kings will arise, and another will arise after them. He will be different from the previous ones, and he will conquer the three kings. (Daniel 7:23-24 ULB)
I turned around to see whose voice was speaking to me, and as I turned I saw seven golden lampstands. In the middle of the lampstands there was one like a Son of Man, … He had in his right hand seven stars, and coming out of his mouth was a sharp two-edged sword…. As for the hidden meaning about the seven stars you saw in my right hand, and the seven golden lampstands: the seven stars are the angels of the seven churches, and the seven lampstands are the seven churches. (Revelation 1:12, 16, 20 ULB)
This passage explains the meaning of the seven lampstands and the seven stars. The two-edged sword represents God's word and judgment.
Translation Strategies
- Translate the text with the symbols. Often the speaker or author explains the meaning later in the passage.
- Translate the text with the symbols. Then explain the symbols in footnotes.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Translate the text with the symbols. Often the speaker or author explains the meaning later in the passage.
- After this I saw in my dream at night a fourth animal, terrifying, frightening, and very strong. It had large iron teeth; it devoured, broke in pieces, and trampled underfoot what was left. It was different from the other animals, and it had ten horns. (Daniel 7:7 ULB) - People will be able to understand what the symbols mean when they read the explanation in Daniel 7:23-24.
-
Translate the text with the symbols. Then explain the symbols in footnotes.
- After this I saw in my dream at night a fourth animal, terrifying, frightening, and very strong. It had large iron teeth; it devoured, broke in pieces, and trampled underfoot what was left. It was different from the other animals, and it had ten horns. (Daniel 7:7 ULB)
- After this I saw in my dream at night a fourth animal,1 terrifying, frightening, and very strong. It had large iron teeth;2 it devoured, broke in pieces, and trampled underfoot what was left. It was different from the other animals, and it had ten horns.3
- The footnotes would look like:
- [1] The animal is a symbol for a kingdom.
- [2] The iron teeth is a symbol for the kingdom's powerful army.
- [3] The horns are a symbol of powerful kings.
- After this I saw in my dream at night a fourth animal, terrifying, frightening, and very strong. It had large iron teeth; it devoured, broke in pieces, and trampled underfoot what was left. It was different from the other animals, and it had ten horns. (Daniel 7:7 ULB)
Symbolic Prophecy
This page answers the question: What is symbolic language and how do I translate it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Symbolic prophecy is a type of message that God gave to a prophet so that the prophet would tell others. These messages use images and symbols to show what God will do in the future.
The main books that have these prophecies are Isaiah, Ezekiel, Daniel, Zechariah, and Revelation. Shorter examples of symbolic prophecy are also found in other books, such as in Matthew 24, Mark 13, and Luke 21.
The Bible tells both how God gave each message and what the message was. When God gave the messages, he often did so in miraculous ways such as in dreams and visions. (See dream and vision for help translating "dream" and "vision.") When prophets saw these dreams and visions, they often saw images and symbols about God and heaven. Some of these images are a throne, golden lamp stands, a powerful man with white hair and white clothes, and eyes like fire and legs like bronze. Some of these images were seen by more than one prophet.
The prophecies about the world also contain images and symbols. For example, in some of the prophecies strong animals represent kingdoms, horns represent kings or kingdoms, a dragon or serpent represents the devil, the sea represents the nations, and weeks represent longer periods of time. Some of these images were also seen by more than one prophet.
The prophecies tell about the evil in this world, how God will judge the world and punish sin, and how God will establish his righteous kingdom in the new world he is creating. They also tell about things that will happen concerning heaven and hell.
Much of prophecy in the Bible is presented as poetry. In some cultures people assume that if something is said in poetry, then it might not be true or very important. However, the prophecies in the Bible are true and very important, whether they are presented in poetic forms or non-poetic forms.
Sometimes the past tense is used in these books for events that happened in the past. However, sometimes the past tense is used for events that would happen in the future. There are two reasons for us. When prophets told about things that they saw in a dream or vision, they often used the past tense because their dream was in the past. The other reason for using the past tense to refer to future events was to emphasize that those events would certainly happen. The events were so certain to happen, it was as if they had already happened. We call this second use of the past tense "the predictive past." See Predictive Past.
Some of these things happened after the prophets told about them, and some of them will happen at the end of this world.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Some of the images are hard to understand because we have never seen things like them before.
- Descriptions of things that we have never seen or that do not exist in this world are hard to translate.
- If God or the prophet used the past tense, readers may have difficulty knowing wehther he was talking about something that had aleady happened or something that would happen later.
Translation Principles
- Translate the images in the text. Do not try to interpret them and translate their meaning.
- When an image appears in more than one place in the Bible, and it is described in the same way, try to translate it the same way in all those places.
- If either poetic forms or non-poetic forms would imply to your readers that the prophecy is not true or is unimportant, use a form that would not imply those things.
- Sometimes it is difficult to understand in what order the events described in the various prophecies happen. Simply write them as they appear in each prophecy.
- Translate tense in a way that the readers can understand what the speaker meant. If readers would not understand the predictive past, it is acceptable to use the future tense.
- Some of the prophecies were fulfilled after the prophets wrote about them. Some of them have not been fulfilled yet. Do not clarify in the prophecy when these prophecies were fulfilled or how they were fulfilled.
Examples from the Bible
The following passages describe powerful beings that Ezekiel, Daniel, and John saw. Images that come up in these visions include hair that is white as wool, a voice like many waters, a golden belt, and legs or feet like polished bronze. Though the prophets saw various details, it would be good to translate the details that are the same in the same way. The underlined phrases in the passage from Revelation also occur in the passages from Daniel and Ezekiel
In the middle of the lampstands there was one like a Son of Man, wearing a long robe that reached down to his feet, and a golden belt around his chest. His head and hair were as white as wool — as white as snow, and his eyes were like a flame of fire. His feet were like burnished bronze, like bronze that had been refined in a furnace, and his voice was like the sound of many rushing waters. He had in his right hand seven stars, and coming out of his mouth was a sharp two-edged sword. His face was shining like the sun at its strongest shining. (Revelation 1:13-16 ULB)
As I looked,
thrones were set in place,
and the Ancient of Days took his seat.
His clothing was as white as snow,
and the hair of his head was like pure wool. (Daniel 7:9 ULB)
I looked up and saw a man dressed in linen, with a belt around his waist made of pure gold from Uphaz. His body was like topaz, his face was like lightning, his eyes were like flaming torches, his arms and his feet were like polished bronze, and the sound of his words was like the sound of a great crowd. (Daniel 10:5-6 ULB)
Behold! The glory of the God of Israel came from the east; his voice was like the sound of many waters, and the earth shone with his glory! (Ezekiel 43:2 ULB)
The following passage shows the use of the past tense to refer to past events. The underlined verbs refer to past events.
The vision of Isaiah son of Amoz, that he saw concerning Judah and Jerusalem, in the days of Uzziah, Jotham, Ahaz, and Hezekiah, kings of Judah.
Hear, heavens, and give ear, earth; for Yahweh has spoken:
"I have nourished and brought up children, but they have rebelled against me. (Isaiah 1:1-2 ULB)
The following passage shows the future tense and different uses of the past tense. The underlined verbs are examples of the predictive past, where the past tense is used to show that the events certainly will happen.
The gloom will be dispelled from her who was in anguish.
In an earlier time he humiliated the land of Zebulun and the land of Naphtali,
but in the later time he will make it glorious, the way to the sea, beyond the Jordan, Galilee of the nations.
The people who walked in darkness have seen a great light;
those who have lived in the land of the shadow of death, the light has shone on them. (Isaiah 9:1-2 ULB)
Translation Issues
Textual Variants
This page answers the question: Why does the ULB have missing or added verses, and should I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Thousands of years ago, people wrote the books of the Bible. Other people then copied them by hand and translated them. They did this work very carefully, and over the years many people made thousands of copies. However people who looked at them later saw that there were small differences between them. Some copiers accidentally left out some words, and some mistook a word for another that looked like it. Occasionally they added words or even whole sentences, either by accident, or because they wanted to explain something. Modern Bibles are translations of the old copies. Some modern Bibles have some of these sentences that were added. In the ULB, these added sentences are usually written in footnotes.
Bible scholars have read many old copies and compared them with each other. For each place in the Bible where there was a difference, they have figured out which wordings are most likely correct. The translators of the ULB based the ULB on wordings that scholars say are most likely correct. Because people who use the ULB may have access to Bibles that are based on other copies, the ULB translators included footnotes that tell about some of the differences between them.
Translators are encouraged to translate the text in the ULB and to write about added sentences in footnotes, as is done in the ULB. However, if the local church really wants those sentences to be included in the main text, translators may put them in the text and include a footnote about them.
Examples from the Bible
Matthew 18:10-11 ULB has a footnote about verse 11.
10See that you do not despise any of these little ones. For I say to you that in heaven their angels always look on the face of my Father who is in heaven. 11[1]
[1] Many authorities, some ancient, insert v. 11. For the Son of Man came to save that which was lost.
John 7:53-8:11 is not in the best earliest manuscripts. It has been included in the ULB, but it is marked off with square brackets ([ ]) at the beginning and end, and there is a footnote after verse 11.
53[Then every man went to his own house.… 11She said, "No one, Lord." Jesus said, "Neither do I condemn you. Go your way; from now on sin no more."][2]
[2]The best earliest manuscripts do not have John 7:53-8:11
Translation Strategies
When there is a textual variant, you may choose to follow the ULB or another version that you have access to.
- Translate the verses that the ULB does and include the footnote that the ULB provides.
- Translate the verses as another version does, and change the footnote so that it fits this situation.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
The translation strategies are applied to Mark 7:14-16 ULB, which has a footnote about verse 16.
-
14He called the crowd again and said to them, "Listen to me, all of you, and understand. 15There is nothing from outside of a person that can defile him when it enters into him. It is what comes out of the person that defiles him." 16[1]
- [1]The best ancient copies omit v. 16. If any man has ears to hear, let him hear.
-
Translate the verses that the ULB does and include the footnote that the ULB provides.
- 14He called the crowd again and said to them, "Listen to me, all of you, and understand. 15There is nothing from outside of a person that can defile him when it enters into him. It is what comes out of the person that defiles him." 16[1]
- [1]The best ancient copies omit verse 16. If any man has ears to hear, let him hear.
- 14He called the crowd again and said to them, "Listen to me, all of you, and understand. 15There is nothing from outside of a person that can defile him when it enters into him. It is what comes out of the person that defiles him." 16[1]
-
Translate the verses as another version does, and change the footnote so that it fits this situation.
- 14He called the crowd again and said to them, "Listen to me, all of you, and understand. 15There is nothing from outside of a person that can defile him when it enters into him. It is what comes out of the person that defiles him. 16If any man has ears to hear, let him hear." [1]
- [1]Some ancient copies do not have verse 16.
- 14He called the crowd again and said to them, "Listen to me, all of you, and understand. 15There is nothing from outside of a person that can defile him when it enters into him. It is what comes out of the person that defiles him. 16If any man has ears to hear, let him hear." [1]
Next we recommend you learn about:
Verse Bridges
This page answers the question: Why are some verse numbers combined, such as “3-5” or “17-18”?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
In rare cases, you will see in the Unlocked Literal Bible (ULB) or the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB) that two or more verse numbers are combined, such as 17-18. This is called a verse bridge. This means that the information in the verses was rearranged so that the story or message could be more easily understood.
29 These were the clans of the Horites: Lotan, Shobal, Zibeon, and Anah, 30 Dishon, Ezer, Dishan: these are clans of the Horites, according to their clan lists in the land of Seir. (Genesis 26:29-30 ULB)
29-30 The people groups who were descendants of Hor lived in Seir land. The names of the people groups are Lotan, Shobal, Zibeon, Anah, Dishon, Ezer, and Dishpan. (Genesis 26:29-30 UDB)
In the ULB text, verses 29 and 30 are separate, and the information about the people living in Seir is at the end of verse 30. In the UDB text, the verses are joined, and the information about them living in Seir is at the beginning. For many languages, this is a more logical order of information.
Examples from the Bible
Sometimes the ULB has separate verses while the UDB has a verse bridge.
4 However, there should be no poor among you (for Yahweh will surely bless you in the land that he gives you as an inheritance to possess), 5 if only you diligently listen to the voice of Yahweh your God, to keep all these commandments that I am commanding you today. (Deuteronomy 15:4-5 ULB)
4-5 Yahweh our God will bless you in the land that he is giving to you. If you obey Yahweh our God and obey all the commandments that I am giving to you today, there will not be any poor people among you. (Deuteronomy 15:4-5 UDB)
There are also a few verse bridges in the ULB.
17-18 Ezrah's sons were Jether, Mered, Epher, and Jalon. Mered's Egyptian wife bore Miriam, Shammai, and Ishbah, who became the father of Eshtemoa. These were the sons of Bithiah, daughter of Pharaoh, whom Mered married. Mered's Jewish wife bore Jered, who became the father of Gedor; Heber, who became the father of Soco; and Jekuthiel, who became the father of Zanoah. (1 Chronicles 4:17-18 ULB)
The ULB moved the underlined sentence from verse 18 to verse 17 to more clearly show which were the sons of Bithiah. Here is the original order, which is confusing to many readers:
17 The sons of Ezrah: Jether, Mered, Epher, and Jalon. She conceived and bore Miriam, Shammai, and Ishbah father of Eshtemoa. 18 And his Judahite wife bore Jered father of Gedor, Heber father of Soco, and Jekuthiel father of Zanoah. These were the sons of Bithiah daughter of Pharaoh, whom Mered married. (1 Chronicles 4:17-18 TNK)
Translation Strategies
Order the information in a way that will be clear to your readers.
- If you put information from one verse before information from an earlier verse, put a hyphen between the two verse numbers.
- If the ULB has a verse bridge, but another Bible you refer to does not have one, you can choose the order that works best for your language.
See how to mark verses in the translationStudio APP.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If information from one verse is put before information from an earlier verse, put the verse numbers before the first verse with a hyphen between them.
- 2 you must select three cities for yourself in the middle of your land that Yahweh your God is giving you to possess. 3 You must build a road and divide the borders of your land into three parts, the land that Yahweh your God is causing you to inherit, so that everyone who kills another person may flee there. (Deuteronomy 19:2-3)
- 2-3 you must divide into three parts the land that he is giving to you. Then select a city in each part. You must make good roads in order that people can get to those cities easily. Someone who kills another person can escape to one of those cities to be safe. (Deuteronomy 19:2-3 UDB)
- 2 you must select three cities for yourself in the middle of your land that Yahweh your God is giving you to possess. 3 You must build a road and divide the borders of your land into three parts, the land that Yahweh your God is causing you to inherit, so that everyone who kills another person may flee there. (Deuteronomy 19:2-3)
-
If the ULB has a verse bridge, but another Bible you refer to does not have one, you can choose the order that works best for your language.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Unknowns
Translate Unknowns
This page answers the question: How can I translate ideas that my readers are not familiar with?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
How do I translate words like lion, fig tree, mountain, priest, or temple when people in my culture have never seen these things and we do not have a word for them?
Description
Unknowns are things that occur in the source text that are not known to the people of your culture. The translationWords pages and the translationNotes will help you understand what they are. After you understand them, you will need to find ways to refer to those things so that people who read your translation will understand what they are.
We have here only five loaves of bread and two fish (Matthew 14:17 ULB)
Bread is a particular food made by mixing finely crushed grains with oil, and then cooking the mixture so that it is dry. (Grains are the seeds of a kind of grass.) In some cultures people do not have bread or know what it is.
Reason this is a translation issue
- Readers may not know some of the things that are in the Bible because those things are not part of their own culture.
- Readers may have difficulty understanding a text if they do not know some of the things that are mentioned in it.
Translation Principles
- Use words that are already part of your language if possible.
- Keep expressions short if possible.
- Represent God's commands and historical facts accurately.
Examples from the Bible
I will turn Jerusalem into piles of ruins, a hideout for jackals (Jeremiah 9:11 ULB)
Jackals are wild animals like dogs that live in only a few parts of the world. So they are not known in many places.
Beware of false prophets, those who come to you in sheep's clothing, but are truly ravenous wolves. (Matthew 7:15 ULB)
If wolves do not live where the translation will be read, the readers may not understand that they are fierce, wild animals like dogs that attack and eat sheep.
Then they tried to give Jesus wine that was mixed with myrrh. But he refused to drink it. (Mark 15:23 ULB)
People may not know what myrrh is and that it was used as a medicine.
to him who made great lights (Psalm 136:7 ULB)
Some languages have terms for things that give light, like the sun and fire, but they have no general term for lights.
your sins ... will be white like snow (Isaiah 1:18 ULB)
People in many parts of the world have not seen snow, but they may have seen it in pictures.
Translation Strategies
Here are ways you might translate a term that is not known in your language:
- Use a phrase that describes what the unknown item is, or what is important about the unknown item for the verse being translated.
- Substitute something similar from your language if doing so does not falsely represent a historical fact.
- Copy the word from another language, and add a general word or descriptive phrase to help people understand it.
- Use a word that is more general in meaning.
- Use a word or phrase that is more specific in meaning.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
1) Use a phrase that describes what the unknown item is, or what is important about the unknown item for the verse being translated.
- Beware of false prophets, those who come to you in sheep's clothing, but are truly ravenous wolves. (Matthew 7:15 ULB)
- Beware of false prophets, those who come to you in sheep's clothing, but are truly hungry and dangerous animals.
"Ravenous wolves" is part of a metaphor here, so the reader needs to know that they are very dangerous to sheep in order to understand this metaphor. (If sheep are also unknown, then you will need to also use one of the translation strategies to translate sheep, or change the metaphor to something else, using a translation strategy for metaphors. See Translating Metaphors.)
- We have here only five loaves of bread and two fish (Matthew 14:17 ULB)
- We have here only five loaves of baked grain seeds and two fish
2) Substitute something similar from your language if doing so does not falsely represent a historical fact.
- your sins ... will be white like snow (Isaiah 1:18 ULB) This verse is not about snow. It uses snow in a figure of speech to help people understand how white something will be.
- your sins ... will be white like milk
- your sins ... will be white like the moon
3) Copy the word from another language, and add a general word or descriptive phrase to help people understand it.
-
Then they tried to give Jesus wine that was mixed with myrrh. But he refused to drink it. (Mark 15:23 ULB) - People may understand better what myrrh is if it is used with the general word "medicine."
- Then they tried to give Jesus wine that was mixed with a medicine called myrrh. But he refused to drink it.
-
We have here only five loaves of bread and two fish (Matthew 14:17 ULB) - People may understand better what bread is if it is used with a phrase that tells what it is made of (seeds) and how it is prepared (crushed and baked).
- We have here only five loaves of baked crushed seed bread and two fish
4) Use a word that is more general in meaning.
-
I will turn Jerusalem into piles of ruins, a hideout for jackals (Jeremiah 9:11 ULB)
- I will turn Jerusalem into piles of ruins, a hideout for wild dogs
-
We have here only five loaves of bread and two fish (Matthew 14:17 ULB)
- We have here only five loaves of baked food and two fish
5) Use a word or phrase that is more specific in meaning.
- to him who made great lights (Psalm 136:7 ULB)
- to him who made the sun and the moon
Next we recommend you learn about:
Copy or Borrow Words
This page answers the question: What does it mean to borrow words from another language and how can I do it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Sometimes the Bible includes things that are not part of your culture and that your language may not have a word for. It also includes people and places that you may not have names for.
When that happens you can "borrow" the word from the Bible into your own language. This means that you basically copy it from the other language. This page tells how to "borrow" words. (There are also other ways to translate words for things that are not in your language. See Translate Unknowns..)
Examples from the Bible
He saw a fig tree on the roadside (Matthew 21:19 ULB)
If there are no fig trees where your language is spoken, there might not be a name for this kind of tree in your language.
Above him were the seraphim; each one had six wings; with two each covered his face, and with two he covered his feet, and with two he flew. (Isaiah 6:2 ULB)
Your language might not have a name for this kind of creature.
The declaration of the word of Yahweh to Israel by the hand of Malachi. (Malachi 1:1 ULB)
Malachi might not be a name that people who speak your language use.
Translation Strategies
There are several things to be aware of when borrowing words from another language.
- Different languages use different scripts, such as the Hebrew, Greek, Latin, Cyrillic, Devanagari, and Korean scripts. These scripts use different shapes to represent the letters in their alphabets.
- Languages that use the same script might pronounce the letters in that script differently. For example, when speaking German, people pronounce the letter "j" the same way that people pronounce the letter "y" when speaking English.
- Languages do not all have the same sounds or combinations of sounds. For example, many languages do not have the soft "th" sound in the English word "think," and some languages cannot start a word with a combination of sounds like "st" as in "stop."
There are several ways to borrow a word.
- If your language uses a different script from the language you are translating from, you can simply substitute each letter shape with the corresponding letter shape of the script of your language.
- You can spell the word as the other language spells it, and pronounce it the way your language normally pronounces those letters.
- You can pronounce the word similarly to the way the other language does, and adjust the spelling to fit the rules of your language.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If your language uses a different script from the language you are translating from, you can simply substitute each letter shape with the corresponding letter shape of the script of your language.
- צְפַנְיָ֤ה - A man's name in Hebrew letters.
- "Zephaniah" - The same name in Roman letters
- צְפַנְיָ֤ה - A man's name in Hebrew letters.
-
You can spell the word as the other language spells it, and pronounce it the way your language normally pronounces those letters.
- Zephaniah - This is a man's name.
- "Zephaniah" - The name as it is spelled in English, but you can pronounce it according to the rules of your language.
- Zephaniah - This is a man's name.
-
You can pronounce the word similarly to the way the other language does, and adjust the spelling to fit the rules of your language.
- Zephaniah - If your language does not have the "z", you could use "s". If your writing system does not use "ph" you could use "f". Depending on how you pronounce the "i" you could spell it with "i" or "ai" or "ay".
- "Sefania"
- "Sefanaia"
- "Sefanaya"
- Zephaniah - If your language does not have the "z", you could use "s". If your writing system does not use "ph" you could use "f". Depending on how you pronounce the "i" you could spell it with "i" or "ai" or "ay".
How to Translate Names
This page answers the question: How can I translate names that are new to my culture?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The Bible has names of many people, groups of people, and places. Some of these names may sound strange and be hard to say. Sometimes readers may not know what a name refers to, and sometimes they may need to understand what a name means. This page will help you see how you can translate these names and how you can help people understand what they need to know about them.
Meaning of names
Most names in the Bible have meaning. Most of the time, names in the Bible are used simply to identify the people and places they refer to. But sometimes the meaning of a name is especially important.
It was this Melchizedek, king of Salem, priest of God Most High, who met Abraham returning from the slaughter of the kings and blessed him. (Hebrews 7:1 ULB)
Here the writer uses the name "Melchizedek" primarily to refer to a man who had that name, and the title "king of Salem" tells us that he ruled over a certain city.
His name "Melchizedek" means "king of righteousness," and also "king of Salem," that is, "king of peace." (Hebrews 7:2 ULB)
Here the writer explains the meanings of Melchizedek's name and title, because those things tell us more about the person. Other times, the writer does not explain the meaning of a name because he expects the reader to already know the meaning. If the meaning of the name is important to understand the passage, you can include the meaning in the text or in a footnote.
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Readers may not know some of the names in the Bible. They may not know whether a name refers to a person or place or something else.
- Readers may need to understand the meaning of a name in order to understand the passage.
- Some names may have different sounds or combinations of sounds that are not used in your language or are unpleasant to say in your language. For strategies to address this problem, see Borrow Words.
- Some people and places in the Bible have two names. Readers may not realize that two names refer to the same person or place.
Examples from the Bible
You went over the Jordan and came to Jericho. The leaders of Jericho fought against you, along with the Amorites (Joshua 24:11 ULB)
Readers might not know that "Jordan" is the name of a river, "Jericho" is the name of a city, and "Amorites" is the name of a group of people.
she said, "Do I really continue to see, even after he has seen me?" Therefore the well was called Beerlahairoi; (Genesis 16:13-14 ULB)
Readers may not understand the second sentence if they do not know that "Beerlahairoi" means "Well of the Living One who sees me."
She named him Moses and said, "Because I drew him from the water." (Exodus 2:11 ULB)
Readers may not understand why she said this if they do not know that the name Moses sounds like the Hebrew words "pull out."
Saul was in agreement with his death (Acts 8:1 ULB)
It came about in Iconium that Paul and Barnabas entered together into the synagogue (Acts 14:1 ULB)
Readers may not know that the names Saul and Paul refer to the same person.
Translation Strategies
- If readers cannot easily understand from the context what kind of a thing a name refers to, you can add a word to clarify it.
- If readers need to understand the meaning of a name in order to understand what is said about it, copy the name and tell about its meaning either in the text or in a footnote.
- Or if readers need to understand the meaning of a name in order to understand what is said about it, and that name is used only once, translate the meaning of the name instead of copying the name.
- If a person or place has two different names, use one name most of the time and the other name only when the text tells about the person or place having more than one name or when it says something about why the person or place was given that name. Write a footnote when the source text uses the name that is used less frequently.
- Or if a person or place has two different names, then use whatever name is given in the source text, and add a footnote that gives the other name.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If readers cannot easily understand from the context what kind of a thing a name refers to, you can add a word to clarify it.
-
You went over the Jordan and came to Jericho. The leaders of Jericho fought against you, along with the Amorites (Joshua 24:11 ULB)
- You went over the Jordan River and came to the city of Jericho. The leaders of Jericho fought against you, along with the tribe of the Amorites
-
Shortly after, some Pharisees came and said to him, "Go and leave here because Herod wants to kill you." (Luke 13:31 ULB)
- Shortly after, some Pharisees came and said to him, "Go and leave here because King Herod wants to kill you.
-
-
If readers need to understand the meaning of a name in order to understand what is said about it, copy the name and tell about its meaning either in the text or in a footnote.
- She named him Moses and said, "Because I drew him from the water." (Exodus 2:11 ULB)
- She named him Moses, which sounds like 'drawn out,' and said, "Because I drew him from the water."
- She named him Moses and said, "Because I drew him from the water." (Exodus 2:11 ULB)
-
Or if readers need to understand the meaning of a name in order to understand what is said about it, and that name is used only once, translate the meaning of the name instead of copying the name.
- ... she said, "Do I really continue to see, even after he has seen me?" Therefore the well was called Beerlahairoi; (Genesis 16:13-14 ULB)
- ... she said, "Do I really continue to see, even after he has seen me?" Therefore the well was called Well of the Living One who sees me;
- ... she said, "Do I really continue to see, even after he has seen me?" Therefore the well was called Beerlahairoi; (Genesis 16:13-14 ULB)
-
If a person or place has two different names, use one name most of the time and the other name only when the text tells about the person or place having more than one name or when it says something about why the person or place was given that name. Write a footnote when the source text uses the name that is used less frequently. For example, Paul is called "Saul" before Acts 13 and "Paul" after Acts 13. You could translate his name as "Paul" all of the time, except in Acts 13:9 where it talks about him having both names.
-
... a young man named Saul (Acts 7:58 ULB)
- ... a young man named Paul1 The footnote would look like:
- [1]Most versions say Saul here, but most of the time in the Bible he is called Paul.
- ... a young man named Paul1 The footnote would look like:
-
But Saul, who is also called Paul, was filled with the Holy Spirit; (Acts 13:9)
- But Saul, who is also called Paul, was filled with the Holy Spirit;
-
-
Or if a person or place has two names, use whatever name is given in the source text, and add a footnote that gives the other name. For example, you could write "Saul" where the source text has "Saul" and "Paul" where the source text has "Paul."
-
a young man named Saul (Acts 7:58 ULB)
- a young man named Saul The footnote would look like:
- [1]This is the same man who is called Paul beginning in Acts 13.
- a young man named Saul The footnote would look like:
-
But Saul, who is also called Paul, was filled with the Holy Spirit; (Acts 13:9)
- But Saul, who is also called Paul, was filled with the Holy Spirit;
-
It came about in Iconium that Paul and Barnabas entered together into the synagogue (Acts 14:1 ULB)
- It came about in Iconium that Paul1 and Barnabas entered together into the synagogue The footnote would look like:
- [1]This is the man that was called Saul before Acts 13.
- It came about in Iconium that Paul1 and Barnabas entered together into the synagogue The footnote would look like:
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Assumed Knowledge and Implicit Information
This page answers the question: How can I be sure that my translation communicates the assumed knowledge and implicit information along with the explicit information of the original message?
- Assumed knowledge is whatever a speaker assumes his audience knows before he speaks and gives them some kind of information. The speaker gives the audience information in two ways:
- Explicit information is what the speaker states directly.
- Implicit information is what the speaker does not state directly because he expects his audience to be able to learn it from what he says.
Description
When someone speaks or writes, he has something specific that he wants people to know or do or think about. He normally states this directly. This is explicit information.
The speaker assumes that his audience already knows certain things that they will need to think about in order to understand this information. Normally he does not tell people these things, because they already know them. This is called assumed knowledge.
The speaker does not always directly state everything that he expects his audience to learn from what he says. Information that he expects people to learn from what he says even though he does not state it directly is implicit information.
Often, the audience understands this implicit information by combining what they already know (assumed knowledge) with the explicit information that the speaker tells them directly.
Reasons this is a translation issue
All three kinds of information are part of the speaker's message. If one of these kinds of information is missing, then the audience will not understand the message. Because the target translation is in a language that is very different than the biblical languages and made for an audience that lives in a very different time and place than the people in the Bible, many times the assumed knowledge or the implicit information is missing from the message. In other words, modern readers do not know everything that the original speakers and hearers in the Bible knew. When these things are important for understanding the message, you can include this information in the text or in a footnote.
Examples from the Bible
Then a scribe came to him and said, "Teacher, I will follow you wherever you go." Jesus said to him, "Foxes have holes, and the birds of the sky have nests, but the Son of Man has nowhere to lay his head." (Matthew 8:20 ULB)
Jesus did not say what foxes and birds use holes and nests for, because he assumed that the scribe would have known that foxes sleep in holes in the ground and birds sleep in their nests. This is assumed knowledge.
Jesus did not directly say here "I am the Son of Man" but, if the scribe did not already know it, then that fact would be implicit information that he could learn because Jesus referred to himself that way. Also, Jesus did not state explicitly that he travelled a lot and did not have a house that he slept in every night. That is implicit information that the scribe could learn when Jesus said that he had nowhere to lay his head.
Woe to you, Chorazin! Woe to you, Bethsaida! If the mighty deeds had been done in Tyre and Sidon which were done in you, they would have repented long ago in sackcloth and ashes. But it will be more tolerable for Tyre and Sidon at the day of judgment than for you. (Matthew 11:21, 22 ULB)
Jesus assumed that the people he was speaking to knew that Tyre and Sidon were very wicked, and that the day of judgment is a time when God will judge every person. Jesus also knew that the people he was talking to believed that they were good and did not need to repent. Jesus did not need to tell them these things. This is all assumed knowledge.
An important piece of implicit information here is that because the people he was speaking to did not repent, they would be judged more severely than the people of Tyre and Sidon would be judged.
Why do your disciples violate the traditions of the elders? For they do not wash their hands when they eat. (Matthew 15:2 ULB)
One of the traditions of the elders was a ceremony in which people would wash their hands in order to be ritually clean before eating. People thought that in order to be righteous, they had to follow all the traditions of the elders. This was assumed knowledge that the Pharisees who were speaking to Jesus expected him to know. By saying this, they were accusing his disciples of not following the traditions, and thus not being righteous. This is implicit information that they wanted him to understand from what they said.
Translation Strategies
If readers have enough assumed knowledge to be able to understand the message, along with any important implicit information that goes with the explicit information, then it is good to leave that knowledge unstated and leave the implicit information implicit. If the readers do not understand the message because one of these is missing for them, then follow these strategies:
- If readers cannot understand the message because they do not have certain assumed knowledge, then provide that knowledge as explicit information.
- If readers cannot understand the message because they do not know certain implicit information, then state that information clearly, but try to do it in a way that does not imply that the information was new to the original audience.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If readers cannot understand the message because they do not have certain assumed knowledge, then provide that knowledge as explicit information.
-
Jesus said to him, "Foxes have holes, and the birds of the sky have nests, but the Son of Man has nowhere to lay his head." (Matthew 8:20 ULB) - Assumed knowledge was that the foxes slept in their holes and birds slept in their nests.
- Jesus said to him, "Foxes have holes to live in, and the birds of the sky have nests to live in, but the Son of Man has nowhere to lay his head and sleep."
-
it will be more tolerable for Tyre and Sidon at the day of judgment than for you (Matthew 11:22 ULB) - Assumed knowledge was that the people of Tyre and Sidon were very, very wicked. This can be stated explicitly.
- ... it will be more tolerable for those cities Tyre and Sidon, whose people were very wicked, at the day of judgment than for you
- Or:
- ... it will be more tolerable for those wicked cities Tyre and Sidon at the day of judgment than for you
- ... it will be more tolerable for those cities Tyre and Sidon, whose people were very wicked, at the day of judgment than for you
-
Why do your disciples violate the traditions of the elders? For they do not wash their hands when they eat. (Matthew 15:2 ULB) - Assumed knowledge was that one of the traditions of the elders was a ceremony in which people would wash their hands in order to be ritually clean before eating, which they must do to be righteous. It was not to remove germs from their hands to avoid sickness, as a modern reader might think.
- Why do your disciples violate the traditions of the elders? For they do not go through the ceremonial handwashing ritual of righteousness when they eat.
-
-
If readers cannot understand the message because they do not know certain implicit information, then state that information clearly, but try to do it in a way that does not imply that the information was new to the original audience.
-
Then a scribe came to him and said, "Teacher, I will follow you wherever you go." Jesus said to him, "Foxes have holes, and the birds of the sky have nests, but the Son of Man has nowhere to lay his head." (Matthew 8:19, 20 ULB) - Implicit information is that Jesus himself is the Son of Man. Other implicit information is that if the scribe wanted to follow Jesus, he would have to live like Jesus without a house.
- Jesus said to him, "Foxes have holes, and the birds of the sky have nests, but I, the Son of Man, have no home to rest in. If you want to follow me, you will live as I live."
-
it will be more tolerable for Tyre and Sidon at the day of judgment than for you (Matthew 11:22 ULB) - Implicit information is that God would not only judge the people; he would punish them. This can be made explicit.
- At the day of judgment, God will punish Tyre and Sidon, cities whose people were very wicked, less severely than he will punish you
- At the day of judgment, God will punish you more severely than Tyre and Sidon, cities whose people were very wicked.
-
Modern readers may not know some of the things that the people in the Bible and the people who first read it knew. This can make it hard for them to understand what a speaker or writer says, and to learn things that the speaker left implicit. Translators may need to state some things explicitly in the translation that the original speaker or writer left unstated or implicit.
Next we recommend you learn about:
When to Make Explicit Information Implicit
This page answers the question: What can I do if some of the explicit information seems confusing, unnatural, or unnecessary in our language?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some languages have ways of saying things that are natural for them but sound strange when translated into other languages. One of the reasons for this is that some languages say things explicitly that the other languages would leave as implicit information.
Reasons this is a translation issue
If you translate all of the explicit information from the source language into the explicit information in the target language, it could sound foreign, unnatural, or perhaps even unintelligent if the target language would not make that information explicit. Instead, it is best to leave that kind of information implicit in the target language.
Examples from the Bible
And Abimelech came to the tower and fought against it and drew near to the door of the tower to burn it with fire. (Judges 9:52 ESV)
In Biblical Hebrew, it was normal to start most sentences with a conjunction such as “and” to show the connection between sentences. In English, it is ungrammatical to do so, is quite tiresome for the English reader, and gives the impression that the author was uneducated. In English, it is best to leave the idea of connection between sentences implicit in most cases and not translate the conjunction explicitly.
In Biblical Hebrew, it was normal to say that something was burned with fire. In English, the idea of fire is included in the action of burning, and so it is unnatural to state both ideas explicitly. It is enough to say that something was burned and leave the idea of fire implicit.
The centurion answered and said, "Lord, I am not worthy that you should enter under my roof…” (Matthew 8:8 ULB)
In the biblical languages, it was normal to introduce direct speech with two verbs of speaking. One verb indicated the mode of address, and the other introduced the words of the speaker. English speakers do not do this, so it is very unnatural and confusing to use two verbs. For the English speaker, the idea of speaking is included in the idea of answering. Using two verbs in English implies two separate speeches, rather than just one. So in English, it is better to use only one verb of speaking.
Translation Strategies
- If the explicit information of the source language sounds natural in the target language, then translate it as explicit information.
- If the explicit information does not sound natural in the target language or seems unnecessary or confusing, leave the explicit information implicit. Only do this if the reader can understand this information from the context. You can test this by asking the reader a question about the passage.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If the explicit information of the source language sounds natural in the target language, then translate it as explicit information.
- There would be no change to the text using this strategy, so no examples are given here.
-
If the explicit information does not sound natural in the target language or seems unnecessary or confusing, leave the explicit information implicit. Only do this if the reader can understand this information from the context. You can test this by asking the reader a question about the passage.
- And Abimelech came to the tower and fought against it and drew near to the door of the tower to burn it with fire. (Judges 9:52 ESV)
- Abimelech came to the tower and fought against it and drew near to the door of the tower to burn it. Or …to set it on fire.
- And Abimelech came to the tower and fought against it and drew near to the door of the tower to burn it with fire. (Judges 9:52 ESV)
In English, it is clear that the action of this verse follows the action of the previous verse without the use of the connector “and” at the beginning, so it was omitted. Also, the words “with fire” were left out, because this information is communicated implicitly by the word “burn.” An alternative translation for “to burn it” is “to set it on fire.” It is not natural in English to use both “burn” and “fire,” so the English translator should choose only one of them. You can test if the readers understood the implicit information by asking, “How would the door burn?” If they knew it was by fire, then they have understood the implicit information. Or, if you chose the second option, you could ask, “What happens to a door that is set on fire?” If the readers answer, “It burns,” then they have understood the implicit information.
- The centurion answered and said, "Lord, I am not worthy that you should enter under my roof…” (Matthew 8:8 ULB)
- The centurion answered, "Lord, I am not worthy that you should enter under my roof…”
In English, the information that the centurion answered by speaking is included in the verb “answered,” so the verb “said” can be left implicit. You can test if the readers understood the implicit information by asking, “How did the centurion answer?” If they knew it was by speaking, then they have understood the implicit information.
Next we recommend you learn about:
When to Keep Information Implicit
This page answers the question: When should I not make implicit information explicit?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Sometimes it is better not to state assumed knowledge or implicit information explicitly.
Description
Sometimes it is better not to state assumed knowledge or implicit information explicitly. This page gives some direction about when not to do this.
Translation Principles
- If a speaker or author intentionally left something unclear, do not try to make it more clear.
- If the original audience did not understand what the speaker meant, do not make it so clear that your readers would find it strange that the original audience did not understand.
- If you need to explicitly state some assumed knowledge or implicit information, try to do it in a way that it does not make your readers think that the original audience needed to be told those things.
- Do not make it explicit if it throws the message out of focus and leads the readers to forget what the main point is.
- Do not make assumed knowledge or implicit information explicit if your readers already understand it.
Examples from the Bible
Out of the eater was something to eat;
out of the strong was something sweet. (Judges 14:14 ULB)
This was a riddle. Samson purposely said this in a way that it would be hard for his enemies to know what it meant. Do not make it clear that the eater and the strong thing was a lion and that the sweet thing to eat was honey.
Jesus said to them, "Take heed and beware of the yeast of the Pharisees and Sadducees." The disciples reasoned among themselves and said, "It is because we took no bread." … (Matthew 16:6,7 ULB)
Possible implicit information here is that the disciples should beware of the false teaching of the Pharisees and Sadducees. But Jesus' disciples did not understand this. They thought that Jesus was talking about real yeast and bread. So it would not be appropriate to state explicitly that the word "yeast" here refers to false teaching. The disciples did not understand what Jesus meant until they heard what Jesus said in Matthew 16:11 -
"How is it that you do not understand that I was not speaking to you about bread? Take heed and beware of the yeast of the Pharisees and Sadducees." Then they understood that he was not telling them to beware of yeast in bread, but to beware of the teaching of the Pharisees and Sadducees. (Matthew 16:11,12 ULB)
Only after Jesus explained that he was not talking about bread did they realize that he was talking about the false teaching of the Pharisees. Therefore it would be wrong to explicitly state the implicit information in Matthew 16:6.
Translation Strategies
This page does not have any translation strategies.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
This page does not have any translation strategies applied.
Biblical Distance
This page answers the question: How can I translate the lengths and distances that are in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The following terms are the most common measures for distance or length that were originally used in the Bible. Most of these are based on the sizes of the hand and forearm.
- The handbreadth was the width of the palm of a man's hand.
- The span or handspan was the width of a man's hand with the fingers spread out.
- The cubit was the length of a man's forearm, from the elbow to the tip of the longest finger.
- The "long" cubit is used only in Ezekiel 40-48. It is the length of a normal cubit plus a span.
- The stadium (plural, stadia) referred to a certain footrace that was about 185 meters in length. Some older English versions translated this word as "furlong", which referred to the average length of a plowed field.
The metric values in the table below are close but not exactly equal to the biblical measures. The biblical measures probably differed in exact length from time to time and place to place. The equivalents below are an attempt to give an average measurement.
| Original Measure | Metric Measure | | -------- | -------- | | handbreadth | 8 centimeters | | span | 23 centimeters | | cubit | 46 centimeters | | "long" cubit | 54 centimeters | | stadia | 185 meters |
Translation Principles
- The people in the Bible did not use modern measures such as meters, liters, and kilograms. Using the original measures can help readers know that the Bible really was written long ago in a time when people used those measures.
- Using modern measures can help readers understand the text more easily.
- Whatever measure you use, it would be good, if possible, to tell about the other kind of measure in the text or a footnote.
- If you do not use the Biblical measures, try not to give the readers the idea that the measurements are exact. For example, if you translate one cubit as ".46 meters" or even as "46 centimeters," readers might think that the measurement is exact. It would be better to say "half a meter," "45 centimeters," or "50 centimeters."
- Sometimes it can be helpful to use the word "about" to show that a measurement is not exact. For example, Luke 24:13 says that Emmaus was sixty stadia from Jerusalem. This can be translated as "about ten kilometers" from Jerusalem.
- When God tells people how long something should be, and when people make things according to those lengths, do not use "about" in the translation. Otherwise it will give the impression that God did not care exactly how long something should be.
Translation Strategies
- Use the measurements from the ULB. These are the same kinds of measurements that the original writers used. Spell them in a way that is similar to the way they sound or are spelled in the ULB. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- Use the metric measurements given in the UDB. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
- Use measurements that are already used in your language. In order to do this you would need to know how your measurements relate to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
- Use the measurements from the ULB and include measurements that your people know in the text or a note.
- Use measurements that your people know, and include the measurements from the ULB in the text or in a note.
Translation Strategies Applied
The strategies are all applied to Exodus 25:10 below.
-
They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be two and a half cubits; its width will be one cubit and a half; and its height will be one cubit and a half. (Exodus 25:10 ULB)
-
Use the measurements given in the ULB. These are the same kinds of measurements that the original writers used. Spell them in a way that is similar to the way they sound or are spelled in the ULB. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- "They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be two and a half kubits; its width will be one kubit and a half; and its height will be one kubit and a half."
-
Use the metric measurements given in the UDB. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
- "They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be one meter; its width will be two thirds of a meter; and its height will be two thirds of a meter."
-
Use measurements that are already used in your language. In order to do this you would need to know how your measurements relate to the metric system and figure out each measurement. For example, if you measure things using the standard foot length, you could translate it as below.
- "They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be 3 3/4 feet; its width will be 2 1/4 feet; and its height will be 2 1/4 feet."
-
Use the measurements from the ULB and include measurements that your people know in the text or a note. The following shows both measurements in the text.
- "They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be two and a half cubits (one meter); its width will be one cubit and a half (two thirds of a meter); and its height will be one cubit and a half (two thirds of a meter)."
-
Use measurements that your people know, and include the measurements from the ULB in the text or in a note. The following shows the ULB measurements in notes.
- "They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be one meter1; its width will be two thirds of a meter 2; and its height will be two thirds of a meter." The footnotes would look like:
- [1] two and a half cubits
- [2] one cubit and a half
- "They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be one meter1; its width will be two thirds of a meter 2; and its height will be two thirds of a meter." The footnotes would look like:
Biblical Volume
This page answers the question: How can I translate the measures of volume that are in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The following terms are the most common units of volume used in the Bible to state how much a certain container could hold. The containers and measurements are given for both liquids (such as wine) and dry solids (such as grain). The metric values are not exactly equal to the biblical measures. The biblical measures probably differed in exact amount from time to time and place to place. The equivalents below are an attempt to give an average measurement.
| Type | Original Measure | Liters | | -------- | -------- | -------- | | Dry | omer | 2 liters | | Dry | ephah | 22 liters | | Dry | homer | 220 liters | | Dry | cor | 220 liters | | Dry | seah | 7.7 liters | | Dry | lethek | 114.8 liters | | Liquid | metrete | 40 liters | | Liquid | bath | 22 liters | | Liquid | hin | 3.7 liters | | Liquid | kab | 1.23 liters | | Liquid | log | 0.31 liters |
Translation Principles
- The people in the Bible did not use modern measures such as meters, liters, and kilograms. Using the original measures can help readers know that the Bible really was written long ago in a time when people used those measures.
- Using modern measures can help readers understand the text more easily.
- Whatever measures you use, it would be good, if possible, to tell about the other kinds of measures in the text or a footnote.
- If you do not use the Biblical measures, try not to give the readers the idea that the measurements are exact. For example, if you translate one hin as "3.7 liters," readers might think that the measurement is exactly 3.7 liters, not 3.6 or 3.8. It would be better to use a more approximate measure such as "three and a half liters" or "four liters."
- When God tells people how much of something to use, and when people use those amounts in obedience to him, do not say "about" in the translation. Otherwise it will give the impression that God did not care exactly how much they used.
When the unit of measure is stated
Translation Strategies
- Use the measurements from the ULB. These are the same kinds of measurements that the original writers used. Spell them in a way that is similar to the way they sound or are spelled in the ULB. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- Use the metric measurements given in the UDB. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
- Use measurements that are already used in your language. In order to do this you would need to know how your measurements relate to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
- Use the measurements from the ULB and include measurements that your people know in the text or a note.
- Use measurements that your people know, and include the measurements from the ULB in the text or in a note.
Translation Strategies Applied
The strategies are all applied to Isaiah 5:10 below.
-
For four hectares of vineyard will yield only one bath, and one homer of seed will yield only an ephah. (Isaiah 5:10 ULB)
-
Use the measurements from the ULB. These are the same kinds of measurements that the original writers used. Spell them in a way that is similar to the way they sound or are spelled in the ULB. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- "For four hektares of vineyard will yield only one bat, and one homer of seed will yield only an efa."
-
Use the measurements given in the UDB. Usually they are metric measurements. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only twenty-two liters, and ten baskets of seed will yield only one basket."
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only twenty-two liters and 220 liters of seed will yield only twenty-two liters."
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only twenty-two liters, and ten baskets of seed will yield only one basket."
-
Use measurements that are already used in your language. In order to do this you would need to know how your measurements relate to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only six gallons, and six and a half bushels of seed will yield only twenty quarts."
-
Use the measurements from the ULB and include measurements that your people know in the text or a note. The following shows both measurements in the text.
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only one bath (six gallons), and one homer (six and a half bushels) of seed will yield only an ephah (twenty quarts)."
-
Use measurements that your people know, and include the measurements from the ULB in the text or in a note. The following shows the ULB measurements in footnotes.
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only twenty-two liters1, and 220 liters2 of seed will yield only twenty-two liters3." The footnotes would look like:
- [1]one bath
- [2]one homer
- [3]one ephah
- "For four hectares of vineyard will yield only twenty-two liters1, and 220 liters2 of seed will yield only twenty-two liters3." The footnotes would look like:
When the unit of measure is implied
Sometimes the Hebrew does not specify a particular unit of volume but only uses a number. In these cases, many English versions, including the ULB and UDB, add the word "measure."
- whenever anyone came to the grainery for twenty measures of grain, there were only ten, and whenever someone came to the wine vat to draw out fifty measures of wine, there were only twenty. (Haggai 2:16 ULB)
Translation Strategies
- Translate literally by using the number without a unit.
- Use a generic word like "measure" or "quantity" or "amount."
- Use the name of an appropriate container, such as "basket" for grain or "jar" for wine.
- Use a unit of measure that you are already using in your translation.
Translation Strategies Applied
The strategies are all applied to Haggai 2:16 below.
-
whenever anyone came to the grainery for twenty measures of grain, there were only ten, and whenever someone came to the wine vat to draw out fifty measures of wine, there were only twenty. (Haggai 2:16 ULB)
-
Translate literally by using the number without a unit.
- whenever anyone came to the grainery for twenty of grain, there were only ten, and whenever someone came to the wine vat to draw out fifty of wine, there were only twenty.
-
Use a generic word like "measure" or "quantity" or "amount."
- whenever anyone came to the grainery for twenty amounts of grain, there were only ten, and whenever someone came to the wine vat to draw out fifty amounts of wine, there were only twenty.
-
Use the name of an appropriate container, such as "basket" for grain or "jar" for wine.
- whenever anyone came to the grainery for twenty baskets of grain, there were only ten, and whenever someone came to the wine vat to draw out fifty jars of wine, there were only twenty.
-
Use a unit of measure that you are already using in your translation.
- whenever anyone came to the grainery for twenty liters of grain, there were only ten liters, and whenever someone came to the wine vat to draw out fifty liters of wine, there were only twenty liters.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Biblical Weight
This page answers the question: How can I translate the values of weight in the Bible?
Description
The following terms are the most common units of weight in the Bible. The term "shekel" means "weight," and many other weights are described in terms of the shekel. Some of these weights were used for money. The metric values in the table below are not exactly equal to the biblical measures. The biblical measures differed in exact amount from time to time and place to place. The equivalents below are only an attempt to give an average measurement.
| Original Measure | Shekels | Grams | Kilograms | |--------------------|----------|---------|------------| |shekel | 1 shekel |11 grams | - | | bekah | 1/2 shekel | 5.7 grams | - | | pim | 2/3 shekel | 7.6 grams | - | | gerah | 1/20 shekel | 0.57 grams | - | | mina | 50 shekels | 550 grams | 1/2 kilogram | | talent | 3,000 shekels | - | 34 kilograms |
Translation Principles
- The people in the Bible did not use modern measures such as meters, liters, and kilograms. Using the original measures can help readers know that the Bible really was written long ago in a time when people used those measures.
- Using modern measures can help readers understand the text more easily.
- Whatever measure you use, it would be good, if possible, to tell about the other kind of measure in the text or a footnote.
- If you do not use the Biblical measures, try not to give the readers the idea that the measurements are exact. For example, if you translate one gerah as ".57 grams" readers might think that the measurement is exact. It would be better to say "half a gram."
- Sometimes it can be helpful to use the word "about" to show that a measurement is not exact. For example, 2 Samuel 21:16 says that Goliath's spear weighed 300 shekels. Instead of translating this as "3300 grams" or "3.3 kilograms," it can be translated as "about three and one half kilograms."
- When God tells people how much something should weigh, and when people use those weights, do not say "about" in the translation. Otherwise it will give the impression that God did not care exactly how much the thing should weigh.
Translation Strategies
- Use the measurements from the ULB. These are the same kinds of measurements that the original writers used. Spell them in a way that is similar to the way they sound or are spelled in the ULB. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- Use the metric measurements given in the UDB. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
- Use measurements that are already used in your language. In order to do this you would need to know how your measurements relate to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
- Use the measurements from the ULB and include measurements that your people know in the text or a note.
- Use measurements that your people know, and include the measurements from the ULB in the text or in a note.
Translation Strategies Applied
The strategies are all applied to Exodus 38:29 below.
-
The bronze from the offering weighed seventy talents and 2,400 shekels. (Exodus 38:29 ULB)
-
Use the measurements from the ULB. These are the same kinds of measurements that the original writers used. Spell them in a way that is similar to the way they sound or are spelled in the ULB. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- "The bronze from the offering weighed seventy talentes and 2,400 sekeles."
-
Use the metric measurements given in the UDB. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
- "The bronze from the offering weighed 2,400 kilograms."
-
Use measurements that are already used in your language. In order to do this you would need to know how your measurements relate to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
- "The bronze from the offering weighed 5,300 pounds."
-
Use the measurements from the ULB and include measurements that your people know in the text or a footnote. The following shows both measurements in the text.
- "The bronze from the offering weighed seventy talents (2,380 kilograms) and 2,400 shekels (26.4 kilograms)."
-
Use measurements that your people know, and include the measurements from the ULB in the text or in a footnote. The following shows the ULB measurements in notes.
-
"The bronze from the offering weighed seventy talents and 2,400 shekels.1"
- The footnote would look like:
[1] This was a total of about 2,400 kilograms.
-
Next we recommend you learn about:
Biblical Money
This page answers the question: How can I translate the values of money in the Bible?
Description:
In early Old Testament times, people weighed their metals such as silver and gold and would give a certain weight of that metal in order to buy things. Later people started to make coins that each contained a standard amount of a certain metal. The daric is one such coin. In New Testament times, people used silver and copper coins.
The two tables below show some of the most well-known units of money found in the Old Testament (OT) and New Testament (NT). The table for Old Testament units shows what kind of metal was used and how much it weighed. The table for New Testament units shows what kind of metal was used and how much it was worth in terms of a day's wage.
| Unit in OT | Metal | Weight | | -------- | -------- | -------- | | daric | gold coin | 8.4 grams | | shekel | various metals | 11 grams | | talent | various metals | 33 kilograms|
| Unit in NT | Metal | Day's Wage | | -------- | -------- | -------- | | denarius/denarii | silver coin | 1 day | | drachma | silver coin | 1 day | | mite | copper coin| 1/64 day | | shekel | silver coin | 4 days | | talent | silver | 6,000 days |
Translation Principle
Do not use modern money values since these change from year to year. Using them will cause the Bible translation to become outdated and inaccurate.
Translation Strategies
The value of most money in the Old Testament was based on its weight. So when translating these weights in the Old Testament, see Biblical Weight. The strategies below are for translating the value of money in the New Testament
- Use the Bible term and spell it in a way that is similar to the way it sounds. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- Describe the value of the money in terms of what kind of metal it was made of and how many coins were used.
- Describe the value of the money in terms of what people in Bible times could earn in one day of work.
- Use the Bible term and give the equivalent amount in the text or a note.
- Use the Bible term and explain it in a note.
Translation Strategies
The translations strategies are all applied to Luke 7:41 below.
-
The one owed five hundred denarii, and the other owed fifty denarii. (Luke 7:41 ULB)
-
Use the Bible term and spell it in a way that is similar to the way it sounds. (see Copy or Borrow Words)
- "The one owed five hundred denali, and the other owed fifty denali." (Luke 7:41 ULB)
-
Describe the value of the money in terms of what kind of metal it was made of and how many pieces or coins were used.
- "The one owed five hundred silver coins, and the other owed fifty silver coins." (Luke 7:41 ULB)
-
Describe the value of the money in terms of what people in Bible times could earn in one day of work.
- "The one owed five hundred days' wages, and the other owed fifty days' wages."
-
Use the Bible term and give the equivalent amount in the text or a footnote.
- "The one owed five hundred denarii1, and the other owed fifty denarii.2" (Luke 7:41 ULB) The footnotes would look like:
- [1] five hundred days's wages
- [2] fifty day's wages
- "The one owed five hundred denarii1, and the other owed fifty denarii.2" (Luke 7:41 ULB) The footnotes would look like:
-
Use the Bible term and explain it in a footnote.
- "The one owed five hundred denarii1, and the other owed fifty denarii." (Luke 7:41 ULB)
- [1] A denarius was the amount of silver that people could earn in one day of work.
- "The one owed five hundred denarii1, and the other owed fifty denarii." (Luke 7:41 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Hebrew Months
This page answers the question: What are the Hebrew months?
Description
The Hebrew calendar used in the Bible has twelve months. Unlike the western calendar, its first month begins in the spring of the northern hemisphere. Sometimes a month is called by its name (Abib, Ziv, Sivan), and sometimes it is called by its order in the Hebrew calendar year (first month, second month, third month).
Reasons this is a translation issue
- Readers may be surprised to read of months that they have never heard of, and they may wonder how those months correspond to the months that they use.
- Readers may not realize that phrases such as "the first month" or "the second month" refer to the first or second month of the Hebrew calendar, not some other calendar.
- Readers may not know when the first month of the Hebrew calendar begins.
- The scripture may tell about something happening in a certain month, but readers will not be able to fully understand what is said about it if they do not know what season of the year that was.
List of Hebrew Months
This is a list of the Hebrew months with information about them that may be helpful in the translation.
Abib - (This month is called Nisan after the Babylonian exile.) This is the first month of the Hebrew calendar. It marks when God brought the people of Israel out of Egypt. It is at the beginning of the spring season when the late rains come and people begin to harvest their crops. It is during the last part of March and the first part April on western calendars. The Passover celebration started on Abib 10, the Festival of Unleavened Bread was right after that, and the Festival of Harvest was a few weeks after that.
Ziv - This is the second month of the Hebrew calendar. This is during the harvest season. It is during the last part of April and the first part of May on western calendars.
Sivan - This is the third month of the Hebrew calendar. It is at the end of the harvest season and the beginning of the dry season. It is during the last part of May and the first part of June on western calendars. The Feast of Weeks is celebrated on Sivan 6.
Tammuz - This is the fourth month of the Hebrew calendar. It is during the dry season. It is during the last part of June and the first part of July on western calendars.
Ab - This is the fifth month of the Hebrew calendar. It is during the dry season. It is during the last part of July and the first part of August on western calendars.
Elul - This is the sixth month of the Hebrew calendar. It is at the end of the dry season and the beginning of the rainy season. It is during the last part of August and the first part of September on western calendars.
Ethanim - This is the seventh month of the Hebrew calendar. This is during the early rain season which would soften the land for sowing. It is during the last part of September and the first part of October on western calendars. The Feast of Ingathering and the Day of Atonement are celebrated in this month.
Bul - This is the eighth month of the Hebrew calendar. It is during the rainy season when people plough their fields and sow seed. It is during the last part of October and the first part of November on western calendars.
Kislev - This is the ninth month of the Hebrew calendar. This is at the end of the sowing season and the beginning of the cold season. It is during the last part of November and the first part of December on western calendars.
Tebeth - This is the tenth month of the Hebrew calendar. It is during the cold season when there may be rain and snow. It is during the last part of December and the first part of January on western calendars.
Shebat - This is the eleventh month of the Hebrew calendar. This is the coldest month of the year, and it has heavy rain fall. It is during the last part of January and the first part of February on western calendars.
Adar - This is the twelfth and last month of the Hebrew calendar. This is during the cold season. It is during the last part of February and the first part of March on western calendars. The feast called Purim is celebrated in Adar.
Examples from the Bible
You are going out of Egypt on this day, in the month of Abib. (Exodus 13:4 ULB)
You must eat unleavened bread from twilight of the fourteenth day in the first month of the year, until twilight of the twenty-first day of the month. (Exodus 12:18 ULB)
Translation Strategies
You may need to make some information about the months explicit. (see Assumed Knowledge and Implicit Information)
- Tell the the number of the Hebrew month.
- Use the months that people know.
- State clearly what season the month occurred in.
- Refer to the time in terms of the season rather than in terms of the month. (If possible, use a footnote to show the Hebrew month and day.)
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
The examples below use these two verses.
- At that time, you will appear before me in the month of Abib, which is fixed for this purpose. It was in this month that you came out from Egypt. (Exodus 23:15 ULB)
-
It will always be a statute for you that in the seventh month, on the tenth day of the month, you must humble yourselves and do no work. (Leviticus 16:29 ULB)
-
Tell the number of the Hebrew month.
- At that time, you will appear before me in the first month of the year, which is fixed for this purpose. It was in this month that you came out from Egypt.
-
Use the months that people know.
- At that time, you will appear before me in the month of March, which is fixed for this purpose. It was in this month that you came out from Egypt.
- It will always be a statute for you that on the day I choose in late September you must humble yourselves and do no work."
-
State clearly what season the month occurred in.
- It will always be a statute for you that in the autumn, on the tenth day of the seventh month, you must humble yourselves and do no work.
-
Refer to the time in terms of the season rather than in terms of the month.
- It will always be a statute for you that in the day I choose in early autumn1 you must humble yourselves and do no work.
- The footnote would look like:
- [1]The Hebrew says, "the seventh month, on the tenth day of the month."
- It will always be a statute for you that in the day I choose in early autumn1 you must humble yourselves and do no work.
Next we recommend you learn about:
Numbers
This page answers the question: How do I translate numbers?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
There are many numbers in the Bible. They can be written as words, such as "five" or as numerals, such as "5." Some numbers are very large, such as "two hundred" (200), "twenty-two thousand" (22,000), or "one hundred million" (100,000,000.) Some languages do not have words for all of these numbers. Translators need to decide how to translate numbers and whether to write them as words or numerals.
Some numbers are exact and others are rounded.
Abram was eighty-six years old when Hagar bore Ishmael to Abram. (Genesis 16:16 ULB)
Eighty-six (86) is an exact number.
That day about three thousand men out of the people died. (Exodus 32:28 ULB)
Here the number three thousand is a round number. It may have been a little more than that or a little less than that. The word "about" shows that it is not an exact number.
Reason this is a translation issue: Some languages do not have words for some of these numbers.
Translation Principles
- Exact numbers should be translated as closely and specifically as they can be.
- Rounded numbers can be translated more generally.
Examples from the Bible
When Jared had lived 162 years, he became the father of Enoch. After he became the father of Enoch, Jared lived eight hundred years. He became the father of more sons and daughters. Jared lived 962 years, and then he died. (Genesis 5:18-20 ULB)
The numbers 162, eight hundred, and 962 are exact numbers and should be translated with something as close to those numbers as possible.
Our sister, may you be the mother of thousands of ten thousands (Genesis 24:60 ULB)
This is a rounded number. It does not say exactly how many descendants she should have, but it was a huge number of them.
Translation Strategies
- Write numbers using numerals.
- Write numbers using your language's words or the gateway language words for those numbers.
- Write numbers using words, and put the numerals in parenthesis after them.
- Combine words for large numbers.
- Use a very general expression for very large rounded numbers and write the numeral in parentheses afterward.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
We will use the following verse in our examples:
Now, see, at great effort I have prepared for Yahweh's house 100,000 talents of gold, one million talents of silver, and bronze and iron in large quantities. (1 Chronicles 22:14 ULB)
-
Write numbers using numerals.
- I have prepared for Yahweh's house 100,000 talents of gold, 1,000,000 talents of silver, and bronze and iron in large quantities.
-
Write numbers using your language's words or the gateway language words for those numbers.
- I have prepared for Yahweh's house one hundred thousand talents of gold, one million talents of silver, and bronze and iron in large quantities.
-
Write numbers using words, and put the numerals in parenthesis after them.
- I have prepared for Yahweh's house one hundred thousand (100,000) talents of gold, one million (1,000,000) talents of silver, and bronze and iron in large quantities.
-
Combine words for large numbers.
- I have prepared for Yahweh's house one hundred thousand talents of gold, a thousand thousand talents of silver, and bronze and iron in large quantities.
-
Use a very general expression for very large rounded numbers and write the numeral in parentheses afterward.
- I have prepared for Yahweh's house a great amount of gold (100,000 talents), ten times that amount of silver (1,000,000 talents), and bronze and iron in large quantities.
Consistency
Be consistent in your translations. Decide how the numbers will be translated, using numbers or numerals. There are different ways of being consistent.
- Use words to represent numbers all of the time. (You might have very long words.)
- Use numerals to represent numbers all of the time.
- Use words to represent the numbers that your language has words for and use numerals for the numbers that your language does not have words for.
- Use words for low numbers and numerals for high numbers.
- Use words for numbers that require few words and numerals for numbers that require more than a few words.
- Use words to represent numbers, and write the numerals in parentheses after them.
Consistency in the ULB and UDB
The Unlocked Literal Bible (ULB) and the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB) use words for numbers that have only one or two words (nine, sixteen, three hundred). They use numerals for numbers that have more than two words (the numerals "130" instead of "one hundred thirty").
When Adam had lived 130 years, he became the father of a son in his own likeness, after his image, and he called his name Seth. After Adam became the father of Seth, he lived eight hundred years. He became the father of more sons and daughters. Adam lived 930 years, and then he died. (Genesis 5:3-5 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Ordinal Numbers
This page answers the question: What are ordinal numbers and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Ordinal numbers are used in the Bible mainly to tell the position of something in a list.
He gave to the church first apostles, second prophets, third teachers, then those who do powerful deeds (1 Corinthians 12:28 ULB)
This is a list of workers that God gave to the church in their order.
Ordinal Numbers in English
Most ordinal numbers in English simply have "-th" added to the end.
| Numeral | Number | Ordinal Number | | -------- | -------- | -------- | | 4 | four | fourth | | 10 | ten | tenth | | 100 | one hundred | one hundredth | | 1,000| one thousand | one thousandth |
Some ordinal numbers in English do not follow that pattern.
| Numeral | Number | Ordinal Number | | -------- | -------- | -------- | | 1 | one | first | | 2 | two | second | | 3 | three | third | | 5 | five | fifth | | 12 | twelve | twelfth |
Reason this is a translation issue:
Some languages do not have special numbers for showing the order of items in a list. There are different ways to deal with this.
Examples from the Bible
The first lot went to Jehoiarib, the second to Jedaiah, the third to Harim, the fourth to Seorim, … the twenty-third to Delaiah, and the twenty-fourth to Maaziah. (1 Chronicles 24:7-18 ULB)
People tossed lots and one went to each of these people in the order given.
You must place in it four rows of precious stones. The first row must have a ruby, a topaz, and a garnet. The second row must have an emerald, a sapphire, and a diamond. The third row must have a jacinth, an agate, and an amethyst. The fourth row must have a beryl, and an onyx, and a jasper. They must be mounted in gold settings. (Exodus 28:17-20 ULB)
This describes four rows of stones. The first row is probably the top row, and the fourth row is probably the bottom row.
Translation Strategies
If your language has ordinal numbers and using them would give the right meaning, consider using them. If not, here are some strategies to consider:
- Use "one" with the first item and "another" or "the next" with the rest.
- Tell the total number of items and then list them or the things associated with them.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Tell the total number of items, and use "one" with the first item and "another" or "the next" with the rest.
-
The first lot went to Jehoiarib, the second to Jedaiah, the third to Harim, the fourth to Seorim, … the twenty-third to Delaiah, and the twenty-fourth to Maaziah. (1 Chronicles 24:7-18 ULB)
- There were twenty-four lots. One lot went to Jehoiarib, another to Jedaiah, another to Harim,… another to Delaiah, and the last went to Maaziah.
- There were twenty-four lots. One lot went to Jehoiarib, the next to Jedaiah, the next to Harim,… the next to Delaiah, and the last went to Maaziah.
-
A river went out of Eden to water the garden. From there it divided and became four rivers. The name of the first is Pishon. It is the one which flows throughout the whole land of Havilah, where there is gold. The gold of that land is good. There is also bdellium and the onyx stone there. The name of the second river is Gihon. This one flows throughout the whole land of Cush. The name of the third river is Tigris, which flows east of Asshur. The fourth river is the Euphrates. (Genesis 2:10-14 ULB)
- A river went out of Eden to water the garden. From there it divided and became four rivers. The name of one is Pishon. It is the one which flows throughout the whole land of Havilah, where there is gold. The gold of that land is good. There is also bdellium and the onyx stone there. The name of the next river is Gihon. This one flows throughout the whole land of Cush. The name of the next river is Tigris, which flows east of Asshur. The last river is the Euphrates.
-
-
Tell the total number of items and then list them or the things associated with them.
- The first lot went to Jehoiarib, the second to Jedaiah, the third to Harim, the fourth to Seorim, … the twenty-third to Delaiah, and the twenty-fourth to Maaziah. (1 Chronicles 24:7-18 ULB)
- They cast twenty-four lots. The lots went to Jerhoiarib, Jedaiah, Harim, Seorim, … Delaiah, and Maaziah.
- The first lot went to Jehoiarib, the second to Jedaiah, the third to Harim, the fourth to Seorim, … the twenty-third to Delaiah, and the twenty-fourth to Maaziah. (1 Chronicles 24:7-18 ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Fractions
This page answers the question: What are fractions and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Fractions are a kind of number that refer to equal parts of a thing or to equal groups within a larger group of people or things. An item or a group of items is divided into two or more parts or groups, and a fraction refers to one or more of those parts or groups.
For the drink offering, you must offer a third of a hin of wine. (Numbers 15:7 ULB)
A hin is a container used for measuring wine and other liquids. They were to think about dividing a hin container into three equal parts and fill up only one of those parts, and offer that amount.
a third of the ships were destroyed. (Revelation 8:9 ULB)
There were many ships. If all those ships were divided into three equal groups of ships, one group of ships was destroyed.
Most fractions in English simply have "-th" added to the end of the number.
| Number of parts the whole is divided into | Fraction | | -------- | -------- | | four | fourth | | ten | tenth | | one hundred | one hundredth | | one thousand | one thousandth |
Some fractions in English do not follow that pattern.
| Number of parts the whole is divided into | Fraction | | -------- | -------- | | two | half | | three | third | | five | fifth |
Reason this is a translation issue: Some languages do not use fractions. They may simply talk about parts or groups, but they do not use fractions to tell how big a part is or how many are included in a group.
Examples From the Bible
Now to one half of the tribe of Manasseh, Moses had given an inheritance in Bashan, but to the other half, Joshua gave an inheritance beside their brothers in the land west of the Jordan. (Joshua 22:7 ULB)
The tribe of Manasseh divided into two groups. The phrase "one half of the tribe of Manasseh" refers one of those groups. The phrase "the other half" refers to the other group.
The four angels who had been prepared for that very hour, that day, that month, and that year, were released to kill a third of humanity. (Revelation 9:15 ULB)
If all the people were to be divided into three equal groups, then the number of people in one group would be killed.
You must also prepare a fourth of a hin of wine as the drink offering. (Numbers 15:5 ULB)
They were to imagine dividing a hin of wine into four equal parts and prepare the amount equal to one of them.
Translation Strategies
If a fraction in your language would give the right meaning, consider using it. If not, you could consider these strategies.
- Tell the number of parts or groups that the item would be divided into, and then tell the number of parts or groups that is being referred to.
- For measurements such as for weight and length, use a unit that your people might know or the unit in the UDB.
- For measurements, use ones that are used in your language. In order to do that you would need to know how your measurements relates to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
Examples of These Translation Strategies Applied
-
Tell the number of parts or groups that the item would be divided into, and then tell the number of parts or groups that is being referred to.
-
A third of the ocean became red like blood (Revelation 8:8 ULB)
- It was like they divided the ocean into three parts, and one part of the ocean became blood.
-
then you must offer with the bull a grain offering of three tenths of an ephah of fine flour mixed with half a hin of oil. (Numbers 15:9 ULB)
- ... then you must divide an ephah of fine flour into ten parts and divide a hin of oil into two parts. Then mix three of those parts of the flour with one of the parts of oil. Then you must offer that grain offering along with the bull.
-
-
For measurements, use the measurements that are given in the UDB. The translators of the UDB have already figured how to represent the amounts in the metric system.
-
two thirds of a shekel (1 Samuel 13:21 ULB)
- eight grams of silver (1 Samuel 13:21 UDB)
-
three tenths of an ephah of fine flour mixed with half a hin of oil. (Numbers 15:9 ULB)
- six and one-half liters of finely ground flour mixed with two liters of olive oil. (Numbers 15:9 UDB)
-
-
For measurements, use ones that are used in your language. In order to do that you would need to know how your measurements relates to the metric system and figure out each measurement.
- three tenths of an ephah of fine flour mixed with half a hin of oil. (Numbers 15:9, ULB)
- six quarts of fine flour mixed with two quarts of oil.
- three tenths of an ephah of fine flour mixed with half a hin of oil. (Numbers 15:9, ULB)
Next we recommend you learn about:
Decimal Numbers
This page answers the question: What are ordinal numbers and how can I translate them?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
The decimal point, or decimal comma, is a mark placed to the left of a number to show that the number refers to part of a whole number. For example .1 meter is not a whole meter but is only one tenth of a meter and .5 meter is not five meters, but is only five tenths of a meter. 3.7 meters is three and seven tenths of a meter. Numbers like these are used in the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB).
In some countries people use a decimal point, and in other countries people use a decimal comma. So translators in countries that use a decimal comma would write "3.7 meters" as "3,7 meters." In some cultures people prefer fractions. (see Fractions)
In the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB) parts of a number are written as decimals or fractions. When they are used with a measurement such as meters, grams, and liters, the are usually written as decimals.
Decimal Numbers in the UDB
| Decimal | Fraction | Simpler Fraction | | -------- | -------- | -------- | |.1 |one tenth | | |.2 |two tenths | one fifth | |.3 |three tenths | | |.4 |four tenths | two fifths| |.5 |five tenths | one half | |.6 |six tenths | three fifths | |.7 |seven tenths | | |.8 |eight tenths | four fifths | |.9 |nine tenths | | |.25 |twenty-five one hundredths | one fourth | |.75 |seventy-five one hundredths | three fourths |
Reasons this is a translation issue
- If translators want to use the measures in the UDB, they will need to be able to understand the decimal numbers that are used with them.
- Translators will need to write the numbers in a way that their readers will understand them.
Examples from the Bible
For telling about parts of a number, the Unlocked Literal Bible (ULB) uses fractions, and the Unlocked Dynamic Bible (UDB) uses mostly decimals when the number is used with a measurement. Another difference between the ULB and the UDB is that when measuring Biblical Distance, Biblical Weight, and Biblical Volume, they use different systems, so the numbers in the ULB and the UDB are not the same for these measures.
They are to make an ark of acacia wood. Its length must be two and a half cubits; its width will be one cubit and a half; and its height will be one cubit and a half. (Exodus 25:10 ULB)
The ULB uses the fraction "half." This can also be written as a decimal: .5.
Tell the people to make a sacred chest from acacia wood. It is to be one meter long, 0.7 meter wide, and 0.7 meter high. (Exodus 25:10 UDB)
The UDB uses the decimal 0.7. This equals seven tenths.
Two and a half cubits is about one meter.
One and a half cubits is about .7 meter or seven tenths of a meter.
Translation Strategies
- Decide whether you want to use only fractions, only decimals, or a combination of the two.
- Decide whether you want to use the measures given in the ULB or the UDB or some other kind of measures.
- If you decide to use fractions and the measures in the ULB, simply translate the numbers and measures in the ULB.
-
If you decide to use decimals and the measures in the UDB, simply translate the numbers and measures in the UDB.
-
If you decide to use decimals and the measures in the ULB, you will need to change the fractions in the ULB to decimals.
- If you decide to use fractions and the measures in the UDB, you will need to change the decimals in the UDB to fractions.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
If you decide to use decimals and the measures in the ULB, you will need to change the fractions in the ULB to decimals.
- three tenths of an ephah of fine flour mixed with oil as a grain offering, and one log of oil. (Leviticus 14:10 ULB)
- " 0.3 ephah of fine flour mixed with oil as a grain offering, and one log of oil."
- three tenths of an ephah of fine flour mixed with oil as a grain offering, and one log of oil. (Leviticus 14:10 ULB)
-
If you decide to use fractions and the measures in the UDB, you will need to change the decimals in the UDB to fractions.
- about 6.5 liters of a fine flour offering, mixed with olive oil, to be an offering, and about one third liter of olive oil. (Leviticus 14:10 UDB)
- "about six and a half liters of a fine flour offering, mixed with olive oil, to be an offering, and about one third liter of olive oil."
- about 6.5 liters of a fine flour offering, mixed with olive oil, to be an offering, and about one third liter of olive oil. (Leviticus 14:10 UDB)
Symbolic Action
This page answers the question: What is a symbolic action and how do I translate it?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
A symbolic action is something that someone does in order to express a certain idea. For example, in some cultures people nod their head up and down to mean "Yes" or turn their head from side to side to mean "No." Symbolic actions do not mean the same things in all cultures. In the Bible, sometimes people perform symbolic actions and sometimes they only refer to the symbolic action.
Examples of symbolic actions
- In some cultures people shake hands when they meet to show that they are willing to be friendly.
- In some cultures people bow when they meet to show respect to each other.
Reason this is a translation issue
An action may have a meaning in one culture, and a different meaning or no meaning at all in another culture. For example, in some cultures raising the eyebrows means "I am surprised" or "What did you say?" In others cultures it means "Yes."
In the Bible people did things that had certain meanings in their culture. When we read the Bible we might not understand what someone meant if we interpret the action based on what it means in our own culture.
Translators need to understand what people in the Bible meant when they used symbolic actions. If an action does not mean the same thing in their own culture, they need to figure out how to translate what the action meant.
Examples from the Bible
Jairus fell down at Jesus' feet. (Luke 8:41 ULB)
Meaning of symbolic action: He did this to show great respect to Jesus.
Look, I stand at the door and knock. If anyone hears my voice and opens the door, I will come in to his home, and have a meal with him, and he with me. (Revelation 3:20 ULB)
Meaning of symbolic action: When people wanted someone to welcome them into their home, they stood at the door and knocked on it.
Translation Strategies
If people would correctly understand what a symbolic action meant to the people in the Bible, consider using it. If not, here are some strategies for translating it.
- Tell what the person did and why he did it.
- Do not tell what the person did, but tell what he meant.
- Use an action from your own culture that has the same meaning. Do this only in poetry, parables, and sermons. Do not do this when there actually was a person who did a specific action.
Examples of Translation Strategies Applied
-
Tell what the person did and why he did it.
-
Jairus fell down at Jesus' feet. (Luke 8:41 ULB)
- Jairus fell down at Jesus' feet in order to show that he greatly respected him.
-
Look, I stand at the door and knock. (Revelation 3:20 ULB)
- Look, I stand at the door and knock on it, asking you to let me in.
-
-
Do not tell what the person did, but tell what he meant.
-
Jairus fell down at Jesus' feet. (Luke 8:41)
- Jairus showed Jesus great respect.
-
Look, I stand at the door and knock. (Revelation 3:20)
- Look, I stand at the door and ask you to let me in.
-
-
Use an action from your own culture that has the same meaning.
-
Jairus fell down at Jesus' feet. (Luke 8:41 ULB) - Since Jairus actually did this, we would not substitute an action from our own culture.
-
Look, I stand at the door and knock. (Revelation 3:20 ULB) - Jesus was not standing at a real door. Rather he was speaking about wanting to have a relationship with people. So in cultures where it is polite to clear one's throat when wanting to be let into a house, you could use that.
- Look, I stand at the door and clear my throat.
-
Biblical Imagery
Biblical Imagery
This page answers the question: What kinds of imagery are commonly used in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Imagery is language in which an image is paired with another idea so that the image represents the idea. This includes metaphors, similes, metonymies, and cultural models. Most of these things in a language come from broad patterns of pairings between images and ideas, but some do not. These pages on Biblical Imagery tell about patterns of imagery in the Bible.
The patterns of pairings found in the Bible are often unique to the Hebrew and Greek languages. It is useful to recognize these patterns because they repeatedly present translators with the same problems on how to translate them. Once translators think through how they will handle these translation challenges, they will be ready to meet them anywhere they see the same patterns.
Common Patterns in Metaphors and Similes
A metaphor occurs when someone speaks of one thing as if it were a different thing. The speaker does this in order to effectively describe the first thing. For example, in "My love is a red, red rose," the speaker is describing the woman he loves as beautiful and delicate, as though she were a flower.
A simile is like a metaphor, except that it uses words such as "like" or "as" as a signal to the audience that it is a figure of speech. A simile using the image above would say, "My love is like a red, red rose."
"see Biblical Imagery - Common Patterns for links to pages showing common patterns of pairings between ideas in metaphors and similes."
Common Metonymies
In metonymy, a thing or idea is called not by its own name, but by the name of something closely associated with it.
"see Biblical Imagery - Common Metonymies for a list of some common metonymies in the Bible"
Cultural Models
Cultural models are mental pictures of parts of life or behavior. These pictures help us imagine and talk about these things. For example, Americans often think of many things, including marriage and friendship, as if they were machines. Americans might say, "His marriage is breaking down," or "Their friendship is going full speed ahead."
The Bible often speaks of God as if he were a shepherd and his people were sheep. This is a cultural model.
Yahweh is my shepherd; I will lack nothing. (Psalm 23:1 ULB)
He led his own people out like sheep and guided them through the wilderness like a flock. (Psalm 78:52 ULB)
Some of the cultural models in the Bible were used much by the cultures in the Ancient Near East, and not only by the Israelites.
"see Biblical Imagery - Cultural Models for a list of cultural models in the Bible."
Biblical Imagery - Common Metonymies
This page answers the question: What are some common metonymies used in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some common metonymies from the Bible are listed below in alphabetical order. The word in all capital letters represents an idea. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
A CUP or bowl represents what is in it
my cup runs over. (Psalm 23:5 ULB)
There is so much in the cup that it runs over the top of the cup.
For every time you eat this bread and drink this cup, you proclaim the Lord's death until he comes. (1 Corinthians 11:26 ULB)
People do not drink cups. They drink what is in the cup.
The MOUTH represents speech or words
A fool's mouth is his ruin. (Proverbs 18:7 ULB)
Oh, how I would encourage you with my mouth! (Job 16:5 ULB)
I heard you when you boasted against me with your mouth; you said many things against me. I heard them. (Ezekiel 35:13 ULB)
In these examples the mouth refers to what a person says.
The MEMORY OF A PERSON represents his descendants
The memory of a person represents his descendants, because they are the ones who should remember and honor him. When the Bible says that someone's memory dies, it means that either he will not have any descendants, or his descendants will all die.
You terrified the nations with your battle cry;
you have destroyed the wicked;
you have blotted out their memory forever.
The enemy crumbled like ruins
when you overthrew their cities.
All remembrance of them has perished. (Psalm 9:5-6 ULB)
His memory will perish from the earth (Job 18:17 ULB)
Yahweh is against evildoers,
in order to wipe out their memory from the earth. (Psalm 34:16 ULB)
ONE PERSON represents a group of people
For the wicked person boasts of his deepest desires;
he blesses the greedy and insults Yahweh. (Psalm 10:3 ULB)
This does not refer to a particular wicked person, but to wicked people in general.
A PERSON'S NAME represents his descendants
Gad—raiders will attack him, but he will attack them at their heels.
Asher's food will be rich, and he will provide royal delicacies.
Naphtali is a doe let loose; he will have beautiful fawns. (Genesis 49:19-21 ULB)
The names Gad, Asher, and Naphtali refer not only to those men, but to their descendants.
A PERSON represents himself and the people with him
It came about that when Abram entered into Egypt, the Egyptians saw that Sarai was very beautiful. (Genesis 12:14 ULB)
Here when it says "Abram" it represents Abram and all the people traveling with him. The focus was on Abram.
PIERCING represents killing
His hand pierced the fleeing serpent. (Job 26:13 ULB)
This means that he killed the serpent.
Look, he is coming with the clouds; every eye will see him, including those who pierced him. (Revelation 1:7 ULB)
"Those who pierced him" refers to those who killed Jesus.
SINS (INIQUITY) represent punishment for those sins
Yahweh has placed on him the iniquity of us all (Isaiah 53:6 ULB)
This means that Yahweh placed on him the punishment that should have gone to all of us.
Biblical Imagery - Common Patterns
This page answers the question: In the Bible, what ideas are often used to represent other ideas?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
This page discusses ideas that are paired together in limited ways. (For a discussion of more complex pairings, see Biblical Imagery - Cultural Models.*)
Description
In all languages, most metaphors come from broad patterns of pairings of ideas in which one idea represents another. For example, some languages have the pattern of pairing height with "much" and pairing being low with "not much," so that height represents "much" and being low represents "not much." This could be because when there is a lot of something in a pile, that pile will be high. So also if something costs a lot money, in some languages people would say that the price is high, or if a city has more people in it than it used to have, we might say that its number of people has gone up. Likewise if someone gets thinner and loses weight, we would say that their weight has gone down.
The patterns found in the Bible are often unique to the Hebrew and Greek languages. It is useful to recognize these patterns because they repeatedly present translators with the same problems on how to translate them. Once translators think through how they will handle these translation challenges, they will be ready to meet them anywhere.
For example, one pattern of pairings in the Bible is of walking with "behaving" and a path with a kind of behavior. In Psalm 1:1 the walking in the advice of the wicked represents doing what wicked people say to do.
Blessed is the man who does not walk in the advice of the wicked (Psalm 1:1 ULB)
This pattern is also seen in Psalm 119:32 where running in the path of God's commands represents doing what God commands. Since running is more intense than walking, the idea of running here might give the idea of doing this whole-heartedly.
I will run in the path of your commandments. (Psalm 119:32 ULB)
Reasons this is a translation Issue
These patterns present three challenges to anyone who wants to identify them:
1) When looking at particular metaphors in the Bible, it is not always obvious what two ideas are paired with each other. For example, it may not be immediately obvious that the expression, it is God who puts strength on me like a belt. (Psalm 18:32 ULB) is based on the pairing of clothing with moral quality. In this case, the image of a belt represents strength. (see "Clothing represents a moral quality" in Biblical Imagery - Man-made Objects)
2) When looking at a particular expression, the translator needs to know whether or not it represents something. This can only be done by considering the surrounding text. The surrounding text shows us, for example, whether "lamp" refers concretely to a container with oil and a wick for giving light or whether "lamp" is an image that represents life. (see "FIRE or LAMP represents life" in Biblical Imagery - Natural Phenomena)
In 1 Kings 7:50, a lamp trimmer is a tool for trimming the wick on an ordinary lamp. In 2 Samuel 21:17 the lamp of Israel represents King David's life. When his men were concerned that he might "put out the lamp of Israel" they were concerned that he might be killed.
The cups, lamp trimmers, basins, spoons, and incense burners were all made of pure gold. (1 Kings 7:50 ULB)
Ishbibenob...intended to kill David. But Abishai the son of Zeruiah rescued David, attacked the Philistine, and killed him. Then the men of David swore to him, saying, "You must not go to battle anymore with us, so that you do not put out the lamp of Israel." (2 Samuel 21:16-17 ULB)
3) Expressions that are based on these pairings of ideas frequently combine together in complex ways. Moreover, they frequently combine with—and in some cases are based on—common metonymies and cultural models. (see Biblical Imagery - Common Metonymies and Biblical Imagery - Cultural Models)
For example, in 2 Samuel 14:7 below, "the burning coal" is an image for the life of the son, who represents what will cause people to remember his father. So there are two patterns of pairings here: the pairing of the burning coal with the life of the son, and the pairing of the son with the memory of his father.
They say, 'Hand over the man who struck his brother, so that we may put him to death, to pay for the life of his brother whom he killed.' And so they would also destroy the heir. Thus they will put out the burning coal that I have left, and they will leave for my husband neither name nor descendant on the surface of the earth. (2 Samuel 14:7 ULB)
Links to Lists of Images in the Bible
The following pages have lists of some of the ideas that represent others in the Bible, together with examples from the Bible. They are organized according to the kinds of image:
A. Biblical Imagery - Body Parts and Human Qualities
B. Biblical Imagery - Human Behavior - Includes both physical and non-physical actions, conditions and experiences
D. Biblical Imagery - Natural Phenomena
E. Biblical Imagery - Man-made Objects
Biblical Imagery - Animals
This page answers the question: What are some examples of animals and animal body parts that are used as images in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some images from the Bible involving body parts and human qualities are listed below in alphabetical order. The word in all capital letters represents an idea. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
An ANIMAL HORN represents strength
God is my rock. I take refuge in him.
He is my shield, the horn of my salvation, my stronghold, and my refuge,
the one who saves me from violence. (2 Samuel 22:3 ULB)
The "horn of my salvation" is the strong one who saves me.
There I will make the horn of David to grow. (Psalm 132:17 ULB)
The "horn of David" is King David's military strength.
BIRDS represent people who are in danger and defenseless
This is because some birds are easily trapped.
My enemies have relentlessly hunted me like a bird, without cause. (Lamentations 3:52 ULB)
Save yourself like a gazelle from the hand of the hunter,
like a bird from the hand of the fowler. (Proverbs 6:5 ULB)
A fowler is a person who catches birds, and a snare is a small trap.
We have escaped like a bird out of the snare of the fowlers;
the snare has been broken, and we have escaped. (Psalm 124:7 ULB)
BIRDS THAT EAT MEAT represent enemies who attack swiftly
In Habakkuk and Hosea, Israel's enemies who would come and attack them were compared to an eagle.
and their horsemen come from a great distance—they fly like an eagle hurrying to eat! (Habakkuk 1:8 ULB)
An eagle is coming over the house of Yahweh.
... Israel has rejected what is good,
and the enemy will pursue him. (Hosea 8:1,3 ULB)
In Isaiah, God called a certain foreign king a bird of prey because he would come quickly and attack Israel's enemies.
I call a bird of prey from the east, the man of my choice from a distant land; (Isaiah 46:11 ULB)
A BIRD'S WINGS represent protection
This is because birds spread their wings over their chicks to protect them from danger.
Protect me like the apple of your eye; hide me under the shadow of your wings
from the presence of the wicked ones who assault me, my enemies who surround me. (Psalms 17:8-9 ULB)
Here is another example of how the wings represent protection.
Be merciful to me, God, be merciful to me,
for I take refuge in you until these troubles are over.
I stay under your wings for protection until this destruction is over. (Psalm 57:1 ULB)
DANGEROUS ANIMALS represent dangerous people
In Psalms, David referred to his enemies as lions.
My life is among lions;
I am among those who are ready to devour me.
I am among people whose teeth are spears and arrows,
and whose tongues are sharp swords.
Be exalted, God, above the heavens (Psalm 57:4 ULB)
Peter called the devil a roaring lion.
Be sober, be watchful. Your adversary—the devil—like a roaring lion is stalking around, looking for someone to devour. (1 Peter 5:8 ULB)
In Matthew, Jesus called false prophets wolves because of the harm they did to people by their lies.
Beware of false prophets, those who come to you in sheep's clothing, but are truly ravenous wolves. (Matthew 7:15 ULB)
In Matthew, John the Baptist called the religious leaders poisonous snakes because of the harm they did by teaching lies.
But when he saw many of the Pharisees and Sadducees coming to him for baptism, he said to them, "You offspring of poisonous snakes, who warned you to flee from the wrath that is coming? (Matthew 3:7 ULB)
EAGLES represent strength
He satisfies your life with good things
so that your youth is renewed like the eagle. (Psalm 103:5 ULB)
For Yahweh says this, "See, the enemy will come flying like an eagle, spreading out his wings over Moab." (Isaiah 48:40 ULB)
SHEEP or a FLOCK OF SHEEP represents people who need to be led or are in danger
My people have been a lost flock. Their shepherds have led them astray in the mountains; (Jeremiah 50:6 ULB)
He led his own people out like sheep and guided them through the wilderness like a flock. (Psalm 78:52 ULB)
Israel is a sheep scattered and driven away by lions. First the king of Assyria devoured him;
then after this, Nebuchadnezzar king of Babylon broke his bones. (Jeremiah 50:17 ULB)
See, I send you out as sheep in the midst of wolves, so be as wise as serpents and harmless as doves. Watch out for people! They will deliver you up to councils, and they will whip you in their synagogues. (Matthew 10:16 ULB)
Biblical Imagery - Body Parts and Human Qualities
This page answers the question: What are some examples of body parts and human qualities that are used as images in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Some images from the Bible involving body parts and human qualities are listed below in alphabetical order. The word in all capital letters represents an idea. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
The BODY represents a group of people
Now you are the body of Christ and individually members of it. (1 Corinthians 12:27 ULB)
Rather we will speak the truth in love and grow up in all ways into him who is the head, Christ. Christ joins the whole body of believers together—it is held together by every supporting ligament so that the whole body grows and builds itself up in love. (Ephesians 4:15-16 ULB)
In these verses, the body of Christ represents the group of people who follow Christ.
The FACE represents someone's presence
Do you not fear me—this is Yahweh's declaration—or tremble before my face? (Jeremiah 5:22 ULB)
To be before someone's face is to be in their presence, that is, to be with them.
The FACE represents someone's attention
Every man of the house of Israel who takes his idols into his heart, or who puts the stumbling block of his iniquity before his face, and who then comes to a prophet—I, Yahweh, will answer him according to the number of his idols. (Ezekiel 14:4 ULB)
To put something before one's face is to look at it intently or pay attention to it.
Many seek the face of the ruler, (Proverbs 29:26 ULB)
If someone seeks another person's face, he hopes that the person will pay attention to him.
Why do you hide your face and forget our affliction and our oppression? (Psalm 44:24 ULB)
To hide one's face from someone is to ignore him.
The FACE represents surface
The famine was over all the face of the whole land. (Genesis 41:56 ULB)
He encloses the face of the moon and spreads his clouds on it. (Job 26:9 ULB)
The HAND represents a person's agency or power
Yahweh has burst through my enemies by my hand like a bursting flood of water. (1 Chronicles 14:11 ULB)
"Yahweh has burst through my enemies by my hand" means "Yahweh has used me to burst through my enemies."
Your hand will seize all your enemies; your right hand will seize those who hate you. (Psalm 21:8 ULB)
"Your hand will seize all your enemies" means "By your power you will seize all your enemies."
Look, Yahweh's hand is not so short that it cannot save. (Isaiah 59:1 ULB)
"His hand is not short" means that he is not weak.
The HEAD represents the ruler, the one who has authority over others
God has subjected all things under Christ's feet and has made him the head over all things in the church, which is his body, the fullness of him who fills all things in all ways. (Ephesians 1:22 ULB)
Wives should be subject to their own husbands, as to the Lord. For the husband is the head of the wife, as Christ also is the head of the church, and he is the Savior of the body. (Ephesian 5:22-23 ULB)
A MASTER represents anything that motivates someone to act
No one can serve two masters, for either he will hate the one and love the other, or else he will be devoted to one and despise the other. You cannot serve God and wealth. (Matthew 6:24 ULB)
To serve God is to be motivated by God. To serve money is to be motivated by money.
A NAME represents the person who has that name
May your God make the name of Solomon better than your name, and make his throne greater than your throne." 1 Kings 1:47 (ULB)
See, I have sworn by my great name—says Yahweh. My name will no longer be called upon by the mouths of any of the men of Judah in all the land of Egypt…." (Jeremiah 44:26 ULB)
If someone's name is great, it means that he is great.
Listen now to the prayer of your servant and to the prayer of your servants who delight to honor your name…. Nehemiah 1:11 (ULB)
To honor someone's name is to honor him.
A NAME represents the fame or reputation of a person
You must no longer profane my holy name with your gifts and your idols. Ezekiel 20:39 (ULB)
To profane God's name is to profane his reputation, that is, to profane how people think about him.
For I will make my great name holy, which you have profaned among the nations…. Ezekiel 36:23 (ULB)
To make God's name holy is to cause people to to see that God is holy.
Your servants have come here from a land very far away, because of the name of Yahweh your God. We have heard a report about him and about everything that he did in Egypt (Joshua 9:9 ULB)
The fact that the men said they heard a report about Yahweh shows that "because of the name of Yahweh" means because of Yahweh's reputation.
The NOSE represents anger
Then…the foundations of the world were exposed at your battle cry, Yahweh—at the blast of the breath of your nostrils. (Psalms 18:15 ULB)
By the blast of your nostrils the waters were piled up…. (Exodus 15:8 ULB)
Smoke went up from out of his nostrils, and blazing fire came out of his mouth…. (2 Samuel 22:9 ULB)
…This is the Lord Yahweh's declaration: 'My fury will arise in my nostrils!' (Ezekiel 38:18 ULB)
A blast of air or smoke coming from someone's nose shows his great anger.
RAISED EYES represents arrogance
but you bring down those with proud, uplifted eyes! (Psalm 18:27 ULB)
Uplifted eyes show that a person is proud.
God humbles a proud man, and he saves the one with lowered eyes. (Job 22:29 ULB)
Lowered eyes show that a person is humble.
The SON OF SOMETHING shares its qualities
no son of wickedness will oppress him. (Psalm 89:22b ULB)
A son of wickedness is a wicked person.
May the groans of the prisoners come before you;
with the greatness of your power keep the children of death alive. (Psalm 79:11 ULB)
Children of death here are people that others plan to kill.
We all were once among these unbelievers and acted according to the evil desires of our flesh, doing the will of the flesh and of the mind, and we were by nature children of wrath like the others. (Ephesians 2:3 ULB)
Children of wrath here are people with whom God is very angry.
Translation Strategies
(see the Translations Strategies on Biblical Imagery - Common Patterns)
Biblical Imagery - Farming
This page answers the question: What are some examples in the Bible of images taken from farming?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some images from the Bible related to farming are listed below. The word in all capital letters represents an idea. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does appear.
A FARMER represents God, and the VINEYARD represents his chosen people
My well beloved had a vineyard on a very fertile hill.
He spaded it and removed the stones, and planted it with the choicest vine.
He built a tower in the middle of it, and also built a winepress.
He waited for it to produce grapes, but it produced wild grapes. (Isaiah 5:1-2)
For the kingdom of heaven is like a landowner who went out early in the morning to hire workers for his vineyard. (Matthew 20:1 ULB)
There was a man, a person with extensive land. He planted a vineyard, set a hedge about it, dug a winepress in it, built a watchtower, and rented it out to vine growers. Then he went into another country. (Matthew 21:33 ULB)
The GROUND represents people's hearts (inner being)
For Yahweh says this to each person in Judah and Jerusalem: 'Plow your own ground,
and do not sow among thorns. (Jeremiah 4:3 ULB)
When anyone hears the word of the kingdom but does not understand it.... This is the seed that was sown beside the road. What was sown on rocky ground is the person who hears the word and immediately receives it with joy....What was sown among the thorn plants, this is the person who hears the word, but the cares of the world and the deceitfulness of riches choke the word.... What was sown on the good soil, this is the person who hears the word and understands it. (Matthew 13:19-23 ULB)
Break up your unplowed ground, for it is time to seek Yahweh.... (Hosea 10:12 ULB)
SOWING represents actions or attitudes, and REAPING represents judgment or reward
Based on what I have observed, those who plow iniquity
and sow trouble reap the same. (Job 4:8 ULB)Do not be deceived. God is not mocked. Whatever a man plants, that is what he will also harvest. For he who sows seed to his own sinful nature will harvest destruction, but he who sows seed to the Spirit, will harvest eternal life from the Spirit. (Galatians 6:7-8 ULB)
THRESHING and WINNOWING represent the separation of evil people from good people
After farmers harvest wheat and other types of grain, they bring them to a threshing floor, a flat place with hard ground, and have oxen pull heavy wheeled carts or sleds without wheels over the grain to thresh it, to separate the usable grains from the useless chaff. Then they take large forks and winnow the threshed grain by throwing it up in the air so the wind can carry off the chaff while the grains fall back to the threshing floor, where they can be gathered and used for food. (see thresh and winnow pages in translationWords for help translating "thresh" and "winnow")
So I will winnow them with a pitchfork at the gates of the land. I will bereave them. I will destroy my people since they will not turn from their ways. (Jeremiah 15:7 ULB)
His winnowing fork is in his hand to thoroughly clear off his threshing floor and to gather the wheat into his storehouse. But he will burn up the chaff with fire that can never be put out. (Luke 3:17 ULB)
GRAFTING represents God's allowing the Gentiles to become his people
For if you were cut out of what is by nature a wild olive tree, and contrary to nature were grafted into a good olive tree, how much more will these Jews, who are the natural branches, be grafted back into their own olive tree? For I do not want you to be unaware, brothers, of this mystery, in order that you will not be wise in your own thinking. This mystery is that a partial hardening has occurred in Israel, until the completion of the Gentiles come in. (Romans 11:24-25 ULB)
RAIN represents God's gifts to his people
...he comes and rains righteousness on you. (Hosea 10:12 ULB)
For the land that drinks in the rain that often comes on it, and that gives birth to the plants useful to those for whom the land was worked—this is the land that receives a blessing from God. But if it bears thorns and thistles, it is worthless and is near to a curse. Its end is in burning. (Hebrews 6:7-8 ULB)
So be patient, brothers, until the Lord's coming. See, the farmer awaits the valuable harvest from the ground. He is patiently waiting for it, until it receives the early and late rains. (James 5:7 ULB)
Biblical Imagery - Human Behavior
This page answers the question: What are some examples of things people do that are used as images in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some images from the Bible involving human behavior are listed below. The word in all capital letters represents an image. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
BEING BENT OVER represents being discouraged
Yahweh supports all who are falling and raises up all those who are bent over. (Psalm 145:14 ULB)
BIRTH PAINS represent the suffering that is necessary to achieve a new condition
Be in pain and labor to give birth, daughter of Zion, like a woman in labor.
For now you will go out of the city, live in the field, and go to Babylon.
There you will be rescued.
There Yahweh will rescue you from the hand of your enemies. (Micah 4:10 ULB)
For nation will rise against nation, and kingdom against kingdom. There will be famines and earthquakes in various places. But all these things are only the beginning of birth pains. (Matthew 24:7-8 ULB)
My little children, I am suffering labor pains for you again, until Christ will have been formed in you! (Galatians 4:19 ULB)
BEING CALLED SOMETHING represents being that thing
The Holy One of Israel is your Redeemer; he is called the God of the whole earth. (Isaiah 54:5b ULB)
This is because he actually is the God of the whole earth.
The one who is wise in heart is called discerning, (Proverbs 16:21a ULB)
This is because he actually is discerning.
He will...be called the Son of the Most High. (Luke 1:32 ULB)
This is because he actually is the Son of the Most High.
So the holy one to be born will be called the Son of God. (Luke 1:35 ULB)
This is because he actually is the Son of God.
Every male that opens the womb will be called dedicated to the Lord. (Luke 2:23 ULB)
This is because he actually will be dedicated to the Lord.
CLEANLINESS represents being acceptable for God's purposes
Noah built an altar to Yahweh. He took some of the clean animals and some of the clean birds, and offered burnt offerings on the altar. Yahweh smelled the pleasing aroma... (Genesis 8:20 ULB)
The priest will examine him again on the seventh day to see if the disease is better and has not spread farther in the skin. If it has not, then the priest will pronounce him clean. It is a rash. He must wash his clothes, and then he is clean. (Leviticus 13:6 ULB)
CLEANSING or PURIFYING represents making something acceptable for God's Purposes
He must go out to the altar that is before Yahweh and make atonement for it, and he must take some of the bull's blood and some of the goat's blood and put it on the horns of the altar all around. He must sprinkle some of the blood on it with his finger seven times to cleanse it and dedicate it to Yahweh, away from the unclean actions of the people of Israel. (Leviticus 16:18-19 ULB)
This is because on this day atonement will be made for you, to cleanse you from all your sins so you will be clean before Yahweh. (Leviticus 16:30 ULB)
UNCLEANLINESS represents not being acceptable for God's purposes
You may eat any animal that has a split hoof and that also chews the cud. However, some animals either chew the cud or have a split hoof, and you must not eat them, animals such as the camel, because it chews the cud but does not have a split hoof. So the camel is unclean for you. (Leviticus 11:3-4 ULB)
And if any of them dies and falls on anything, that thing will be unclean, whether it is made of wood, cloth, leather, or sackcloth. Whatever it is and whatever it is used for, it must be put into water; it will be unclean until evening. Then it will be clean. (Leviticus 11:32 ULB)
MAKING SOMETHING UNCLEAN represents making it unacceptable for God's purposes.
Or if anyone touches anything God has designated as unclean, whether it be the carcass of an unclean wild animal or the carcass of any livestock that has died, or creeping animal, even if the person did not intend to touch it, he is unclean and guilty. (Leviticus 5:2 ULB)
BEING CUT OFF FROM SOMETHING represents being separated from it
Uzziah, the king, was a leper to the day of his death, and lived in a separate house, since he was a leper; for he was cut off from the house of Yahweh. (2 Chronicles 26:21 ULB)
BEING CUT OFF represents being killed
So you must keep the Sabbath, for it must be treated by you as holy, reserved for him. Everyone who defiles it must surely be put to death. Whoever works on the Sabbath, that person must surely be cut off from his people. (Exodus 31:14-15 ULB)
Whoever does not humble himself on that day must be cut off from his people. Whoever does any work on that day, I, Yahweh, will destroy him from among his people. (Leviticus 23:29-30 ULB)
But he was cut off from the land of the living. (Isaiah 53:8 ULB)
COMING AND STANDING BEFORE SOMEONE represents serving him
How blessed are your people, and how blessed are your servants who constantly stand before you, because they hear your wisdom. (1 Kings 10:8 ULB)
Covenant faithfulness and trustworthiness come before you. (Psalm 89:14 ULB)
Covenant faithfulness and trustworthiness are also personified here. (see Personification)
DRUNKENNESS represents suffering and WINE represents judgment
Too much wine makes a person weak and he staggers. So too, when God judges people, they become weak and stagger. So the idea of wine is used to represent God's judgment.
You have shown your people severe things;
you have made us drink the wine of staggering. (Psalm 60:3 ULB)
Another example from Psalm.
But God is the judge;
he brings one down and raises up another.
For Yahweh holds a cup in his hand of foaming wine,
which is mixed with spices, and pours it out.
Surely all the wicked of the earth will drink it to the last drop. (Psalm 75:8 ULB)
An example from Revelation.
he also will drink the wine of God's wrath, the wine that has been prepared and poured unmixed into the cup of his anger. (Revelation 14:10 ULB)
EATING UP represents destroying
God brings [Israel] out of Egypt.
He has strength like a wild ox.
He will eat up the nations who fight against him.
He will break their bones to pieces.
He will shoot them with his arrows. Numbers 24:8 ULB)
Another word for "eat up" is devour.
Therefore as the tongue of fire devours stubble, and as the dry grass goes down in flame,
so their root will rot, and their blossom will blow away like dust, (Isaiah 5:24 ULB)
Another example from Isaiah.
Therefore Yahweh will raise up against him, Rezin, his adversary, and will stir up his enemies,
the Arameans on the east, and the Philistines on the west.
They will devour Israel with open mouth. (Isaiah 9:11-12 ULB)
An example from Deuteronomy.
I will make my arrows drunk with blood,
and my sword will devour flesh
with the blood of the killed and the captives,
and from the heads of the leaders of the enemy. (Deuteronomy 32:42 ULB)
FALLING UPON or BEING UPON represents affecting
Yahweh God caused a deep sleep to fall upon the man, so the man slept. (Genesis 2:21 ULB)
Would not his majesty make you afraid?
Would not his dread fall upon you? (Job 13:11 ULB)
Then the Spirit of Yahweh fell on me and he said to me… (Ezekiel 11:5 ULB)
Now look, the hand of the Lord is upon you, and you will become blind. (Acts 13:11 ULB)
FOLLOWING SOMEONE represents being loyal to him
They broke away from Yahweh, the God of their fathers, who had brought them out of the land of Egypt. They went after other gods, the very gods of the peoples who were around them, and they bowed down to them. They provoked Yahweh to anger because they broke away from Yahweh and worshiped Baal and the Ashtoreths.
For Solomon followed Ashtoreth, the goddess of the Sidonians, and he followed Milcom, the disgusting idol of the Ammonites. (1 Kings 11:5 ULB)
Not one of them who despised me will see it, except for my servant Caleb, because he had another spirit. He has followed me fully; I will bring him into the land which he went to examine. His descendants will possess it. (Numbers 14:23-24 ULB)
GOING BEFORE, ACCOMPANYING, OR FOLLOWING A KING WITH HIS OTHER ATTENDANTS represents serving him
See, his reward is with him, and his recompense is going before him. (Isaiah 62:11 ULB)
Righteousness will go before him and make a way for his footsteps. (Psalm 85:13 ULB)
INHERITING is permanently possessing something
Then the King will say to those on his right hand, "Come, you who have been blessed by my Father, inherit the kingdom prepared for you from the foundation of the world." (Matthew 25:34)
The blessing of God's complete rule is given as the permanent possession to those to whom the King is speaking.
Now this I say, brothers and sisters, that flesh and blood cannot inherit the kingdom of God. Neither does what is perishable inherit what is imperishable. (1 Corinthians 15:50 ULB)
People cannot receive the kingdom of God in its complete form as a permanent possession while they are still in their mortal bodies.
An INHERITANCE is something that someone permanently possesses
You will bring them and plant them on the mountain of your inheritance. (Exodus 15:17 ULB)
The mountain where God will be worshiped is viewed as his permanent possession.
Pardon our iniquity and our sin, and take us as your inheritance. (Exodus 34:9 ULB)
Moses asks God to still accept the people of Israel as his special possession, that is, as the people permanently belonging to him.
the richness of the glory of his inheritance among those who are set apart for him. (Ephesians 1:18 ULB)
The wonderful things that God will give all who are set apart for him is viewed as their permanent possession.
An HEIR is someone who permanently possesses something
For it was not through the law that the promise was given to Abraham and to his descendants, this promise that they would be heirs of the world. (Romans 4:13 ULB)
The promise was that Abraham and his descendants would permanently possess the entire world.
God has spoken to us by a Son, whom he appointed to be the heir of all things. (Hebrews 1:2 ULB)
God's Son will receive all things as a permanent possession.
It was by faith that Noah...condemned the world and became an heir of the righteousness that comes through faith. (Hebrews 11:7 ULB)
Noah received righteousness as a permanent possession.
LYING DOWN represents DYING
When your days are fulfilled and you lie down with your fathers, I will raise up a descendant after you, (2 Samuel 7:12 ULB)
Ask them, 'Are you really more beautiful than anyone else? Go down and lie with the uncircumcised!'
They will fall among those who were killed by the sword! Egypt is given to the sword; her enemies will seize her and her servants! (Ezekiel 32:19-20 ULB)
REIGNING OR RULING represents controlling
This happened so that, as sin ruled in death, even so grace might rule through righteousness for everlasting life through Jesus Christ our Lord. (Romans 5:21 ULB)
Therefore do not let sin rule in your mortal body in order that you obey its lusts. (Romans 6:12 ULB)
RESTING or a RESTING PLACE represents a permanent beneficial situation
Naomi her mother-in-law said to her, "My daughter, should I not seek a place for you to rest, so that things may go well for you?" (Ruth 3:1 ULB)
Therefore I vowed in my anger that they would never enter into my resting place. (Psalm 95:11 ULB)
This is my resting place forever; I will live here, for I desire her [Zion]. (Psalm 132:14 ULB)
The nations will seek him out, and his resting place will be glorious. (Isaiah 11:10 ULB)
RISING, STANDING UP represents acting
Rise up for our help and redeem us for the sake of your covenant faithfulness. (Psalm 44:26 ULB)
SEEING SOMETHING represents being there
You will not let the one who has covenant faithfulness see the pit. (Psalm 16:10 ULB)
SELLING represents handing over to someone's control. BUYING represents removing from someone's control
[Yahweh] sold [the Israelites] into the hand of Cushan Rishathaim king of Aram Naharaim. (Judges 3:8 ULB)
SITTING IS RULING
A throne will be established in covenant faithfulness, and one from David's tent will faithfully sit there. ( Isaiah 16:5 ULB)
STANDING represents successfully resisting
So the wicked will not stand in the judgment, nor sinners in the assembly of the righteous. (Psalm 1:2 ULB)
WALKING represents behaving and PATH (WAY) represents behavior
Blessed is the man who does not walk in the advice of the wicked. Psalm 1:1 ULB)
For Yahweh approves of the way of the righteous. (Psalm 1:6 ULB)
Turn from me the path of deceit. (Psalm 119:28 ULB)
I will run in the path of your commandments. (Psalm 119:32 ULB)
Biblical Imagery - Man-made Objects
This page answers the question: What are some examples things people make that are used as images in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some images from the Bible involving man-made objects are listed below in alphabetical order. The word in all capital letters represents an image. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
BRONZE represents strength
He trains…my arms to bend a bow of bronze. Psalm 18:34 ULB)
CHAINS represent control
Let us tear off the shackles they put on us and throw off their chains. Psalm 2:3
CLOTHING represents moral qualities (emotions, attitudes, spirit, life)
It is God who puts strength on me like a belt. (Psalm 18:32 ULB)
Righteousness will be the belt of his waist, and faithfulness the belt around his hips. (Isaiah 11:5 ULB)
May my adversaries be clothed with shame; may they wear their shame like a robe. (Psalm 109:29 ULB)
I will clothe his enemies with shame. (Psalm 132:18 ULB)
A SNARE (A LIGHT TRAP FOR BIRDS WORKED BY CORDS) represents death
For he will rescue you from the snare of the hunter. (Psalm 91:3 ULB)
The cords of death surrounded me, and the snares of sheol confronted me. (Psalm 116:3 ULB)
The cords of the wicked have ensnared me. (Psalm 119:61 ULB)
The wicked have set a snare for me. (Psalm 119:110 ULB)
The wicked is ensnared by his own actions. (Psalm 9:16 ULB)
They mingled with the nations and learned their ways and worshiped their idols, which became a snare to them. (Psalm 106:35-36 ULB)
In this case the snare was a persuasion to do evil, which leads to death.
A TENT represents a house, home, people in one's home, descendants
God will likewise destroy you forever; he will take you up and pluck you out of your tent. (Psalm 52:5 ULB)
The house of the wicked will be destroyed, but the tent of the upright will flourish. (Proverbs 14:11 ULB)
A throne will be established in covenant faithfulness, and one from David's tent will faithfully sit there. (Isaiah 16:5 ULB)
Biblical Imagery - Natural Phenomena
This page answers the question: What are some examples of things in nature that are used as images in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some images from the Bible involving natural phenomena are listed below. The word in all capital letters represents an image. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
LIGHT represents someone's face (This often combines with FACE represents someone's presence)
Yahweh, lift up the light of your face on us. (Psalm 4:6 ULB)
For they did not obtain the land for their possession by their own sword,
neither did their own arm save them;
but your right hand, your arm, and the light of your face,
because you were favorable to them. (Psalm 44:3 ULB)
they did not reject the light of my face. (Job 29:24 ULB)
Yahweh, they walk in the light of your face. (Psalm 89:15 ULB)
LIGHT represents goodness, and DARKNESS represents evil
But if your eye is bad, your whole body is full of darkness. Therefore, if the light that is in you is actually darkness, how great is that darkness! (Matthew 6:23 ULB)
SHADOW or DARKNESS represents death
Yet you have severely broken us in the place of jackals and covered us with the shadow of death. (Psalm 44:19)
FIRE represents extreme feelings, particularly love or anger
Because iniquity will be increased, the love of many will be extinguished. (Matthew 24:12 ULB)
Surging waters cannot quench love. (Song of Solomon 8:7 ULB)
For a fire is kindled by my anger and is burning to the lowest sheol. (Deuteronomy 32:22 ULB)
Therefore the anger of Yahweh was set on fire against Israel. (Judges 3:8 ULB)
When Yahweh heard this, he was angry; so his fire burned against Jacob, and his anger attacked Israel. (Psalm 78:21 ULB)
FIRE OR A LAMP represents life
They say, 'Hand over the man who struck his brother, so that we may put him to death, to pay for the life of his brother whom he killed.' And so they would also destroy the heir. Thus they will put out the burning coal that I have left, and they will leave for my husband neither name nor descendant on the surface of the earth. 2 Samuel 14:7 ULB)
You must not go to battle anymore with us, so that you do not put out the lamp of Israel. (2 Samuel 21:17 ULB)
I will give one tribe to Solomon's son, so that David my servant may always have a lamp before me in Jerusalem. (1 Kings 11:36 ULB)
Nevertheless for David's sake, Yahweh his God gave him a lamp in Jerusalem by raising up his son after him in order to strengthen Jerusalem. (1 Kings 15:4 ULB)
Indeed, the light of the wicked person will be put out; the spark of his fire will not shine. The light will be dark in his tent; his lamp above him will be put out. (Job 18:5-6 ULB)
For you give light to my lamp; Yahweh my God lights up my darkness. (Psalm 18:28 ULB)
A dimly burning wick he will not quench. (Isaiah 42:3 ULB)
A WIDE SPACE reperesents safetey, security, and ease
They came against me on the day of my distress but Yahweh was my support! He set me free in a wide open place; he saved me because he was pleased with me. (Psalms 18:18-19 ULB)
You have made a wide place for my feet beneath me, so my feet have not slipped. (2 Samuel 22:37 ULB)
You made people ride over our heads; we went through fire and water, but you brought us out into a spacious place. (Psalms 66:12 ULB)
A NARROW SPACE represents danger or difficulties
Answer me when I call, God of my righteousness; give me room when I am hemmed in. Have mercy on me and listen to my prayer. Psalm 4:1 ULB)
For a prostitute is a deep pit, and an immoral woman is a narrow well. (Proverbs 23:27 ULB)
LIQUID represents a moral quality (emotion, attitude, spirit, life)
Yahweh has burst through my enemies before me like a bursting flood of water. (2 Samuel 5:20 ULB)
He will make a full end to his enemies with an overwhelming flood. (Nahum 1:8 ULB)
My heart drips because of sadness. (Psalm 119:28 ULB)
I am being poured out like water. (Psalm 22:14 ULB)
It will come about afterward that I will pour out my Spirit on all flesh. (Joel 2:28 ULB)
My God, my soul has melted within me. (Psalm 42:6 ULB)
For it is great, the anger of Yahweh that has been poured out on us. (2 Chronicles 34:21 ULB)
WATER represents what someone says
A quarreling wife is a constant dripping of water. (Proverbs 19:13 ULB)
His lips are lilies, dripping myrrh. (Song of Solomon 5:13 ULB)
My groaning is poured out like water. (Job 3:24 ULB)
The words of a man's mouth are deep waters; the fountain of wisdom is a flowing stream. (Proverbs 18:3 ULB)
FLOODING WATER represents disaster
I have come into deep waters, where the floods flow over me. (Psalm 69:2 ULB)
Do not let the floods of water overwhelm me. (Psalm 69:15 ULB)
Reach out your hand from above; rescue me out of many waters from the hands of these foreigners. (Psalm 144:7 ULB)
A SPRING OF WATER represents the origins of something
The fear of Yahweh is a fountain of life. (Proverbs 14:27 ULB)
A ROCK represents protection
Who is a rock except our God? (Psalm 18:31 ULB)
Yahweh, my rock, and my redeemer. (Psalm 19:14 ULB)
Biblical Imagery - Plants
This page answers the question: What are some examples of plants that are used as images in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Some images from the Bible involving plants are listed below in alphabetical order. The word in all capital letters represents an idea. The word does not necessarily appear in every verse that has the image, but the idea that the word represents does.
A BRANCH represents a person's descendant
In the examples below, Isaiah wrote about one of Jesse's descendants and Jeremiah wrote about one of David's descendants.
A shoot will sprout from the root of Jesse, and a branch out of his root will bear fruit.
The Spirit of Yahweh will rest upon him, the spirit of wisdom and understanding. (Isaiah 11:1 ULB)See, days are coming—this is Yahweh's declaration—when I will raise up for David a righteous branch.
He will reign as king; he will bring prosperity and carry out justice and righteousness in the land. (Jeremiah 23:5 ULB)
In Job when it says "his branch will be cut off," it means that he will not have any descendants.
His roots will be dried up beneath;
above will his branch be cut off.
His memory will perish from the earth;
he will have no name in the street. (Job 18:17 ULB)
A PLANT represents a person
God will likewise destroy you forever; he will…root you out of the land of the living. (Psalm 52:5 ULB)
A PLANT represents an emotion or attitude
Just as planting one kind of seeds results in that kind of plant growing, behaving in one way results in that kind of consequence.
The emotion or attitude in the verses is underlined below.
Sow righteousness for yourselves, and reap the fruit of covenant faithfulness. (Hosea 10:12 ULB)
Based on what I have observed, those who plow iniquity and sow trouble, reap the same. (Job 4:8 ULB)
For the people sow the wind and reap the whirlwind. (Hosea 8:7 ULB)
You have turned…the fruit of righteousness into bitterness. (Amos 6:12 ULB)
What fruit then did you have at that time of the things of which you are now ashamed? (Romans 6:21 ULB)
A TREE represents a person
He will be like a tree planted by the streams of water that produces its fruit in its season, whose leaves do not wither; whatever he does will prosper. (Psalm 1:3 ULB)
I have seen the wicked and terrifying person spread out like a green tree in its native soil. (Psalm 37:35 ULB)
I am like a green olive tree in God's house. (Psalm 52:8 ULB)
Biblical Imagery - Cultural Models
This page answers the question: What are cultural models and what are some cultural models found in the Bible?
In order to understand this topic, it would be good to read:
Description
Cultural models are mental pictures of parts of life or behavior. These pictures help us imagine and talk about these topics. For example, Americans often think of many things, even marriage and friendship, as if they were machines. Americans might say "His marriage is breaking down" or "Their friendship is going full speed ahead." In this example, human relationships are modeled as a MACHINE.
Some cultural models, or mental pictures, found in the Bible are listed below. First there are models for God, then models for humans, things, and experiences. Each heading has the model written in capital letters. That word or phrase does not necessarily appear in every verse, but the idea does.
God is modeled as a HUMAN BEING
Although the Bible explicitly denies that God is a human being, he is often spoken of as doing things that humans do. But God is not human, so when the Bible says that God speaks, we should not think that he has vocal chords that vibrate. And when it says something about him doing something with his hand, we should not think that he has a physical hand.
If we hear the voice of Yahweh our God any longer, we will die. (Deuteronomy 5:25 ULB)
I have been strengthened by the hand of Yahweh my God (Ezra 7:28 ULB)
The hand of God also came on Judah, to give them one heart to carry out the command of the king and leaders by the word of Yahweh (2 Chronicles 30:12 ULB)
The word "hand" here is a metonym that refers to God's power. (See: Metonymy)
God is modeled as a KING
For God is the King over all the earth; (Psalm 47:7 ULB)
For the kingdom is Yahweh's;
he is the ruler over the nations. (Psalm 22:28 ULB)Your throne, God, is forever and ever;
a scepter of justice is the scepter of your kingdom. (Psalm 45:6 ULB)This is what Yahweh says,
"Heaven is my throne, and the earth is my footstool. (Isaiah 66:1 ULB)God reigns over the nations;
God sits on his holy throne.
The princes of the peoples have gathered together
to the people of the God of Abraham;
for the shields of the earth belong to God;
he is greatly exalted. (Psalm 47:8-9 ULB)
God is modeled as a SHEPHERD and his people are modeled as SHEEP
Yahweh is my shepherd; I will lack nothing. (Psalm 23:1 ULB)
His people are sheep.
For he is our God, and we are the people of his pasture and the sheep of his hand. (Psalm 95:7 ULB)
He leads his people like sheep.
He led his own people out like sheep and guided them through the wilderness like a flock. (Psalm 78:52 ULB)
He is willing to die in order to save his sheep.
I am the good shepherd, and I know my own, and my own know me. The Father knows me, and I know the Father, and I lay down my life for the sheep. I have other sheep that are not of this fold. Those, also, I must bring, and they will hear my voice so that there will be one flock and one shepherd. (John 10:14-15 ULB)
God is modeled as a WARRIOR
Yahweh is a warrior; (Exodus 15:3 ULB)
Yahweh will go out as a warrior; he will proceed as a man of war. He will stir up his zeal.
He will shout, yes, he will roar his battle cries; he will show his enemies his power. (Isaiah 42:13 ULB)Your right hand, Yahweh, is glorious in power;
your right hand, Yahweh, has shattered the enemy. (Exodus 15:6 ULB)But God will shoot them;
suddenly they will be wounded with his arrows. (Psalm 65:7 ULB)
For you will turn them back; you will draw your bow before them. (Psalm 21:12 ULB)
A leader is modeled as a SHEPHERD and those he leads are modeled as SHEEP
Then all the tribes of Israel came to David at Hebron and said, "Look...when Saul was king over us, it was you who led the Israelite army. Yahweh said to you, 'You will shepherd my people Israel, and you will become ruler over Israel.' " (2 Samuel 5:1-2 ULB)
"Woe to the shepherds who destroy and scatter the sheep of my pasture—this is Yahweh's declaration." (Jeremiah 23:1 ULB)
Therefore be careful about yourselves, and about all the flock of which the Holy Spirit has made you overseers. Be careful to shepherd the assembly of the Lord, which he purchased with his own blood. 29I know that after my departure, vicious wolves will enter in among you, and not spare the flock. I know that from even among your own selves some men shall come and say corrupt things, in order to draw away the disciples after them. (Acts 20:28-30 ULB)
The eye is modeled as a LAMP
Variations of this model and the model of the EVIL EYE are found in many parts of the world. In most of the cultures represented in the Bible, these models included the following elements:
People see objects, not because of light around the object, but because of light that shines from their eyes onto those objects.
The eye is the lamp of the body. Therefore, if your eye is good, the whole body is filled with light. (Matthew 6:22 ULB)
This light shining from the eyes carries with itself the viewer's character.
The appetite of the wicked craves evil; his neighbor sees no kindness in his eyes. (Proverbs 21:10 ULB)
Envy and cursing are modeled as looking with an EVIL EYE at someone, and favor is modeled as looking with a GOOD EYE at someone
The primary emotion of a person with the evil eye is envy. The Greek word translated as "envy" in Mark 7 is "eye," which refers here to an evil eye.
He said, "It is that which comes out of the person that defiles him. For from within a person, out of the heart, proceed evil thoughts…, envy …. (Mark 7:20-22 ULB)
The context for Matthew 20:15 includes the emotion of envy. "Is your eye evil?" means "Are you envious?"
Is it not legitimate for me to do what I wish with my own possessions? Or is your eye evil because I am good? (Matthew 20:15 ULB)
If a person's eye is evil, that person is envious of other people's money.
The eye is the lamp of the body. Therefore, if your eye is good, the whole body is filled with light. But if your eye is bad, your whole body is full of darkness. Therefore, if the light that is in you is actually darkness, how great is that darkness! No one can serve two masters, for either he will hate the one and love the other, or else he will be devoted to one and despise the other. You cannot serve God and wealth. (Matthew 6:22-24 ULB)
A person who is envious might put a curse or enchantment on someone by looking at him with an evil eye.
Foolish Galatians, whose evil eye has harmed you? (Galatians 3:1 ULB)
A person with a good eye can put a blessing on someone by looking at him.
If I have found favor in your eyes... (1 Samuel 27:5 ULB)
Life is modeled as BLOOD
In this model, the blood of a person or an animal represents its life.
But you must not eat meat with its life—that is its blood—in it. (Genesis 9:4 ULB)
If blood is spilled or shed, someone has been killed.
Whoever sheds man's blood, by man will his blood be shed, (Genesis 9:6 ULB)
In this way, this person would not die by the hand of the one who wanted to avenge the blood that was shed, until the accused person would first stand before the assembly. (Joshua 20:9 ULB)
If blood cries out, nature itself is crying out for vengeance on a person who killed someone. (This also includes personification, because the blood is pictured as someone that can cry out. See: Personification)
Yahweh said, "What have you done? Your brother's blood is calling out to me from the ground. (Genesis 4:10 ULB)
A country is modeled as a WOMAN, and its gods are modeled as HER HUSBAND
It came about, as soon as Gideon was dead, the people of Israel turned again and prostituted themselves by worshiping the Baals. They made Baal Berith their god. (Judges 8:33 ULB)
The nation of Israel is modeled as GOD'S SON
When Israel was a young man I loved him, and I called my son out of Egypt. (Hosea 11:1 ULB)
The sun is modeled as BEING IN A CONTAINER AT NIGHT
Yet their words go out over all the earth and their speech to the end of the world. He has pitched a tent for the sun among them. The sun is like a bridegroom coming out of his chamber and like a strong man who rejoices when he runs his race. (Psalm 19:4-5 ULB)
Psalm 110 pictures the sun as being in the womb before it comes out in the morning.
from the womb of the dawn your youth will be to you like the dew. (Psalm 110:3 ULB)
Things that can move fast are modeled as having WINGS
This is especially true of things that move in the air or the sky.
The sun is modeled as a disc with wings, which allow it to "fly" through the air from east to west during the daytime. In Psalm 139, "the wings of the morning" refers to the sun. In Malachi 4 God called himself the "sun of righteousness" and he spoke of the sun as having wings.
If I fly away on the wings of the morning and go to live in the uttermost parts across the sea... (Psalm 139:9 ULB)
But for you who fear my name, the sun of righteousness will rise with healing in its wings. (Malachi 4:2 ULB)
The wind moves quickly and is modeled as having wings.
He was seen flying on the wings of the wind. (2 Sam. 22:11 ULB)
He rode on a cherub and flew; he glided on the wings of the wind. (Psalm 18:10 ULB)
you walk on the wings of the wind (Psalm 104:3 ULB)
Futility is modeled as something that the WIND can blow away
In this model, the wind blows away things that are worthless, and they are gone.
Psalm 1 and Job 27 show that wicked people are worthless and will not live long.
The wicked are not so,
but are instead like the chaff that the wind drives away. (Psalm 1:4 ULB)The east wind carries him away, and he leaves;
it sweeps him out of his place. (Job 27:21 ULB)
The writer of Ecclesiastes says that everything is worthless.
Like a vapor of mist,
like a breeze in the wind,
everything vanishes, leaving many questions.
What profit does mankind gain from all the work that they labor at under the sun? (Ecclesiastes 1:2-3 ULB)
In Job 30:15, Job complains that his honor and prosperity are gone.
Terrors are turned upon me;
my honor is driven away as if by the wind;
my prosperity passes away as a cloud. (Job 30:15 ULB)
Human warfare is modeled as DIVINE WARFARE
When there was a war between nations, people believed that the gods of those nations were also at war.
This happened while the Egyptians were burying all their firstborn, those whom Yahweh had killed among them, for he also inflicted punishment on their gods. (Numbers 33:4 ULB)
And what nation is like your people Israel, the one nation on earth whom you, God, went and rescued for yourself?...You drove out nations and their gods from before your people, whom you rescued from Egypt. (2 Samuel 7:23 ULB)
The servants of the king of Aram said to him, "Their god is a god of the hills. That is why they were stronger than we were. But now let us fight against them in the plain, and surely there we will be stronger than they." (1 Kings 20:23 ULB)
Constraints in life are modeled as PHYSICAL BOUNDARIES
The verses below are not about real physical boundaries but about difficulties or the lack of difficulties in life.
He has built a wall around me, and I cannot escape. He has made my shackles heavy. (Lamentations 3:7 ULB)
He has blocked my path with walls of hewn stone; every way I take is crooked. (Lamentations 3:9 ULB)
Measuring lines have been laid for me in pleasant places (Psalm 16:6 ULB)
Dangerous places are modeled as NARROW PLACES
In Psalm 4 David asks God to rescue him.
Answer me when I call, God of my righteousness;
give me room when I am hemmed in.
Have mercy on me and listen to my prayer. (Psalm 4:1 ULB)
A distressing situation is modeled as a WILDERNESS
When Job was distressed because of all the sad things that happened to him, he spoke as if he were in a wilderness. Jackals and ostriches are animals that live in the wilderness.
My heart is troubled and does not rest;
days of affliction have come on me.
I go about with darkened skin but not because of the sun;
I stand up in the assembly and cry for help.
I am a brother to jackals,
a companion of ostriches. (Job 30:27-29 ULB)
Wellbeing is modeled as PHYSICAL CLEANLINESS, and evil is modeled as PHYSICAL DIRTINESS
Leprosy is a disease. If a person had it, he was said to be unclean.
Behold, a leper came to him and bowed before him, saying, "Lord, if you are willing, you can make me clean." Jesus reached out his hand and touched him, saying, "I am willing. Be clean." Immediately he was cleansed of his leprosy. (Matthew 8:2-3 ULB)
An "unclean spirit" is an evil spirit.
When an unclean spirit has gone away from a man, it passes through waterless places and looks for rest, but does not find it. (Matthew 12:43 ULB)
